Abstract
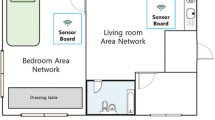
Internet of Things (IoT) solutions are becoming irreplaceable in various application domains. IoT enables control over many systems in a smart environment, such as the heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system, lighting, and appliances in a smart home or office. By enhancing IoT solutions with a cognitive capability it becomes possible to, for example, adjust ambient conditions according to user preferences without the need for direct user intervention. This functionality constitutes a fore-coming phase in IoT evolution—Cognitive IoT. In this paper, we propose an agent-based smart environment system and compare it to a centralized implementation. In both approaches, feed-forward artificial neural networks are trained under supervision and used to adjust the lighting conditions to the specific user. The agent-based approach offers better preference prediction precision as each user is supported by one agent with a neural network specialized only for his preferences as opposed to the centralized approach where all user preferences are predicted by one neural network. Additionally, the agent-based approach enables easier addition of new users.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton, K.: That ’Internet of Things’ Thing. RFID J. (2009)
Atzori, L., Iera, A., Morabito, G.: The Internet of Things: A Survey. Comput. Netw., 2787–2805 (2010)
Busoniu, L., Babuska, R., De Schutter, B.: Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning: An Overview. Studies Comput. Intell. 310, 183–221 (2010)
Cupkova, D., Kajti, E., Mocnej, J., Papcun, P., Koziorek, J., Zolotov, I.: Intelligent Human-Centric Lighting for Mental Wellbeing Improvement. Int. J. Distrib. Sensor Netw., 15 (2019)
Czarnowski, I., Jedrzejowicz, P.: Machine Learning and Multiagent Systems as Interrelated Technologies, pp. 1–28 (2013)
Hayashi, S., Martono, N., Kanamori, K., Ohwada, H.: Improving Behavior Prediction Accuracy by Using Machine Learning for Agent Based Simulation 9621 (2016)
Haykin, S.: Cognitive Dynamic Systems: Perception-Action Cycle, Radar and Radio (2012)
Jamnal, G., Liu, X.: A Cognitive-IoE Approach to Ambient-intelligent Smart Home (2017)
Jedrzejowicz, P.: Machine Learning and Agents, pp. 2–15 (2011)
Khalil, K., Abdelaziz, M., Nazmy, T., M.Salem, A.B.: Machine Learning Algorithms for Multi-Agent Systems, pp. 1–5 (2015)
Perwej, D.Y., Haq, K., Parwej, D.F., M., M.: The Internet of Things (IoT) and its Application Domains. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 182, 36–49 (2019)
Spychalski, P., Arendt, R.: Machine Learning in Multi-Agent Systems using Associative Arrays. Parallel Comput. 75 (2018)
Wu, Q., Ding, G., Xu, Y., Feng, S., Du, Z., Wang, J., Long, K.: Cognitive Internet of Things: A New Paradigm Beyond Connection. IEEE Int. Things J. 1(2), 129–143 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported in part by Croatian Science Foundation under the project IP-2019-04-1986 (IoT4us: Human-centric smart services in interoperable and decentralized IoT environments).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mandaric, K., Skocir, P., Jezic, G. (2020). Agent-Based Approach for User-Centric Smart Environments. In: Jezic, G., Chen-Burger, J., Kusek, M., Sperka, R., Howlett, R., Jain, L. (eds) Agents and Multi-Agent Systems: Technologies and Applications 2020. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 186. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5764-4_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5764-4_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-5763-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-5764-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)