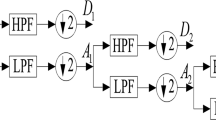
Abstract
This paper proposed a novel combination of prediction model based on Adaptive Cauchy and Chaos Quantum-behaved Particle Swarm Optimization (ACCQPSO) and Least Squares Support Vector Machine (LSSVM) to forecast the short-term output power more accurately. To improve the performance of QPSO, chaotic sequences are used to initialize the origin particles, and particle premature convergence criterion, Cauchy and Chaos algorithm are employed, which can effectively increase the diversity of population and avoid the premature convergence. The kernel parameters of LSSVM are optimized by ACCQPSO to obtain hybrid forecasting model. To verify the proposed method, the seven days actual data recorded in a wind farm located in Anhui of China are utilized for application validation. The results show that the proposed combinational model achieves higher prediction accuracy.
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61633016 and 61533010, in part by the Key Project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality under Grant No. 15220710400.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, Q., Peng, C.Y.: Wind power grid connected capacity prediction using LSSVM optimized by the Bat algorithm. Energies 8(12), 14346–14360 (2015)
Foley, A.M., Leahy, P.G., Marvuglia, A., et al.: Current methods and advances in forecasting of wind power generation. Renew. Energy 37(1), 1–8 (2012)
Montoya, F.G., Manzano-Agugliaro, F., Lopez-Marquez, S., et al.: Wind turbine selection for wind farm layout using multi-objective evolutionary algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(15), 6585–6595 (2014)
Chitsaz, H., Amjady, N., Zareipour, H.: Wind power forecast using wavelet neural network trained by improved clonal selection algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 89, 588–598 (2015)
Jiang, P., Qin, S.S., Wu, J., et al.: Time series analysis and forecasting for wind speeds using support vector regression coupled with artificial intelligent algorithms. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 1–14 (2015)
Amjady, N., Keynia, F., Zareipour, H.: Wind power prediction by a new forecast engine composed of modified hybrid neural network and enhanced particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2(3), 265–276 (2011)
Yuan, X., Chen, C., Yuan, Y.B., et al.: Short-term wind power prediction based on LSSVM-GSA model. Energy Convers. Manag. 101, 393–401 (2015)
Guo, Z.H., Zhao, J., Zhang, W.Y., et al.: A corrected hybrid approach for wind speed prediction in Hexi Corridor of China. Energy 36(3), 1668–1679 (2011)
Hu, J.M., Wang, J.Z., Ma, K.L.: A hybrid technique for short-term wind speed prediction. Energy 81, 563–574 (2015)
Li, G., Shi, J.: On comparing three artificial neural networks for wind speed forecasting. Appl. Energy 87(7), 2313–2320 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xiong, N., Fei, M., Sun, S., Yang, T. (2017). A Novel Combination of Forecasting Model Based on ACCQPSO-LSSVM and Its Application. In: Li, K., Xue, Y., Cui, S., Niu, Q., Yang, Z., Luk, P. (eds) Advanced Computational Methods in Energy, Power, Electric Vehicles, and Their Integration. ICSEE LSMS 2017 2017. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 763. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6364-0_62
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6364-0_62
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-6363-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-6364-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)