Abstract
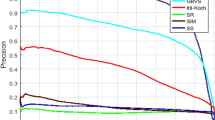
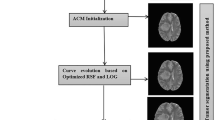
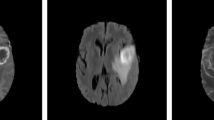
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most clinically used and gifted modality to identify brain abnormalities in individuals who might be at risk for brain cancer. To date, automated brain tumor segmentation from MRI modalities remains a sensitive, computationally expensive, and a demanding task. This paper presents an automated and robust segmentation method to enable investigators to make successful diagnosis and planning of radiosurgery by reducing the risk factor and study duration. The proposed system consists of following steps: (1) remove the non-brain part from MRI, (2) estimate saliency map of MRI, (3) use the salient region (tumor) as an identification marker and segment the salient object by finding the “optimal” closed contour around the tumor. The system has been tested on real patient images with excellent results. The qualitative and quantitative evaluations by comparing with ground truths and with other existing approaches demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ejaz N, Tariq TB, Baik SW (2012) Adaptive key frame extraction for video summarization using an aggregation mechanism. J Vis Commun Image Represent 23(7):1031–1040
Cabezas M, Oliver A, Lladó X, Freixenet J, Cuadra MB (2011) A review of atlas-based segmentation for magnetic resonance brain images. J Comput Methods Programs Biomed 104(3):e158–e177
Boldrey E (1949) A survey of brain tumors for the general practitioner of surgery. Am J Surg 78(3):340–346
Wang X, Pang Q (2011) The research on segmentation of complex object. Int Congr Image Signal Process (CISP) 3:1177–1281
Angelini ED, Clatz O, Emmanuel M, Konukoglu E, Capelle L, Duffau H (2007) Glioma dynamics and computational models: a review of segmentation, registration, and in silico growth algorithms and their clinical applications. J Curr Med Imaging Rev 3(4):262–276(15)
Hamamci A, Kucuk N, Karaman K, Engin K, Unal G (2012) Tumor-cut: segmentation of brain tumors on contrast enhanced MR images for radiosurgery applications. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(3):798–804
Vezhnevets V, Konouchine V (2005) “GrowCut”—interactive multi-label N-D image segmentation by cellular automata. Presented at the Graph-icon, Novosibirsk Akademgorodok
Jaffer A, Zia S, Latif G, Mirza AM, Mehmood I, Ejaz N, Baik SW (2012) Anisotropic diffusion based brain MRI segmentation and 3D reconstruction. Int J Comput Intell Syst 5(3):494–504
Boesen K, Rehm K, Schaper K, Stoltzner S, Woods R, Lüders E, Rottenberg D (2004) Quantitative comparison of four brain extraction algorithms. J Neuroimage 22(3):1255–1261
Blackwell HR (1946) Contrast thresholds of the human eye. J Opt Soc Am (1917–1983) 36(11):624–632
Wang XT, Wu JT (2012) Active contours for specific target detection. Electron Lett 48(2):83–84
Harvard Medical School http://med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/
Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences http://www.pims.gov.pk/radiology.htm
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by: (1) The Industrial Strategic technology development program, 10041772, (The Development of an Adaptive Mixed-Reality Space based on Interactive Architecture) funded by the MKE (Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Korea) and, (2) The Ministry of Knowledge Economy (MKE), Korea, under IT/SW Creative research program supervised by the National IT Industry Promotion Agency (NIPA)” (NIPA-2012-H0502-12-1013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mehmood, I., Baik, R., Baik, S.W. (2013). Automatic Segmentation of Region of Interests in MR Images Using Saliency Information and Active Contours. In: Kim, K., Chung, KY. (eds) IT Convergence and Security 2012. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 215. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5860-5_64
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5860-5_64
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-5859-9
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-5860-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)