Abstract
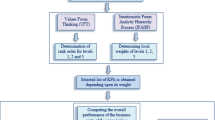
Amidst stiff competition, Small and Medium scale Enterprises (SMEs) need to continuously improve their supply chain sustainable performance. Due to customer pressure and government interventions, the focus has also shifted to enhancing the social and environmental performance of the SC. However, the challenge faced by SMEs is to identify the necessary socio-ecological key factors (KF)s required for a better sustainable performance and how to constantly assess the KFs for improving the SC performance. Hence, the research objective of the study is development of a decision model for assessing the social and environmental key factors or Indian SMEs and analyzing their interrelationships. To attain the research objective, the KFs for social and environmental performance are first identified through an extensive literature survey. Further, the KFs are evaluated using fuzzy-DEMATEL technique. The fuzzy-DEMATEL method is used to draw a directed graph for visibly capturing the causal relationships between the multiple KFs. The structural graph helps to portray a contextual relationship among 12 identified KFs including green market trends, business risk protection, and green collaborations. The result reveals that product responsibility and stakeholders’ involvement are both significant factors affecting other factors and play key roles in overall sustainable enhancement of SC for SMEs. The research is based on data collected from an electronics firm, analyzed to extract cause factors, which foster sustainability satisfaction from the SME’s perspective. The results of the study provide a benchmark for decision-makers to estimate the uncertain environment for developing a socio-ecological responsive and performance-driven SC.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keeble, B.R.: The Brundtland report: ‘our common future’. Med. War 4(1), 17–25 (1988)
Voegtlin, C., Scherer, A.G.: Responsible innovation and the innovation of responsibility: governing sustainable development in a globalized world. J. Bus. Ethics 143(2), 227–243 (2017)
Golicic, S.L., Smith, C.D.: A meta-analysis of environmentally sustainable supply chain management practices and firm performance. J. Supply Chain Manag. 49(2), 78–95 (2013)
Saeidi, S.P., Sofian, S., Saeidi, P., Saeidi, S.P., Saaeidi, S.A.: How does corporate social responsibility contribute to firm financial performance? The mediating role of competitive advantage, reputation, and customer satisfaction. J. Bus. Res. 68(2), 341–350 (2015)
Mani, V., Agarwal, R., Gunasekaran, A., Papadopoulos, T., Dubey, R., Childe, S.J.: Social sustainability in the supply chain: construct development and measurement validation. Ecol. Ind. 71, 270–279 (2016)
Govindan, K., Mangla, S.K., Luthra, S.: Prioritising indicators in improving supply chain performance using fuzzy AHP: insights from the case example of four Indian manufacturing companies. Prod. Plan. Control 28(6–8), 552–573 (2017)
Luthra, S., Govindan, K., Mangla, S.K.: Structural model for sustainable consumption and production adoption—a grey-DEMATEL based approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 125, 198–207 (2017)
Author, F.: Contribution title. In: 9th International Proceedings on Proceedings, pp. 1–2. Publisher, Location (2010)
Soleimani, H., Govindan, K., Saghafi, H., Jafari, H.: Fuzzy multi-objective sustainable and green closed-loop supply chain network design. Comput. Ind. Eng. 109, 191–203 (2017)
Opricovic, S., Tzeng, G.H.: Compromise solution by MCDM methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 156(2), 445–455 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Solanki, R., Darbari, J.D., Agarwal, V., Jha, P.C. (2020). A Fuzzy Multi-criteria Decision Model for Analysis of Socio-ecological Performance Key Factors of Supply Chain. In: Das, K., Bansal, J., Deep, K., Nagar, A., Pathipooranam, P., Naidu, R. (eds) Soft Computing for Problem Solving. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1048. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0035-0_55
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0035-0_55
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-0034-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-0035-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)