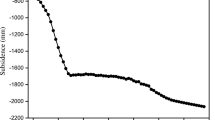
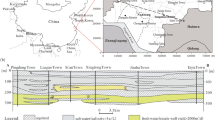
Abstract
Among the existing study of land subsidence, there is almost no consideration about the effects of building load and groundwater exploitation at the same time. Based on the consideration of these issues, this study designs the physical model test to simulate the subsidence effected by the building load and analysis the tendency of subsidence from the soil mechanics. Lastly, taking the typical geological structure of floodplain as an example, a coupling model is established considering both effects of building load and groundwater exploitation, its high accuracy of fitting and prediction shows that the coupling model can be used to simulate the land subsidence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue, Y., Zhang, Y., Ye, S., Wu, J., Wei, Z., Li, Q., Yu, J.: Research on the problems of land subsidence in China. Geol. J. China Univ. 2, 153–160 (2006)
Jianping, Y., Fang, L.: Research advances of monitoring and controlling technology for urban land subsidence. Bull. Surveying Mapp. 03, 1–4 (2008)
Qinfen, L., Zheng, F., Hanmei, W.: A mathematical model and forecast of groundwater workable reserves for Shanghai. Shanghai Geol. 02, 36–43 (2000)
Liu, H.: The study on the land subsidence with the effect of high-rise buildings in Tianjin Binhai New Area, Chang’an University (2010)
Heng, S., Jianping, Y.: On mathematical model of urban land subsidence based on building load. Bull. Surveying Mapp. 04, 15–17 (2013)
Yuxin, J., Yan, G., Guangxin, L.: Analysis on the land subsidence induced by city construction. Geotech. Eng. Tech. 02, 78–82 (2007)
Jie, Y., Gao, Y., Li, G.: Statistical pattern of building spacing and its influence additional stress. Ind. Constr. S1, 62–65+61 (2010)
Shengzhong, W., Pengfei, F.: Land subsidence computational theories and methods. J. Taiyuan Univ. Technol. 02, 162–166 (2000)
Zhao, H., Qian, H., Li, Y., Peng, J.: Land subsidence model under dual effects of groundwater pumping and construction loading. J. Earth Sci. Environ 01, 57–59 (2008)
Demin, D., Fengshan, Ma., Yamin, Z., Jie, W., Jie, G.: Characteristics of land subsidence due to both high-rise building and exploitation of groundwater in urban area. J. Eng. Geol. 03, 433–439 (2011)
Lei, W.: Application of Terzaghi’s 1D consolidation theory in research of the urban land subsidence, Jilin University (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, B., Yue, J., Li, J., Yue, S. (2016). Coupling Model of Land Subsidence Considering Both Effects of Building Load and Groundwater Exploitation. In: Bian, F., Xie, Y. (eds) Geo-Informatics in Resource Management and Sustainable Ecosystem. GRMSE 2015. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 569. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49155-3_66
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49155-3_66
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-49154-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-49155-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)