Abstract
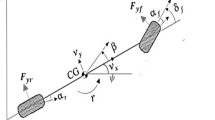
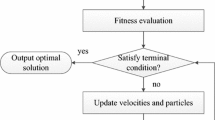
This paper proposes an intelligent tuning methods of linear and nonlinear parameters for composite nonlinear feedback (CNF) control using multi objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) and multi objective genetic algorithm (MOGA). The main advantage of the methods lies in its efficient fitness/objective evaluation approach of the algorithms such that it can be computed rapidly to obtain an optimal CNF with good system response. In order to yield an efficient technique for fitness evaluation, it is achieved by utilizing a multi objective approach, thus avoiding the use of single objective approach to evaluate the fitness. MATLAB simulations are used to test the effectiveness of the proposed techniques. Nonlinear vehicle model is constructed to validate the controller performance. The model is also simplified to a linear model for designing the CNF. The superiority of the proposed methods over the manual tuning method are improved with 98 percent reduction in error.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, Z., Pachter, M., Banda, S.: Toward improvement of tracking performance nonlinear feedback for linear systems. Int. J. Control 70, 1–11 (1998)
Ma, D., Cao, Y., Fan, D.: Design and implementation of an electro-optical tracking servo system via composite nonlinear control approach. In: Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA), pp. 1139–1142 (2010)
Chen, B.M., Weiyao, L.: On improving transient performance in tracking control for a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems with input saturation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 52, 1307–1313 (2007)
Yingjie, H., Chen, B.M., Chao, W.: Composite nonlinear control with state and measurement feedback for general multivariable systems with input saturation. In: IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 4469–4474 (2003)
Chen, B.M., Lee, T.H., Kemao, P., Venkataramanan, V.: Composite nonlinear feedback control for linear systems with input saturation: theory and an application. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 48, 427–439 (2003)
Weiyao, L., Thum, C.K., Chen, B.M.: A hard-disk-drive servo system design using composite nonlinear-feedback control with optimal nonlinear gain tuning methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 57, 1735–1745 (2010)
Kiencke, U., Nielsen, L.: Automotive Control Systems for Engine, Driveline and Vehicle. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Baṣlamiṣli, S.Ç., Köse, İ.E., Anlaç, G.: Handling stability improvement through robust active front steering and active differential control. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 49, 657–683 (2010)
Pacejka, H.B.: Tyre and Vehicle Dynamics. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2002)
Jazar, R.N.: Vehicle Dynamics: Theory and Application. Springer, New York (2008)
Ramli, L., Sam, Y.M., Mohamed, Z., Khairi Aripin, M., Fahezal Ismail, M.: Composite nonlinear feedback control with multi-objective particle swarm optimization for active front steering system. Jurnal Teknologi 72, 13–20 (2015). Scopus
Mirzaei, M.: A new strategy for minimum usage of external yaw moment in vehicle dynamic control system. Transp. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol. 18, 213–224 (2010)
Weiyao, L., Chen, B.M.: On selection of nonlinear gain in composite nonlinear feedback control for a class of linear systems. In: IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 1198–1203 (2007)
Ismail, F.S.: Self organizing genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization problems. Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (2011)
He, J.: Integrated vehicle dynamics control using active steering, driveline and braking. University of Leeds (United Kingdom), Ann Arbor (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Science+Business Media Singapore
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ramli, L., Sam, Y.M., Mohamed, Z. (2016). A Comparison of Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithm Based on Multi-objective Approach for Optimal Composite Nonlinear Feedback Control of Vehicle Stability System. In: Zhang, L., Song, X., Wu, Y. (eds) Theory, Methodology, Tools and Applications for Modeling and Simulation of Complex Systems. AsiaSim SCS AutumnSim 2016 2016. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 643. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2663-8_67
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2663-8_67
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-2662-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-2663-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)