Abstract
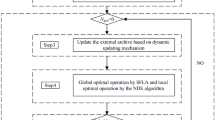
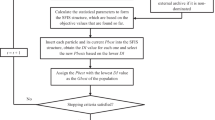
Operation optimization of the cascaded hydropower stations is of great significance to utilization efficiency of water, safety and stability of the grid, and comprehensive benefits of the reservoirs. In this study, a multi-objective operation optimization model of cascaded hydropower stations is established, and a novel multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) algorithm is proposed to deal with the optimization problem of multi-objective, multi-constraint, high-dimension, and strong-coupling. A turbulence mechanism and a circular elimination strategy, are presented to strengthen the performance of MOPSO algorithm. The result of a case study indicates that, with the proposed techniques, the pro-posed algorithm performs well on both convergence and diversity of Pareto solutions, which implies that the proposed MOPSO algorithm can be used as an effective optimization tool to handle the multi-objective operation optimization of the cascaded hydropower stations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, X.Y., Wang, Y.Q., Cheng, C.T., Guo, Y.A., Li, H.G.: Optimal operation model for hydropower reservoirs considering probability of non-failure and failure extent. Water Resour. Res. 2(3), 165–170 (2013)
Xie, R.C., Ji, C.M., Wang, C.C., Zhang, Y.K., Yu, S.: Energy storage operation charts of hydropower station reservoir group based on improved discriminate coefficient method. Water Power 39(5), 62–64 (2012)
Ji, C.M., Jiang, Z.Q., Sun, Q., Wu, H., Yu, S.: Optimization of cascade total output dispatching figure based on the optimal output distribution. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 23(4), 184–191 (2014)
Zhang, S.H.: The Theory and Practice of Cascade Reservoirs Power Generation Optimized Operation. Xian University of Technology (2007)
Duan, W.H., Mei, Y.D., Chen, L.H., Bao, Z.F., Qu, L.N.: Long term optimal operation of cascade hydropower plants on jinshajiang river. Hydropower Autom. Dam Monit. 31(1), 17–20 (2007)
Ji, C.M., Li, K.F., Zhang, Y.K., Zhao, B.K.: Stochastic multi-objective decision-making model of the reservoir operation based on chance-constrained programming. Power Syst. Prot. Control 40(19), 36–40 (2012)
Ding, S.H., Dong, Z.C., Wang, D.Z., Li, Q.H.: MOP of feeding reservoir group optimal operation based on SPEA. Adv. Water Sci. 19(5), 679–684 (2008)
Xu, J.J., Chen, J., Yin, Z.J.: Key issues in the joint operation of large cascade reservoirs in Yangtze river basin. J. Yangtze river Sci. Res. Inst. 28(12), 48–52 (2011)
Ai, X.S., Ran, B.Y.: FS DDDP method and its application to optimal operation of groups of reservoirs. Hydropower Autom. Dam Monit. 31(1), 13–16 (2007)
Nagesh-Kumar, D., Janga-Reddy, M.: Ant colony optimization for multi-purpose reservoir operation. Water Resour. Manag. 20(6), 879–898 (2006)
Janga-Reddy, M., Nagesh-Kumar, D.: Evolving strategies for crop planning and operation of irrigation reservoir system using multi-objective differential evolution. Irrig. Sci. 26(2), 177–190 (2008)
Foued, B.A., Sameh, M.: Application of goal programming in a multi-objective reservoir operation model in Tunisia. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 133(2), 352–361 (2001)
Basu, M.: An interactive fuzzy satisfying method based on evolutionary programming technique for multiobjective short-term hydrothermal scheduling. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 69(2–3), 277–285 (2004)
Hu, G.Q., He, R.M.: Model and algorithm of multi-objective fuzzy optimal scheduling for cascaded hydroelectric power plant. Trans. China Electrotechnical Soc. 22(1), 154–158 (2007)
Hu, G.Q., He, R.M.: Long-term multi-objective fuzzy optimization scheduling model of cascaded hydroelectric station. Electr. Power Autom. Equipment 27(4), 23–27 (2007)
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwa, S., Meyarivan, T.: A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6(2), 182–197 (2002)
Zitzler, E., Laumanns, M., Thiele, L.: SPEA2: improving the strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm. Technical report 103, Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory (TIK), Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich, Gloriastrasse 35, CH-8092 Zurich, Switzerland (2001)
Chang, L.C., Chang, F.J.: Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for operating parallel reservoir system. J. Hydrol. 377(1–2), 12–20 (2009)
Chen, X.B., Wang, X.J., Feng, S.Y.: A multi-objective optimization method considering power output and firm power for reservoir dispatching. Syst. Eng. Theor. Pract. 4(4), 95–101 (1998)
Li, M., Lin, D., Kou, J.: A hybrid niching PSO enhanced with Recombination-replacement crowding strategy for multimodal function optimization. Softw. Comput. 12(3), 975–987 (2012)
Hu, W., Yen, G.G., Zhang, X.: Multiobjective particle swarm optimization based on Pareto entropy. Software 25(5), 1025–1050 (2014)
Coello, A.C., Pulido, G.T., Lechuga, M.S.: Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 8(3), 256–279 (2004)
Reyes-Sierra, M., Coello, A.C.: Multi-objective particle swarm optimizers: a survey of the state-of-the-art. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Res. 2(3), 287–308 (2006)
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., Meyarivan, T.: A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6(2), 182–197 (2002)
Fuqua, W.C., Winans, W.C., Greenberg, E.P.: Quorum sensing in bacteria: the LuxR LuxI family of cell density responsive transcriptional regulators. J. Bacteriol. 176(2), 269–275 (1994)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Hubei Key Laboratory of Cascaded Hydropower Stations Operation & Control (China Three Gorges University) through grant number 2013KJX01 and 2015 Scientific Research Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate of CTGU via the Grant Number 2015CX068.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cheng, S., Jiang, X., Chen, W. (2015). Multi-objective Optimal Operation of Cascaded Hydropower Stations Based on MOPSO with Bacteria Quorum Sensing Inspired Turbulence Mechanism. In: Gong, M., Linqiang, P., Tao, S., Tang, K., Zhang, X. (eds) Bio-Inspired Computing -- Theories and Applications. BIC-TA 2015. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 562. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49014-3_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49014-3_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-49013-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-49014-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)