Abstract
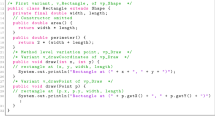
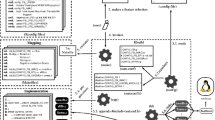
Separate variability modeling adds variability to a modeling language without requiring modifications of the language or the supporting tools. We define a core language for separate variability modeling using a single kind of variation point to define transformations of software artifacts in object models. Our language, Featherweight VML, has several distinctive features. Its architecture and operations are inspired by the recently proposed Common Variability Language (CVL). Its semantics is considerably simpler than that of CVL, while remaining confluent (unlike CVL). We simplify complex hierarchical dependencies between variation points via copying and flattening. Thus, we reduce a model with intricate dependencies to a flat executable model transformation consisting of simple unconditional local variation points. The core semantics is extremely concise: it boils down to two operational rules, which makes it suitable to serve as a specification for implementations of trustworthy variant derivation. Featherweight VML offers insights in the execution of other variability modeling languages such as the Orthogonal Variability Model and Delta Modeling. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to comprehensively formalize variant derivation, encompassing feature models, variation points, implementation artifacts and transformations.
Supported by ARTEMIS JU under grant agreement n° 295397 and by Danish Agency for Science, Technology and Innovation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bąk, K., Czarnecki, K., Wąsowski, A.: Feature and meta-models in Clafer: Mixed, specialized, and coupled. In: Malloy, B., Staab, S., van den Brand, M. (eds.) SLE 2010. LNCS, vol. 6563, pp. 102–122. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Benavides, D., Cortés, A.R., Trinidad, P., Segura, S.: A survey on the automated analyses of feature models. In: JISBD, pp. 367–376 (2006)
Berger, T., Rublack, R., Nair, D., Atlee, J.M., Becker, M., Czarnecki, K., Wasowski, A.: A survey of variability modeling in industrial practice. In: VaMoS, p. 7 (2013)
Berger, T., She, S., Lotufo, R., Czarnecki, K., Wąsowski, A.: Feature-to-code mapping in two large product lines. In: Bosch, J., Lee, J. (eds.) SPLC 2010. LNCS, vol. 6287, pp. 498–499. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Bodden, E., Tolêdo, T., Ribeiro, M., Brabrand, C., Borba, P., Mezini, M.: Spllift: statically analyzing software product lines in minutes instead of years. In: PLDI, pp. 355–364 (2013)
Clarke, D., Diakov, N., Hähnle, R., Johnsen, E.B., Schaefer, I., Schäfer, J., Schlatte, R., Wong, P.Y.H.: Modeling Spatial and Temporal Variability with the HATS Abstract Behavioral Modeling Language. In: Bernardo, M., Issarny, V. (eds.) SFM 2011. LNCS, vol. 6659, pp. 417–457. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Clarke, D., Helvensteijn, M., Schaefer, I.: Abstract delta modeling. In: Visser, E., Järvi, J. (eds.) GPCE, pp. 13–22. ACM (2010)
Classen, A., Boucher, Q., Heymans, P.: A text-based approach to feature modelling: syntax and semantics of TVL. Sci. Comput. Program. 76(12), 1130–1143 (2011)
Clements, P., Northrop, L.M.: Software Product Lines: Practices and Patterns. Addison-Wesley (2002)
CVL Joint Submission Team. Common Variability Language (CVL). OMG Revised Submission (2012)
Czarnecki, K., Antkiewicz, M.: Mapping features to models: A template approach based on superimposed variants. In: Glück, R., Lowry, M. (eds.) GPCE 2005. LNCS, vol. 3676, pp. 422–437. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Czarnecki, K., Grünbacher, P., Rabiser, R., Schmid, K., Wasowski, A.: Cool features and tough decisions: A comparison of variability modeling approaches. In: VaMoS, pp. 173–182 (2012)
Czarnecki, K., Helsen, S.: Feature-based survey of model transformation approaches. IBM Systems Journal 45(3), 621–646 (2006)
Czarnecki, K., Helsen, S., Eisenecker, U.W.: Formalizing cardinality-based feature models and their specialization. Software Process: Improvement and Practice 10(1), 7–29 (2005)
Czarnecki, K., Pietroszek, K.: Verifying feature-based model templates against well-formedness ocl constraints. In: GPCE 2006, pp. 211–220. ACM (2006)
Haber, A., Kolassa, C., Manhart, P., Nazari, P.M.S., Rumpe, B., Schaefer, I.: First-class variability modeling in matlab/simulink. In: VaMoS, p. 4 (2013)
Haugen, Ø.: Cvl: common variability language or chaos, vanity and limitations. In: VaMoS, p. 1 (2013)
Heidenreich, F., Kopcsek, J., Wende, C.: Featuremapper: mapping features to models. In: ICSE Companion, pp. 943–944 (2008)
Hutchinson, J., Rouncefield, M., Whittle, J.: Model-driven engineering practices in industry. In: ICSE, pp. 633–642 (2011)
Janota, M., Kiniry, J.: Reasoning about feature models in higher-order logic. In: SPLC, pp. 13–22 (2007)
Kang, K.C., Cohen, S.G., Hess, J.A., Novak, W.E., Peterson, A.S.: Feature-Oriented Domain Analysis (FODA) Feasibility Study. Technical report, CMU SEI (November 1990)
Object Management Group. Meta Object Facility (MOF) Core Specification Version 2.0 (2006)
Oldevik, J., Haugen, Ø., Møller-Pedersen, B.: Confluence in domain-independent product line transformations. In: Chechik, M., Wirsing, M. (eds.) FASE 2009. LNCS, vol. 5503, pp. 34–48. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Pohl, K., Böckle, G., van der Linden, F.J.: Software Product Line Engineering: Foundations, Principles and Techniques. Sprinter (2005)
Prehofer, C.: Feature-oriented programming: A new way of object composition. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 13(6), 465–501 (2001)
Schaefer, I., Bettini, L., Bono, V., Damiani, F., Tanzarella, N.: Delta-oriented programming of software product lines. In: Bosch, J., Lee, J. (eds.) SPLC 2010. LNCS, vol. 6287, pp. 77–91. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Schaefer, I., Rabiser, R., Clarke, D., Bettini, L., Benavides, D., Botterweck, G., Pathak, A., Trujillo, S., Villela, K.: Software diversity: state of the art and perspectives. STTT 14(5), 477–495 (2012)
Schmid, K., Rabiser, R., Grünbacher, P.: A comparison of decision modeling approaches in product lines. In: VaMoS, pp. 119–126 (2011)
Schobbens, P.-Y., Heymans, P., Trigaux, J.-C., Bontemps, Y.: Generic semantics of feature diagrams. Computer Networks 51(2), 456–479 (2007)
Stahl, T., Voelter, M.: Model-Driven Software Development. John Wiley & Sons (2004)
Thüm, T., Kästner, C., Erdweg, S., Siegmund, N.: Abstract features in feature modeling. In: SPLC, pp. 191–200 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Iosif-Lazăr, A.F., Schaefer, I., Wąsowski, A. (2014). A Core Language for Separate Variability Modeling. In: Margaria, T., Steffen, B. (eds) Leveraging Applications of Formal Methods, Verification and Validation. Technologies for Mastering Change. ISoLA 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8802. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45234-9_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45234-9_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-45233-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-45234-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)