Abstract
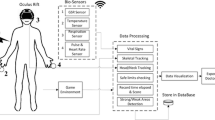
This work presents a virtual system for the rehabilitation of the upper extremities, using the MYO Smart Band device for the acquisition of electromyographic signals produced by the user. Processing and managing of these signals are done through the SDK provided by the manufacturer of the bracelet which is compatible with the MATLAB software. The virtual environment is developed in the Unity 3D graphics engine, in which three-dimensional objects that were previously designed in the 3ds Max software are implemented. The application presents the user with a virtual scenario set in a natural landscape, in which there is a van that must be driven on a certain path (the complexity is increasing). The videogame is of low complexity, since it seeks to avoid situations of stress while the rehabilitation process takes place. Each task in the application is associated with a hand and forearm movement of the user; it means the patient is given an alternative tool that allows him/her to perform exercises that improve his/her extremity active mobility, mitigating the routine effects of a conventional session. To validate this proposal, it is tested by five retired military personnel in passive state, to whom the using task ease (SEQ) usability test is applied. The result is (58,8 ± 0,27), which shows that this interactive interface has a good acceptance when being in the range between 40 and 65.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drakos, N.D., et al.: In good conscience: developing and sustaining military combat trauma expertise. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 227(2), 293–294 (2018)
Russell, C.A., Gibbons, S.W., Abraham, P.A., Howe, E.R., Deuster, P., Russell, D.W.: Narrative approach in understanding the drivers for resilience of military combat medics. J. R. Army Med. Corps. 164(3), 155–159 (2018)
Wells, T.S., Seelig, A.D., Ryan, M.A., Jones, J.M., Hooper, T.I., Jacobson, I.G., Boyko, E.J.: Hearing loss associated with US military combat deployment. Noise Health 17(74), 34–42 (2015)
Writer, B.W., Meyer, E.G., Schillerstrom, J.E.: Prazosin for military combat-related PTSD nightmares: a critical review. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 26(1), 24–33 (2014)
Stinner, D.J.: Improving outcomes following extremity trauma: the need for a multidisciplinary approach. Mil. Med. 181(4), 26–29 (2016)
Wilken, J.M., Roy, C.W., Shaffer, S.W., Patzkowski, J.C., Blanck, R.V., Owens, J.G., Hsu, J.R.: Physical performance limitations after severe lower extremity trauma in military service members. J. Orthop. Trauma 32(4), 183–189 (2018)
Galarza, E.E., et al.: Virtual reality system for children lower limb strengthening with the use of electromyographic sensors. In: International Symposium on Visual Computing, ISVC 2018, pp. 215–225. Springer (2018)
Gelman, D., Eisenkraft, A., Chanishvili, N., Nachman, D., Glazer, S.C., Hazan, R.: The history and promising future of phage therapy in the military service. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 85(1), 18–26 (2018)
Cools, A., Whiteley, R., Kaczmarek, P.K.: Rehabilitation of upper extremity injuries in the handball player. In: Handball Sports Medicine, pp. 433–459. Springer, Germany (2018)
Quevedo, W.X., et al.: Assistance system for rehabilitation and valuation of motor skills. In: International Conference on Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Computer Graphics, AVR 2017, pp. 166–174. Springer (2017)
Achanccaray, D., Acuña, K., Carranza, E., Andreu-Perez, J.: A virtual reality and brain computer interface system for upper limb rehabilitation of post stroke patients. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2017)
Levin, M.F., Weiss, P.L., Keshner, E.A.: Emergence of virtual reality as a tool for upper limb rehabilitation: incorporation of motor control and motor learning principles. Phys. Ther. 95(3), 415–425 (2015)
Liu, L., Chen, X., Lu, Z., Cao, S., Wu, D., Zhang, X.: Development of an EMG-ACC-based upper limb rehabilitation training system. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 25(3), 244–253 (2017)
López, V.M., Zambrano, P.A., Pilatasig, M., Silva, F.M.: Interactive system using myoelectric muscle sensors for the strengthening upper limbs in children. In: International Conference on Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Computer Graphics, AVR 2018, pp. 18–29. Springer (2018)
Acknowledgements
To the authorities of Universidad Técnica de Ambato (UTA), Dirección de Investigación y Desarrollo (DIDE), Instituto Tecnológico Superior Guayaquil Ambato and Celec EP, for supporting this work and future research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Andrea Sánchez, Z. et al. (2020). Virtual Rehabilitation System Using Electromyographic Sensors for Strengthening Upper Extremities. In: Rocha, Á., Pereira, R. (eds) Developments and Advances in Defense and Security. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 152. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9155-2_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9155-2_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-9154-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-9155-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)