Abstract
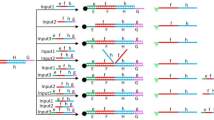
DNA strand displacement has great potential for use in logic circuits. In the paper, the two DNA-based logic circuits that behave as half-subtract and half-adder were implemented relying on strand displacement and fluorescence labeling technique. The half-adder and half-subtract were achieved by simply modifying the sequences of the input strands, while retaining the same DNA logical structure as a universal platform. By taking advantage of the branch migration mechanism, separation and combination of fluorescent group were controlled, two series of fluorescence signals were defined as the output signal. We simulated within the Visual DSD design tool which analyzes their performance and proves the correctness of the circuits. The system reported herein is rather concise compared to other molecular logic gate systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin, X.: Probe machine. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(7), 1405–1416 (2016)
Shi, X., Wei, L., Wang, Z., Pan, L., Cui, G., Jin, X., LaBean, T.H.: Programmable DNA tile self-assembly using a hierarchical sub-tile strategy. Nanotechnology 25(7), 075602 (2014)
Shi, X., Wang, Z., Deng, C., Song, T., Pan, L., Chen, Z.: A novel bio-sensor based on DNA strand displacement. PLoS ONE 9(10), e108856 (2014)
Yang, J., Dong, C., Dong, Y., Liu, S., Pan, L., Zhang, C.: Logic nanoparticle beacon triggered by the binding-induced effect of multiple inputs. ACS Appl. Mater. 6(16), 14486–14492 (2014). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0108856
Adleman, L.M.: Molecular computation of solutions to combinatorial problems. Science 266(5187), 1021–1024 (1994)
Qian, L., Winfree, E.: Scaling up digital circuit computation with DNA strand displacement cascades. Science 332(6034), 1196–1201 (2011)
Qian, L., Winfree, E., Bruck, J.: Neural network computation with DNA strand displacement cascades. Nature 475(7356), 368–372 (2011)
Lin, H.Y., Chen, J.Z., Li, H.Y., Yang, C.N.: A simple three-input DNA-based system works as a full-subtractor. Sci. Rep. 5(6), 2045–2322 (2015)
Yang, C.N., Hsu, C.Y., Chuang, Y.C.: Molecular beacon-based half-adder and half-subtractor. Chem. Commun. 48(1), 112–114 (2012)
Saghatelian, A., Guckian, K.M., Thayer, D.A., et al.: DNA detection and signal amplification via an engineered allosteric enzyme. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(2), 344–345 (2003)
Wang, Z., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., Cui, G.: A DNA code converter model for decimal numbers displaying. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 562, 447–455 (2015)
Xu, S.L., Li, H.L., Miao, Y.Q., et al.: Implementation of half adder and half subtractor with a simple and universal DNA-based platform. NPG Asia Mater. 5, e76 (2013)
Matthew, L., Simon, Y.: Visual DSD: a design and analysis tool for DNA strand displacement systems. Bioinformatics 27(22), 3211–3213 (2011)
Lakin, M.R., Yourssef, S., Cardelli, L., Phillips, A.: Abstractions for DNA circuit design. J. R. Soc. Interface 9(68), 470–486 (2012)
Yang, J., Ma, J., Liu, S., Zhang, C.: A molecular cryptograph model based on structures of DNA self-assembly. Comput. Sci. Technol. 59(11), 1192–1198 (2014)
Sun, J., Shen, Y.: Quasi-ideal memory system. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 45(7), 1353–1362 (2015)
Sun, J., Quan, Y., Shen, Y.: Compound synchronization for four chaotic systems of integer order, fractional order. Europhys. Lett. 106(4), 40005 (2014)
Sun, J., Shen, Y., Zhang, G., Xu, C., Cui, G.: Combination-combination synchronization among four identical or different chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 73(3), 1211–1222 (2013)
Junwei, S., Guangzhao, C., Yanfeng, W., Yi, S.: Combination complexsynchronization of three chaotic complex systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(2), 953–965 (2015)
Song, T., Pan, L.: Spiking neural P systems with request rules. Neurocomputing 193(12), 193–200 (2016)
Song, T., Liu, X., Zhao, Y., Zhang, X.: Spiking neural P systems with white hole neurons. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. (2016). doi:10.1109/TNB.2016.2598879
Song, T., Pan, Z., Wong, D.M., Wang, X.: Design of logic gates using spiking neural P systems with homogeneous neurons and astrocytes-like control. Inf. Sci. 372, 380–391 (2016)
Wang, X., Song, T., Gong, F., Pan, Z.: On the computational power of spiking neural P systems with self-organization. Sci. Rep. doi:10.1038/srep27624
Shi, X., Wu, X., Song, T., Li, X.: Construction of DNA nanotubes with controllable diameters and patterns by using hierarchical DNA sub-tiles. Nanoscale. doi:10.1039/C6NR02695H
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by the NSFC (No. U1304620, 61472372, 61272022), Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan (Grant No. 124200510017), and Innovation Scientists Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Zhengzhou (Grant No. 131PLJRC648), Basic and Frontier technologies Research Program of Henan Province (132300410183), Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan Province (154200510012). Scientific Research Fund Project of Zhengzhou University of Light Industry (2014XJJ013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Z., Ai, J., Wang, Y., Cui, G., Yao, L. (2016). A Universal Platform for Building DNA Logic Circuits. In: Gong, M., Pan, L., Song, T., Zhang, G. (eds) Bio-inspired Computing – Theories and Applications. BIC-TA 2016. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 681. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3611-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3611-8_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-3610-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-3611-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)