Abstract
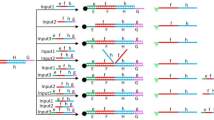
DNA strand displacement reaction (DSDR) has become a significant issue in DNA computing in recent years. The voting device has been playing an important role in some occasions. A 4-people voting device was designed based on DSDR in this paper. The process of DSDR is programmed and simulated in visual DSD. The simulated results demonstrate that the molecular model of voting device is feasible and reliable, which has wide prospects in complicated molecular logic circuits study.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Păun, G., Rozenberg, G., Salomaa, A.: The Oxford Handbook of Membrane Computing. Oxford University Press Inc., Oxford (2010)
Song, T., Pan, L.: Spiking neural P systems with rules on synapses working in maximum spikes consumption strategy. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 14(1), 38–44 (2015)
Adleman, L.M.: Molecular computation of solutions to combinatorial problems. Science 226, 1021–1024 (1994)
Carlson, R.: The changing economics of DNA synthesis. Nat. Biotechnol. 27, 1091–1094 (2009)
Turberfield, A.J., Mitchell, J.C., Yurke, B., Mills Jr, A.P., Blakey, M.I., Simmel, F.C.: DNA fuel for free-running nanomachines. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 118102 (2003)
Yin, P., Choi, H.M.T., Calvert, C.R., Pierce, N.A.: Programming biomolecular self-assembly pathways. Nature 451, 318–322 (2008)
Gothelf, K.V., LaBean, T.H.: DNA-programmed assembly of nanostructures. Org. Biomol. Chem. 3, 4023–4037 (2005)
Zhang, D.Y., Turberfield, A.J., Yurke, B., Winfree, E.: Engineering entropy-driven reactions and networks catalyzed by DNA. Science 318, 1121–1125 (2007)
Seelig, G., Soloveichik, D., Zhang, D.Y., Winfree, E.: Enzyme-free nucleic acid logic circuits. Science 314, 1585–1588 (2006)
Chiniforooshan, E., Doty, D., Kari, L., Seki, S.: Scalable, time-responsive, digital, energy-efficient molecular circuits using DNA strand displacement. In: Sakakibara, Y., Mi, Y. (eds.) DNA 16 2010. LNCS, vol. 6518, pp. 25–36. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Srinivas, N., Ouldridge, T.E., Sulc, P., Schaeffer, J.M., Yurke, B., Louis, A.A., Doye, J.P.K., Winfree, E.: On the biophysics and kinetics of toehold-mediated DNA strand displacement. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(22), 10641–10658 (2013)
Wang, X., Miao, Y., Cheng, M.: Finding motifs in DNA sequences using low-dispersion sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 21(4), 320–329 (2014)
Zhang, D.Y., Winfree, E.: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 17303–17314 (2009)
Soloveichik, D., Seelig, G., Winfree, E.: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, vol. 107, pp. 5393–53989 (2010)
Phillips, A., Cardelli, L.: J. Royal Soc. Interface 6, S419–S436 (2009)
Song, T., Pan, L.: Spiking neural P systems with rules on synapses working in maximum spiking strateg. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 14(4), 465–477 (2015)
Song, T., Pan, L., Jiang, K., et al.: Normal forms for some classes of sequential spiking neural P systems. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 12(3), 255–264 (2013)
Eckhoff, G., Codrea, V., Ellington, A.D., Chen, X.: J. Syst. Chem. 1, 13 (2010)
Qian, L., Winfree, E.: A simple DNA gate motif for synthesizing large-scale circuits. In: Goel, A., Simmel, F.C., Sosík, P. (eds.) DNA Computing. LNCS, vol. 5347, pp. 70–89. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Lund, K., Manzo, A.J., Dabby, N., Michelotti, N., Johnson-Buck, A., Nangreave, J., Taylor, J.S., Pei, R., Stojanovic, M.N., Walter, N.G., Winfree, E., Yan, H.: Nature 465, 206–210 (2010)
Song, T., Pan, L., Wang, J., et al.: Normal forms of spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 11(4), 352–359 (2012)
Qian, L., Soloveichik, D., Winfree, E.: Efficient turing-universal computation with DNA polymers. In: Sakakibara, Y., Mi, Y. (eds.) DNA 16 2010. LNCS, vol. 6518, pp. 123–140. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Chiniforooshan, E., Doty, D., Kari, L., Seki, S.: Scalable, time-responsive, digital, energy-efficient molecular circuits using DNA strand displacement. In: Sakakibara, Y., Mi, Y. (eds.) DNA 16 2010. LNCS, vol. 6518, pp. 25–36. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Gaber, R., Lebar, T., Majerle, A., Ster, B., Dobnikar, A., Bencina, M., Jerala, R.: Designable DNA-binding domain enable construction of logic circuit in mammalian cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 10(3), 203–208 (2014)
Zhang, Z., Li, J., Pan, L., Ye, Y., Zeng, X., Song, T., Zhang, X., Wang, E.: A novel visualization of DNA sequences, reflecting GC-content. Match Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 72(2), 533–550 (2014)
Zeng, X., Xu, L., Liu, X., Pan, L.: On languages generated by spiking neural P systems with weights. Inf. Sci. 278, 423–433 (2014)
Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Luo, B., Pan, L.: Computational power of tissue P systems for generating control languages. Inf. Sci. 278, 285–297 (2014)
Song, T., Pan, L., Păun, G.: Asynchronous spiking neural P systems with local synchronization. Inf. Sci. 219, 197–207 (2013)
Zhang, X., Pan, L., Păun, A.: On the universality of axon P systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 26(11), 2816–2829 (2015). doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2396940
Shi, X., Wang, Z., Deng, C., Song, T., Pan, L., Chen, Z.: A novel bio-sensor based on DNA strand displacement. PLoS One 9(10), e108856 (2014)
Acknowledgments
The research is supported by the NSFC (Nos. U1304620, 61472372, 61272022), Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan (Grant No. 124200510017), and Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Zhengzhou (Grant No. 131PLJRC648), Basic and Frontier technologies Research Program of Henan Province (132300410183), and Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan Province (154200510012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Z., Sun, Z., Cai, Z., Wang, Y., Cui, G. (2015). The Design of Voting Device Based on DNA Strand Displacement Reaction. In: Gong, M., Linqiang, P., Tao, S., Tang, K., Zhang, X. (eds) Bio-Inspired Computing -- Theories and Applications. BIC-TA 2015. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 562. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49014-3_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49014-3_42
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-49013-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-49014-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)