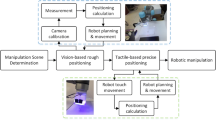
Abstract
The computer vision techniques have been widely used in the robotic manipulation for perception and positioning. However, duo to the inaccuracy of camera calibration and measurement, there is a greatly need for more accurate method to estimate the object pose especially for robotic precise manipulation. In this paper, we propose a novel pose estimation method of object in robotic manipulation using a vision-based tactile sensor. The structure of the tactile sensor and the proposed model are introduced in detail, and verification experiments have been performed. The results show the advantages and better performance of the proposed method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fazeli, N., Oller, M., Wu, J., Wu, Z., Tenenbaum, J., Rodriguez, A.: See, feel, act: hierarchical learning for complex manipulation skills with multisensory fusion. Sci. Robot. 4(26), eaav3123 (2019)
Lars, K., Nick, H., Tom, D., Marc, H., Tomas, K.: Artificial intelligence for long-term robot autonomy: a survey. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3, 4023–4030 (2018)
Hansen, E., Andersen, R., Madsen, S., Bøgh, S.: Transferring human manipulation knowledge to robots with inverse reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, SII 2020, pp. 933–937. Hawaii Convention Center, Honolulu, United States (2020)
Park, H., Park, J., Lee, D., Park, J., Baeg, M., Bae, J.: Compliance-based robotic peg-in-hole assembly strategy without force feedback. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 64(8), 6299–6309 (2017)
Chan, Y., Yu, H., Khurshid, R.: Effects of force-torque and tactile haptic modalities on classifying the success of robot manipulation tasks. In: 2019 IEEE World Haptics Conference, pp. 586–591. IEEE, Tokyo, Japan (2019)
Zhu, W., Liu, H., Ke, Y.: Sensor-based control using an image point and distance features for rivet-in-hole insertion. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 67(6), 4692–4699 (2020)
Zhu, W., Mei, B., Yan, G., Ke, Y.: Measurement error analysis and accuracy enhancement of 2D vision system for robotic drilling. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 30(2), 160–171 (2014)
Liu, H., Zhu, W., Ke, Y.: Pose alignment of aircraft structures with distance sensors and CCD cameras. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 48, 30–38 (2017)
Liu, H., Zhu, W., Dong, H., Ke, Y.: An adaptive ball-head positioning visual servoing method for aircraft digital assembly. Assembly Autom. 39(2), 287–296 (2019)
Poggi, M., Aleotti, F., Tosi, F., Mattoccia, S.: On the uncertainty of self-supervised monocular depth estimation. In: 2020 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–26. IEEE, China (2020)
Fang, B., Sun, F., Yang, C., Xue, H., Liu, H.: A dual-modal vision-based tactile sensor for robotic hand grasping. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4740–4745. IEEE, Brisbane, Australia (2018)
Fang, B., Xue, H., Sun, F., Yang, Y., Zhu, R.: A cross-modal tactile sensor design for measuring robotic grasping forces. Ind. Robot 46(3), 337–344 (2019)
Sun, F., Fang, B., Xue, H., Liu, H., Huang, H.: A novel multi-modal tactile sensor design using thermochromic material. Sci. Chin. 62(11), 185–187 (2019)
Liu, H., Guo, D., Sun, F.: Object recognition using tactile measurements: kernel sparse coding methods. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 65(3), 656–665 (2016)
Ma, D., Donlon, E., Dong, S., Rodriguez, A.: Dense tactile force estimation using GelSlim and inverse FEM. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1–7. IEEE, Montreal, Canada (2019)
Dong, S., Rodriguez, A.: Tactile-based insertion for dense box-packing. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1–8. IEEE, Macau, China (2020)
Du, G., Wang, K., Lian, S., Zhao, K.: Vision-based robotic grasp detection from object localization, object pose estimation to grasp estimation: a review. Artificial Intelligence Review, pp. 1–36 (2020)
Sünderhauf, N., et al.: The limits and potentials of deep learning for robotics. Int. J. Robot. Res. 37(4–5), 405–420 (2018)
Caldera, S., Rassau, A., Chai, D.: Review of deep learning methods in robotic grasp detection. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2(3), 57 (2018)
Han, X., Liu, H., Sun, F., Zhang, X.: Active object detection with multi-step action prediction using deep q-network. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 15(6), 3723–3731 (2019)
Acknowledgement
This research was sponsored by the Major Project of the New Generation of Artificial Intelligence (No. 2018AAA0102900) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant (No. 2019TQ0170).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, D., Sun, F., Zhou, Q., Wang, Z. (2021). A Novel Pose Estimation Method of Object in Robotic Manipulation Using Vision-Based Tactile Sensor. In: Sun, F., Liu, H., Fang, B. (eds) Cognitive Systems and Signal Processing. ICCSIP 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1397. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2336-3_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2336-3_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-2335-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-2336-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)