Abstract
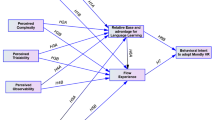
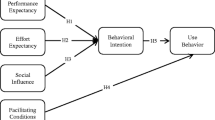
Innovations of technology keep expanding particularly within the sector of virtual reality and this have sparked competition, transforming the manner of businesses operation. This has stimulated the acceptance towards virtual reality learning in developing nations in the Middle East. Accordingly, the factors impacting consumer acceptance of virtual reality learning are examined in this study, which will further expand the current knowledge particularly on what motivates individuals to utilize virtual reality. A quantitative strategy supports this study and the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) was utilized in deciding the components influencing the reception of people towards virtual generated reality learning. An online survey was performed in the Middle Eastern developing countries to gather data from sample obtained through the technique of snowball sampling. The 432 valid obtained responses were analyzed using SPSS. Scale reliability, normality, correlation and multiple linear regressions were tested for conceptual model establishment. The model was tested for fit by comparing the observed results from the survey tool. The results show that the intent of a person to accept virtual reality learning was significantly impacted by (according to their succession of influencing strength), Execution Expectancy, Effort Expectancy, Social Influence, Facilitating Conditions, Personal Innovativeness (PInn). This examination clarifies how segment factors and factors sway the reception of virtual reality learning administrations in developing countries. This consequently will greatly contribute to increased acceptance level of virtual reality learning in these regions. Furthermore, behavioral intention was significantly impacted by Personal Innovativeness (PInn) on actual acceptance Use behavior. Hence, educational bodies in the Middle East should consider investing massively in virtual reality learning and in other innovations of information technology to increase their support towards efficient service delivery while also increasing the services of virtual reality learning.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hiltz, S.R., Turoff, M.: Video plus virtual classroom for distance education: experience with graduate courses. In: Invited Paper for Conference on Distance Education in DoD, National Defense University, February 1993
Paulsen, M.F., Rekkedal, T.: The electronic college: selected articles from the EKKO project. NKI Forlaget (1990)
Hsu, E.Y., Hiltz, S.R.: Management gaming on a computer mediated conferencing system: a case of collaborative learning through computer conferencing. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, vol. 4, pp. 367–371. IEEE, January 1991
Weedman, J.: Task and non-task functions of a computer conference used in professional eduction: a measure of flexibility. Int. J. Man Mach. Stud. 34(2), 303–318 (1991)
Harasim, L.M.: Learning Networks: A Field Guide to Teaching and Learning Online. MIT Press, Cambridge (1995)
Radvansky, B.A., Dombeck, D.A.: An olfactory virtual reality system for mice. Nat. Commun. 9(1), 839 (2018)
Tamim, R.M.: Blended learning for learner empowerment: voices from the middle east. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 50(1), 70–83 (2018)
Agarwal, R., Prasad, J.: A conceptual and operational definition of personal innovativeness in the domain of information technology. Inf. Syst. Res. 9(2), 204–215 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.9.2.204
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M.G., Davis, G.B., Davis, F.D.: User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view. MIS Q. 425–478 (2003)
Nunnally, J.C., Bernstein, I.H.: Psychometric theory (1978)
Ringle, C.M., Wende, S., Will, A.: Smart PLS 2.0 M3, University of Hamburg: Book Smart Pls, 2, M3 (2005)
Henseler, J., Ringle, C.M., Sinkovics, R.R.: The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. Adv. Int. Mark. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1108/S1474-7979(2009)0000020014
Hair, J.F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C.M., Mena, J.A.: An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. J. Acad. Mark. 40, 414–433 (2012)
Fernandes, V.: (Re)discovering the PLS approach in management science. Management (France) (2012)
Hair, J., Black, W., Babin, B., Anderson, R., Tatham, R.: Multivariate Data Analysis, 6th edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mustafa, M., Alzubi, S., Alshare, M. (2020). The Moderating Effect of Demographic Factors Acceptance Virtual Reality Learning in Developing Countries in the Middle East. In: Singh, M., Gupta, P., Tyagi, V., Flusser, J., Ören, T., Valentino, G. (eds) Advances in Computing and Data Sciences. ICACDS 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1244. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6634-9_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6634-9_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-6633-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-6634-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)