Abstract
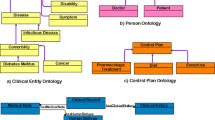
The realisation of a complex web portal, including the modelling of content, is a challenging process. The contents describe different interconnected entities that form a complex structure. The entities and their relations have to be systematically analysed, and the content has to be specified and integrated into a content management system (CMS). Ontologies provide a suitable solution for modelling and specifying complex entities and their relations. However, the functionality for automated import of ontologies is not available in current content management systems.
In order to describe the content of a web portal, we developed an ontology. Based on this ontology, we implemented a pipeline that allows the specification of the portal’s content and its import into the CMS Drupal. Our method is generic. It enables the development of web portals with the focus on a suitable representation of structured knowledge (entities, their properties and relations). Furthermore, it makes it possible to represent existing ontologies in such a way that their content can be understood by users without knowledge of ontologies and their semantics.
Our approach has successfully been applied in building the LHA (Leipzig Health Atlas) portal, which provides access to metadata, data, publications and methods from various research projects at the University of Leipzig.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
“Systems Medicine is the implementation of Systems Biology approaches in medical concepts, research and practice. […]” (https://www.casym.eu/what-is-systems-medicine/).
- 2.
Funded by the German Ministry of Education and Research (reference number: 031L0026, program: i:DSem – Integrative Datensemantik in der Systemmedizin).
References
Horgan RP, Kenny LC (2011) “Omic” technologies: genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics. Obstet Gynaecol 13(3):189–195
ISO 14721:2012. Space data and information transfer systems – Open archival information system (OAIS) – Reference model. https://www.iso.org/standard/57284.html
MEDLINE/PubMed XML data elements. https://www.nlm.nih.gov/bsd/licensee/data_elements_doc.html
Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/
Hanauer DA, Rhodes DR, Sinha-Kumar C, Chinnaiyan AM (2007) Bioinformatics approaches in the study of cancer. Curr Mol Med 7(1):133–141(9)
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, Antipin Y, Reva B, Goldberg AP, Sander C, Schultz N (2012) The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Am Assoc Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
Grossman RL, Heath AP, Ferretti V, Varmus HE, Lowy DR, Kibbe WA, Staudt LM (2016) Toward a shared vision for cancer genomic data. N Engl J Med 375:1109–1112. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1607591
Hoehndorf R, Ngomo A-CN, Herre H (2009) Developing consistent and modular software models with ontologies. In: Fujita H, Marik V (eds) New trends in software methodologies, tools and techniques: proceedings of the Eighth SoMeT_09. Volume 199. IOS Press, pp 399–412. [Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications]
Herre H, Heller B, Burek P, Hoehndorf R, Loebe F, Michalek H (2006) General formal ontology (GFO): a foundational ontology integrating objects and processes. Part I: basic principles (Version 1.0). Onto-Med report. Research Group Ontologies in Medicine (Onto-Med), University of Leipzig
Herre H (2010) General formal ontology (GFO): a foundational ontology for conceptual modelling. In: Poli R, Healy M, Kameas A (eds) Theory and applications of ontology: computer applications. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 297–345
Beger C, Uciteli A, Herre H (2017) Light-weighted automatic import of standardized ontologies into the content management system Drupal. Stud Health Technol Inform 243:170–174
Humfrey N. RDF library for PHP. http://www.easyrdf.org/
Leipzig Health Atlas (LHA). https://www.health-atlas.de/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Uciteli, A., Beger, C., Rillich, K., Meineke, F.A., Loeffler, M., Herre, H. (2018). Ontology-Based Modelling of Web Content: Example Leipzig Health Atlas. In: Hoppe, T., Humm, B., Reibold, A. (eds) Semantic Applications. Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-55433-3_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-55433-3_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-55432-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-55433-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)