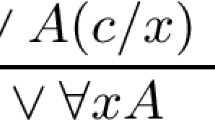Abstract
We introduce a family of logics for reasoning about relational evidence: evidence that involves an ordering of states in terms of their relative plausibility. We provide sound and complete axiomatizations for the logics. We also present several evidential actions and prove soundness and completeness for the associated dynamic logics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andréka, H., Ryan, M., Schobbens, P.: Operators and laws for combining preference relations. J. Logic Comput. 12(1), 13–53 (2002)
Baltag, A., Bezhanishvili, N., Özgün, A., Smets, S.: Justified belief and the topology of evidence. In: Väänänen, J., Hirvonen, Å., de Queiroz, R. (eds.) WoLLIC 2016. LNCS, vol. 9803, pp. 83–103. Springer, Heidelberg (2016). doi:10.1007/978-3-662-52921-8_6
Baltag, A., Fiutek, V., Smets, S.: DDL as an “Internalization” of dynamic belief revision. In: Trypuz, R. (ed.) Krister Segerberg on Logic of Actions, vol. 1, pp. 253–283. Springer, Dordrecht (2014). doi:10.1007/978-94-007-7046-1_12
Baltag, A., Occhipinti Liberman, A.: Evidence logics with relational evidence. Preprint arxiv:1706.05905 (2017)
Baltag, A., Smets, S.: Protocols for belief merge: reaching agreement via communication. Logic J. IGPL 21(3), 468–487 (2013)
Baltag, A., Smets, S., et al.: Talking your way into agreement: belief merge by persuasive communication. In: MALLOW (2009)
Christensen, D.: Higher-order evidence. Philos. Phenomenolog. Res. 81(1), 185–215 (2010)
Dietrich, F., List, C.: Probabilistic opinion pooling generalized. Part one: general agendas. Soc. Choice Welfare 48(4), 747–786 (2017)
Girard, P.: Modal logic for lexicographic preference aggregation. In: van Benthem, J., Gupta, A., Pacuit, E. (eds.) Games, Norms and Reasons. Synthese Library (Studies in Epistemology, Logic, Methodology, and Philosophy of Science), vol. 353, pp. 97–117. Springer, Dordrecht (2011). doi:10.1007/978-94-007-0714-6_6
Harel, D., Kozen, D., Tiuryn, J.: Dynamic Logic (Foundations of Computing). The MIT Press, Cambridge (2000)
Kooi, B., van Benthem, J.: Reduction axioms for epistemic actions. AiML-2004: Advances in Modal Logic, UMCS-04-9-1 in Technical Report Series, pp. 197–211 (2004)
Liu, F.: Reasoning about Preference Dynamics. Springer Nature, New York (2011)
Paris, J., Vencovská, A.: Pure Inductive Logic. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2015)
van Benthem, J.: Belief update as social choice. In: Girard, P., Roy, O., Marion, M. (eds.) Dynamic Formal Epistemology. Synthese Library (Studies in Epistemology, Logic, Methodology, and Philosophy of Science), vol. 351, pp. 151–160. Springer, Dordrecht (2011). doi:10.1007/978-94-007-0074-1_8
van Benthem, J., Fernández-Duque, D., Pacuit, E.: Evidence and plausibility in neighborhood structures. Ann. Pure Appl. Logic 165(1), 106–133 (2014)
van Benthem, J., Pacuit, E.: Dynamic logics of evidence-based beliefs. Stud. Logica 99(1–3), 61–92 (2011)
Benthem, J., Pacuit, E.: Logical dynamics of evidence. In: Ditmarsch, H., Lang, J., Ju, S. (eds.) LORI 2011. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 6953, pp. 1–27. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-24130-7_1
van Eijck, J.: Yet more modal logics of preference change and belief revision. In: New Perspectives on Games and Interaction. Amsterdam University Press (2009)
Acknowledgement
We thank the two anonymous referees for their useful comments. We also thank Johan van Benthem, Benedikt Löwe, Ulle Endriss and Aybüke Özgün for their valuable feedback on a previous version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany
About this paper
Cite this paper
Baltag, A., Occhipinti, A. (2017). Evidence Logics with Relational Evidence. In: Baltag, A., Seligman, J., Yamada, T. (eds) Logic, Rationality, and Interaction. LORI 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10455. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-55665-8_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-55665-8_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-55664-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-55665-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)