Abstract
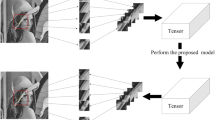
Video inpainting is the process of improving the information content in a video by removing irrelevant video objects and restoring lost or deteriorated parts utilizing the spatiotemporal features that are available from adjacent frames. This paper proposes an effective video inpainting technique utilizing the multi-dimensional data decomposition technique. In Tensor Robust Principal Component Analysis (TRPCA), a multi-dimensional data corrupted by gross errors is decomposed into a low multi-rank component and a sparse component. The proposed method employs an improved version of TRPCA called Re-weighted low-rank Tensor Decomposition (RWTD) to separate the true information and the irrelevant sparse components in a video. Through this, manual identification of the components which have to be removed is avoided. Subsequent inpainting algorithm fills the region with appropriate and visually plausible data. The capabilities of the proposed method are validated by applying into videos having moving sparse outliers in it. The experimental results reveal that the proposed method performs well compared with other techniques.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Moran, “Video inpainting,” vol. 1, pp. 12–25, 2009.
W. Zhang, S. Cheung, and M. Chen, “Hiding privacy information in video surveillance system,” in Image Processing, 2005. ICIP 2005. IEEE International Conference on, vol. 3. IEEE, 2005, pp. II–868.
Y. Umeda and K. Arakawa, “Removal of film scratches using exemplar-based inpainting with directional median filter,” in Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), 2012 International Symposium on. IEEE, 2012, pp. 6–11.
S. Yoo and R.-H. Park, “Red-eye detection and correction using inpainting in digital photographs,” IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 1006–1014, 2009.
V. V. Mahalingam, Digital inpainting algorithms and evaluation. University of Kentucky, 2010.
M. Bertalmio, A. L. Bertozzi, and G. Sapiro, “Navier-stokes, fluid dynamics, and image and video inpainting,” in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2001. CVPR 2001. Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on, vol. 1. IEEE, 2001, pp. I–I.
W.-Q. Yan and M. S. Kankanhalli, “Erasing video logos based on image inpainting,” in Multimedia and Expo, 2002. ICME’02. Proceedings. 2002 IEEE International Conference on, vol. 2. IEEE, 2002, pp. 521–524.
A. Newson, A. Almansa, M. Fradet, Y. Gousseau, and P. Pérez, “Video inpainting of complex scenes,” SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 1993–2019, 2014.
T. K. Shih, N. C. Tang, and J.-N. Hwang, “Exemplar-based video inpainting without ghost shadow artifacts by maintaining temporal continuity,” IEEE transactions on circuits and systems for video technology, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 347–360, 2009.
M. V. Venkatesh, S.-c. S. Cheung, and J. Zhao, “Efficient object-based video inpainting,” Pattern Recognition Letters, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 168–179, 2009.
P. Kumar and P. Puttaswamy, “Moving text line detection and extraction in tv video frames,” in Advance Computing Conference (IACC), 2015 IEEE International. IEEE, 2015, pp. 24–28.
C. Lu, J. Feng, Y. Chen, W. Liu, Z. Lin, and S. Yan, “Tensor robust principal component analysis: Exact recovery of corrupted low-rank tensors via convex optimization,” in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, (CVPR), 2016.
M. E. Kilmer, K. Braman, N. Hao, and R. C. Hoover, “Third-order tensors as operators on matrices: A theoretical and computational framework with applications in imaging,” SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 148–172, 2013.
B. M. and S. N. George, “Reweighted low-rank tensor decomposition and its applications in video denoising,” CoRR, vol. abs/1611.05963, 2016. [Online]. Available.
D. Goldfarb and Z. Qin, “Robust low-rank tensor recovery: Models and algorithms,” SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 225–253, 2014.
C. D. Martin, R. Shafer, and B. LaRue, “An order-p tensor factorization with applications in imaging,” SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. A474–A490, 2013. [Online]. Available.
T. G. Kolda and B. W. Bader, “Tensor decompositions and applications,” SIAM Review, vol. 51, no. 3, pp. 455–500, 2009. [Online]. Available.
V. Chandrasekaran, S. Sanghavi, P. A. Parrilo, and A. S. Willsky, “Rank-sparsity incoherence for matrix decomposition,” SIAM Journal on Optimization, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 572–596, 2011.
M. Yan and W. Yin, “Self equivalence of the alternating direction method of multipliers,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1407.7400, 2014.
X. Yuan, “Alternating direction methods for sparse covariance selection,” preprint, 2009.
Z. Lin, R. Liu, and Z. Su, “Linearized alternating direction method with adaptive penalty for low-rank representation,” in Advances in neural information processing systems, 2011, pp. 612–620.
Y. Xu and W. Yin, “A block coordinate descent method for regularized multiconvex optimization with applications to nonnegative tensor factorization and completion,” SIAM Journal on imaging sciences, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 1758–1789, 2013.
https://media.xiph.org/video/derf/. [Online]. Available.
A. Sobral, T. Bouwmans, and E.-h. Zahzah, “Lrslibrary: Low-rank and sparse tools for background modeling and subtraction in videos,” in Robust Low-Rank and Sparse Matrix Decomposition: Applications in Image and Video Processing. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ravindran, A., Baburaj, M., George, S.N. (2018). Video Inpainting Based on Re-weighted Tensor Decomposition. In: Chaudhuri, B., Kankanhalli, M., Raman, B. (eds) Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Computer Vision & Image Processing . Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 703. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7895-8_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7895-8_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-7894-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-7895-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)