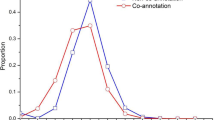
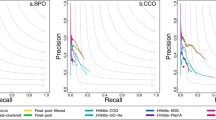
Abstract
Detection of unannotated protein functions in a protein interaction network generates a lot of beneficial information in the field of drug discovery of various kinds of diseases. Though most of the various computational methods have succeeded in predicting functions of huge amount of unknown proteins at recent times but the main problem is the simultaneous increase of false positives in most of the predicted results. In this work, a bottom-up predictor of existing Apriori algorithm has been implemented for protein function prediction by exploiting two most important neighborhood properties: closeness centrality and edge clustering coefficient of protein interaction network. The method is also unique in the fact that the functions of the leaf nodes in the interaction network have been back propagated and thus labeled up to the root node (target protein) using a bottom-up level to level approach. An overall precision, recall and F-score of 0.86, 0.65 and 0.74 respectively have been obtained in this work which are found to be better than most of the current state-of-the-art.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwikowski, B., Uetz, P., Fields, S.: A network of protein-protein interactions in yeast. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 1257–1261 (2000)
Hishigaki, H., Nakai, K., Ono, T., Tanigami, A., Takagi, T.: Assessment of prediction accuracy of protein function from protein–protein interaction data. Yeast. 18, 523–531 (2001)
Chen, J., Hsu, W., Lee, M.L., Ng, S.-K.: Labeling network motifs in protein interactomes for protein function prediction. In: IEEE 23rd International Conference on Data Engineering, pp. 546–555. IEEE (2007)
Vazquez, A., Flammini, A., Maritan, A., Vespignani, A.: Global protein function prediction from protein-protein interaction networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 697–700 (2003)
Karaoz, U., Murali, T.M., Letovsky, S., Zheng, Y., Ding, C., Cantor, C.R., Kasif, S.: Whole-genome annotation by using evidence integration in functional-linkage networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 2888–2893 (2004)
Deng, M., Mehta, S., Sun, F., Chen, T.: Inferring domain–domain interactions from protein–protein interactions. Genome Res., 1540–1548 (2002)
Nabieva, E., Jim, K., Agarwal, A., Chazelle, B., Singh, M.: Whole-proteome prediction of protein function via graph-theoretic analysis of interaction maps. Bioinformatics 21(Suppl 1), i302–310 (2005)
Wu, D.D.: An efficient approach to detect a protein community from a seed. In: IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, pp. 1–7. IEEE (2005)
Letovsky, S., Kasif, S.: Predicting protein function from protein/protein interaction data: a probabilistic approach. Bioinformatics 19, i197–i204 (2003)
Arnau, V., Mars, S., Marín, I.: Iterative cluster analysis of protein interaction data. Bioinformatics 21, 364–378 (2005)
Samanta, M.P., Liang, S.: Predicting protein functions from redundancies in large-scale protein interaction networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 12579–12583 (2003)
King, A.D., Przulj, N., Jurisica, I.: Protein complex prediction via cost-based clustering. Bioinformatics 20, 3013–3020 (2004)
Asthana, S., King, O.D., Gibbons, F.D., Roth, F.P.: Predicting protein complex membership using probabilistic network reliability. Genome Res. 14, 1170–1175 (2004)
Xiong, W., Liu, H., Guan, J., Zhou, S.: Protein function prediction by collective classification with explicit and implicit edges in protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinf. 14(Suppl 1), S4 (2013)
Saha, S., Chatterjee, P., Basu, S., Kundu, M., Nasipuri, M.: Improving prediction of protein function from protein interaction network using intelligent neighborhood approach. In: International Conference on Communications, Devices and Intelligent Systems (CODIS), pp. 584–587. IEEE (2012)
Saha, S., Chatterjee, P., Basu, S., Kundu, M., Nasipuri, M.: FunPred-1: protein function prediction from a protein interaction network using neighborhood analysis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 19, 675–691 (2014)
Saha, S., Chatterjee, P.: Protein function prediction from protein interaction network using physico-chemical properties of amino acids. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 4, 55–65 (2014)
Piovesan, D., Giollo, M., Leonardi, E., Ferrari, C., Tosatto, S.C.E.: INGA: protein function prediction combining interaction networks, domain assignments and sequence similarity. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, W134–140 (2015)
Zhao, B., Wang, J., Member, S., Li, M., Li, X., Li, Y.: A new method for predicting protein functions from dynamic weighted interactome networks. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 15, 131–139 (2016)
Wu, Q., Ye, Y., Ng, M.K., Ho, S.-S., Shi, R.: Collective prediction of protein functions from protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinf. 15(Suppl 2), S9 (2014)
Sandhan, T., Yoo, Y., Choi, J.Y., Kim, S.: Graph pyramids for protein function prediction. BMC Med. Genomics 8, S12 (2015)
Huang, L., Liao, L., Wu, C.H.: Inference of protein-protein interaction networks from multiple heterogeneous data. EURASIP J. Bioinforma. Syst. Biol. 2016, 8 (2016)
Saha, S., Chatterjee, P., Basu, S., Nasipuri, M.: Gene ontology based function prediction of human protein using protein sequence and neighborhood property of PPI network. In: Satapathy, S.C., Bhateja, V., Udgata, Siba K., Pattnaik, P.K. (eds.) Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Frontiers in Intelligent Computing: Theory and Applications. AISC, vol. 516, pp. 109–118. Springer, Singapore (2017). doi:10.1007/978-981-10-3156-4_11
Saha, S., Chatterjee, P., Basu, S., Nasipuri, M.: Functional group prediction of un-annotated protein by exploiting its neighborhood analysis in saccharomyces cerevisiae protein interaction network. In: Chaki, R., Saeed, K., Cortesi, A., Chaki, N. (eds.) Advanced Computing and Systems for Security. AISC, vol. 568, pp. 165–177. Springer, Singapore (2017). doi:10.1007/978-981-10-3391-9_11
Zhao, B., Hu, S., Li, X., Zhang, F., Tian, Q., Ni, W.: An efficient method for protein function annotation based on multilayer protein networks. Hum. Genomics. 10, 1–15 (2016)
Peng, W., Wang, J., Wang, W., Liu, Q., Wu, F.-X., Pan, Y.: Iteration method for predicting essential proteins based on orthology and protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Syst. Biol. 6, 87 (2012)
Freeman, L.C.: A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness. Sociometry 40, 35–41 (1977)
Freeman, L.C.: Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc. Networks. 1, 215–239 (1978)
Opsahl, T., Agneessens, F., Skvoretz, J.: Article Node centrality in weighted networks Generalizing degree and shortest paths. Soc. Networks (2010)
Moosavi, S., Rahgozar, M., Rahimi, A.: Protein function prediction using neighbor relativity in protein-protein interaction network. Comput. Biol. Chem. 43, 11–16 (2013)
Chatterjee, P., Basu, S., Kundu, M., Nasipuri, M., Plewczynski, D.: PPI_SVM: prediction of protein-protein interactions using machine learning, domain-domain affinities and frequency tables. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 16, 264–278 (2011)
Chatterjee, P., Basu, S., Kundu, M., Nasipuri, M., Plewczynski, D.: PSP_MCSVM: brainstorming consensus prediction of protein secondary structures using two-stage multiclass support vector machines. J. Mol. Model. 17, 2191–2201 (2011)
Chatterjee, P., Basu, S., Zubek, J., Kundu, M., Nasipuri, M., Plewczynski, D.: PDP-RF: Protein Domain Boundary Prediction Using Random Forest Classifier. In: Kryszkiewicz, M., Bandyopadhyay, S., Rybinski, H., Pal, Sankar K. (eds.) PReMI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9124, pp. 441–450. Springer, Cham (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-19941-2_42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Prasad, A., Saha, S., Chatterjee, P., Basu, S., Nasipuri, M. (2017). Protein Function Prediction from Protein Interaction Network Using Bottom-up L2L Apriori Algorithm. In: Mandal, J., Dutta, P., Mukhopadhyay, S. (eds) Computational Intelligence, Communications, and Business Analytics. CICBA 2017. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 776. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6430-2_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6430-2_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-6429-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-6430-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)