Abstract
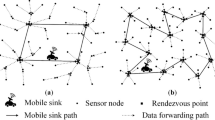
Wireless sensor networks based on mobile sink (MS) can significantly alleviate the problem of network congestion and energy hole, but it results in large delay because of restriction of moving speed and lead to the loss of data due to the limited communication time. In this paper, a grid-based efficient scheduling and data gathering scheme (GES-DGS) is proposed for maximizing the amount of data collected and reducing energy consumption simultaneously within the delay of network tolerance. The main challenges of our scheme are how to optimize the trajectory and the sojourn times of MS and how to deliver the sensed data to MS in an energy-efficient way. To deal with the above problems, we first divide the monitoring field into multiple grids and construct the hop gradient of each grid. Second, we design a heuristic rendezvous point selection strategy to determine the trajectory of MS and devise a routing protocol based on hops and energy. With extensive simulation, we demonstrate that GES-DGS scheme not only significantly extends network lifespan compared with MS-based data gathering schemes, but also pro-actively adapts to the changes in delay in specific applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Z., Shen, H.: A grid-based reliable multi-hop routing protocol for energy-efficient wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1550147718765962
Xing, G., Wang, T., Xie, Z., et al.: Rendezvous planning in wireless sensor networks with mobile elements. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 7(12), 1430–1443 (2008)
Wen, W., Zhao, S., Shang, C., et al.: EAPC: Energy-aware path construction for data collection using mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sens. J. PP(99), 1 (2017)
Yun, Y.S., Xia, Y.: Maximizing the lifespan of wireless sensor networks with mobile sink in delay-tolerant applications. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 9(9), 1308–1318 (2010)
Cayirpunar, O., Tavli, B., Kadioglu-Urtis, E., et al.: Optimal mobility patterns of multiple base stations for wireless sensor network lifespan maximization. IEEE Sens. J. 17(21), 7177–7188 (2017)
Cheng, C.F., Li, L.H., Wang, C.C.: Data gathering with minimum number of relay packets in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sens. J. PP(99), 1 (2017)
Huynh, T.T., Dinh-Duc, A.V., Tran, C.H.: Delay-constrained energy-efficient cluster-based multi-hop routing in wireless sensor networks. J. Commun. Netw. 18(4), 580–588 (2016)
Somasundara, A.A., Kansal, A., Jea, D.D., et al.: Controllably mobile infrastructure for low energy embedded networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 5(8), 958–973 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61170232 and 81160183, Australian Research Council Discovery Project under Grant DP150104871 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the New Teachers’ Scientific Research Fund of People’s Public Security University of China under its projects number 2018JKF609.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, Z., Shen, H., Zhao, X., Wang, T. (2019). Efficient Scheduling Strategy for Data Collection in Delay-Tolerant Wireless Sensor Networks with a Mobile Sink. In: Park, J., Shen, H., Sung, Y., Tian, H. (eds) Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies. PDCAT 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 931. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-5907-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-5907-1_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-5906-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-5907-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)