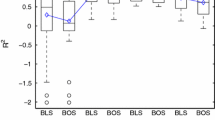
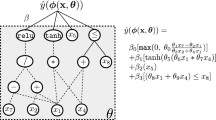
Abstract
This paper proposes a new approach to improve generalisation of standard regression techniques when there are hundreds or thousands of input variables. The input space X is composed of observational data of the form (x i , y(x i )), i = 1... n where each x i denotes a k-dimensional input vector of design variables and y is the response. Genetic Programming (GP) is used to transform the original input space X into a new input space Z = (z i , y(z i )) that has smaller input vector and is easier to be mapped into its corresponding responses. GP is designed to evolve a function that receives the original input vector from each x i in the original input space as input and return a new vector z i as an output. Each element in the newly evolved z i vector is generated from an evolved mathematical formula that extracts statistical features from the original input space. To achieve this, we designed GP trees to produce multiple outputs. Empirical evaluation of 20 different problems revealed that the new approach is able to significantly reduce the dimensionality of the original input space and improve the performance of standard approximation models such as Kriging, Radial Basis Functions Networks, and Linear Regression, and GP (as a regression techniques). In addition, results demonstrate that the new approach is better than standard dimensionality reduction techniques such as Principle Component Analysis (PCA). Moreover, the results show that the proposed approach is able to improve the performance of standard Linear Regression and make it competitive to other stochastic regression techniques.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop, C.M., Nasrabadi, N.M.: Pattern recognition and machine learning, vol. 1. Springer, New York (2006)
Estébanez, C., Aler, R., Valls, J.M.: Genetic programming based data projections for classification tasks. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology (2005)
Forrester, A., Sóbester, A., Keane, A.: Engineering design via surrogate modelling: a practical guide. John Wiley & Sons (2008)
García, S., Herrera, F.: An extension on statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets for all pairwise comparisons. Journal of Machine Learning Research 9(66), 2677–2694 (2008)
Icke, I., Bongard, J.: Improving genetic programming based symbolic regression using deterministic machine learning. In: 2013 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), pp. 1763–1770 (2013)
Kattan, A., Galvan, E.: Evolving radial basis function networks via gp for estimating fitness values using surrogate models. In: 2012 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), pp. 1–7 (2012)
Koza, J.R.: Genetic Programming: On the programming of computers by means of natural selection, vol. 1. MIT Press (1992)
McConaghy, T.: Latent variable symbolic regression for high-dimensional inputs. In: Genetic Programming Theory and Practice VII, pp. 103–118. Springer (2010)
McConaghy, T.: Ffx: Fast, scalable, deterministic symbolic regression technology. In: Genetic Programming Theory and Practice IX, pp. 235–260. Springer (2011)
Molga, M., Smutnick, C.: Test functions for optimization needs (2005)
Poli, R., Langdon, W.W.B., McPhee, N.F., Koza, J.R.: A field guide to genetic programming. Lulu.com (2008)
Smits, G., Kordon, A., Vladislavleva, K., Jordaan, E., Kotanchek, M.: Variable selection in industrial datasets using pareto genetic programming. In: Yu, T., Riolo, R.L., Worzel, B. (eds.) Genetic Programming Theory and Practice III, Genetic Programming, May 12-14, vol. 9, ch. 6, pp. 79–92. Springer, Ann Arbor (2005)
Sobester, A., Nair, P., Keane, A.: Evolving intervening variables for response surface approximations. In: Proceedings of the 10th AIAA/ISSMO Multi-disciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, pp. 1–12. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (2004), http://eprints.soton.ac.uk/22962/ , aIAA 2004-4379
Zhang, Y., Zhang, M.: A multiple-output program tree structure in genetic programming. In: Mckay, R.I., Cho, S.B. (eds.) Proceedings of the Second Asian-Pacific Workshop on Genetic Programming, Cairns, Australia, December 6-7, p. 12 (2004), http://www.mcs.vuw.ac.nz/~mengjie/papers/yun-meng-apwgp04.pdf
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kattan, A., Kampouridis, M., Agapitos, A. (2014). Generalisation Enhancement via Input Space Transformation: A GP Approach. In: Nicolau, M., et al. Genetic Programming. EuroGP 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8599. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44303-3_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44303-3_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-44302-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-44303-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)