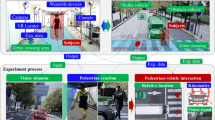
Abstract
This study advances the concept of “ambulanceye” as a conjecture on the future of medical rescues, assuming that the advanced driver assistant systems (ADAS) can be equipped in ambulances and contribute to driving security through timely danger caution. Recognition of the danger is based on detecting and tracking of eigenobjects (defined as the potential dangerous objects in the video). Simulated performances shown that ambulanceye can overcome ocular restriction resulted from weathering extremes and other accidents that can cause sights blurred. Nevertheless, considerable uncertainties still remain in real-time analyses and characterization of eigenobjects trace. A next research priority is to develop an ADAS system for efficient eigenobjects recognition and tracking.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kovar, L., Gleicher, M.: Automated extraction and parameterization of motions in large data sets. ACM Trans. Graph. 23(3), 559–568 (2004)
Philip Chen, C.L., Zhang, C.Y.: Data-intensive applications, challenges, techniques and technologies: a survey on big data. Inf. Sci. 275(11), 314–347 (2014)
Marx, V.: The big challenges of big data. Nat. 498(7453), 255–260 (2013)
Richtárik, P., Takáč, M.: Parallel coordinate descent methods for big data optimization. Math. Prog. 156(1), 1–52 (2016)
Vazhkudai, S., Schopf, J.M.: Using regression techniques to predict large data transfers. Int. J. High Perform. Comput. Appl. 17(3), 249–268 (2003)
Waldrop, M.: Big data: wikiomics. Nat. 455(7209), 22–25 (2008)
Kim, G.H., Trimi, S., Chung, J.H.: Big-data applications in the government sector. Commun. ACM 57(3), 78–85 (2014)
Mervis, J.: Agencies rally to tackle big data. Sci. 336(6077), 22–22 (2012)
Wigan, M.R., Clarke, R.: Big data’s big unintended consequences. Comput. 46(6), 46–53 (2013)
Talia, D.: Clouds for scalable big data analytics. Comput. 46(5), 98–101 (2013)
Westgate, B.S., Woodard, D.B., Matteson, D.S., Henderson, S.G.: Large-network travel time distribution estimation for ambulances. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 252(1), 322–333 (2016)
Shin, D.M., Yoon, B.G., Han, Y.T.: Analysis of ambulance traffic accident during driving. vol. 30(1), pp. 130–137 (2016)
Shin, D.M., Kim, S.Y., Han, Y.T.: A study on the comparative analysis of fire-fighting ambulances about the aspects of safety and efficiency using the question investigation. vol. 29(2), pp. 44–53 (2015)
Ambrose, J.: Emergency response driving education within UK ambulance services. J. Paramedic Pract. 5(6), 351–353 (2013)
Sundström, A., Albertsson, P.: Self- and peer-assessments of ambulance drivers’ driving performance. Iatss Res. 36(1), 40–47 (2012)
Raaber, N., Duvald, I., Riddervold, I., Christensen, E.F., Kirkegaard, H.: Geographic information system data from ambulances applied in the emergency department: effects on patient reception. Scand. J. Trauma Resuscitation Emerg. Med. 24(1), 1–9 (2016)
Fu, Q., Li, B., Yang, L., Wu, Z., Zhang, X.: Ecosystem services evaluation and its spatial characteristics in central Asia’s arid regions: a case study in Altay prefecture, china. Sustain. 7(7), 8335–8353 (2015)
Xie, Z., Liu, G.: Blood perfusion construction for infrared face recognition based on bio-heat transfer. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 24(6), 2733–2742 (2014)
Jin, L., Niu, Q., Jiang, Y., Xian, H., Qin, Y., Xu, M.: Driver sleepiness detection system based on eye movements variables. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2013(5), 1–7 (2013)
Wang, T., Dong, J., Sun, X., Zhang, S., Wang, S.: Automatic recognition of facial movement for paralyzed face. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 24(6), 2751–2760 (2014)
Vithya, G., Sundaram, B.V.: Inpatient critical stage monitoring in smart hospitals by contextual Fuzzy based QoS routing for WBMS network nurse call system. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 94, 1–16 (2016)
Nandyala, C.S., Kim, H.K.: From cloud to Fog and IoT-based real-time U-healthcare monitoring for smart homes and hospitals. Int. J. Smart Home 10(2), 187–196 (2016)
Chen, X., Wang, L., Ding, J., et al.: Patient flow scheduling and capacity planning in a smart hospital environment. IEEE Access 4, 135–148 (2016)
Al-Refaie, A., Chen, T., Judeh, M.: Optimal operating room scheduling for normal and unexpected events in a smart hospital. Oper. Res. pp. 1–24 (2016)
Vecchia, G.D., Gallo, L., Esposito, M., et al.: An infrastructure for smart hospitals. Multimed. Tools Appl. 59(1), 341–362 (2012)
Yao, W., Chu, C.H., Li, Z.: Leveraging complex event processing for smart hospitals using RFID. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 34(3), 799–810 (2011)
Fang, Y.L., Zhang, A., Wang, H., Li, H., Zhang, Z.W., Chen, S.X., Luan, L.Y.: Health risk assessment of trace elements in Chinese raisins produced in Xinjiang province. Food Control 21(5), 732–739 (2010)
Jing, L.: Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 77(1–3), 125–141 (2008)
Dewan, M.A.A., Granger, E., Marcialis, G.L., et al.: Adaptive appearance model tracking for still-to-video face recognition. Pattern Recogn. 49(C), 129–151 (2016)
Babenko, B., Yang, M.H., Belongie, S.: Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(8), 1619–1632 (2011)
Wu, Y., Jia, N., Sun, J.: Real-time multi-scale tracking based on compressive sensing. Vis. Comput. Int. J. Comput. Graph. 31(4), 471–484 (2015)
Mei, X., Ling, H.: Robust visual tracking and vehicle classification via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 33(11), 2259–2272 (2011)
Yamins, D.L.K., Dicarlo, J.J.: Using goal-driven deep learning models to understand sensory cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 19(3), 356–365 (2016)
Chen, L., Qu, H., Zhao, J., Principe, J.C.: Efficient and robust deep learning with Correntropy- induced loss function. Neural Comput. Appl. 27(4), 1019–1031 (2016)
Ghesu, F.C., Krubasik, E., Georgescu, B., Singh, V.: Marginal space deep learning: efficient architecture for volumetric image parsing. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1217–1228 (2016)
Erfani, S.M., Rajasegarar, S., Karunasekera, S., Leckie, C.: High-dimensional and large-scale anomaly detection using a linear one-class SVM with deep learning. Pattern Recogn. 58, 121–134 (2016)
Greenspan, H., Ginneken, B.V., Summers, R.M.: Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: overview and future promise of an exciting new technique. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1153–1159 (2016)
Wang, Y., Luo, Z., Jodoin, P.M.: Interactive deep learning method for segmenting moving objects. Pattern Recogn. Lett. (2016). doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2016.09.014
Ngo, T.A., Lu, Z., Carneiro, G.: Combining deep learning and level set for the automated segmentation of the left ventricle of the heart from cardiac cine magnetic resonance. Med. Image Anal. 35, 159–171 (2016)
Leng, J., Jiang, P.: A deep learning approach for relationship extraction from interaction context in social manufacturing paradigm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 100(C), 188–199 (2016)
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the CAS ‘Light of West China’ Program (XBBS-2014-16), the Shenzhen Basic Research Project (JCYJ20150630114942260), the “Thousand Talents” plan (Y474161) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program (2013AA122302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, W., Chen, X., Zhou, H., Zheng, H., Sun, D., Qian, J. (2017). Ambulanceye – The Future of Medical Rescues. In: Sun, F., Liu, H., Hu, D. (eds) Cognitive Systems and Signal Processing. ICCSIP 2016. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 710. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5230-9_59
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5230-9_59
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-5229-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-5230-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)