Abstract
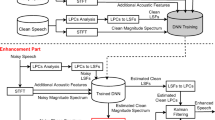
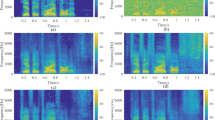
With the wide applications of sound reinforcement system, howling has become a major problem affecting system performance due to the acoustic coupling between the speaker system and the microphone when there exists a positive feedback loop. To suppress the howling noise, in recent years, researchers have proposed many acoustic feedback control methods such as frequency shift method, notch filtering, and adaptive feedback cancellation method. However, current methods mainly involve using adaptive filters in either time or frequency domain, which can suppress howling to some extent but may lead to sound distortion, or have limited suppression ability. In this paper, we propose a novel method to suppress howling noise from speech signal by training deep neural networks (DNN) as an adaptive filter in time–frequency domain, where short-time Fourier transform (STFT) is performed to convert the signal from the time domain to time–frequency domain, and to extract complex values as signal features, so that a supervised end-to-end DNN is constructed which can nonlinearly map the complex values of the howling speech to the complex values of the clean speech, aiming for cancelling the howling noise from the feedback signals. Experimental results have demonstrated that the proposed method can suppress the howling noise effectively, and at the same time greatly improve the quality and intelligibility of the processed speech.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Waterschoot T, Moonen M (2011) Fifty years of acoustic feedback control: state of the art and future challenges. Proc IEEE 99(2):288–327
Siqueira MG (2000) Steady-state analysis of continuous adaptation in acoustic feedback reduction systems for hearing-aids. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 8(4):443–453
Wang G, Liu Q, Wang W (2020) Adaptive feedback cancellation with prediction error method and howling suppression in train public address system. Signal Process 167:107–279
Sankowsky-Rothe T, Schepker H, Doclo S, Blau M (2020) Acoustic feedback path modeling for hearing aids: comparison of physical position based and position independent models. J Acoust Soc Am 147(1):85–100
Schroeder RM (2005) Improvement of acoustic-feedback stability by frequency shifting. J Acoust Soc Am 36(9):1718–1724
Leotwassana W, Punchalard R, Silaphan W (2003) Adaptive howling canceller using adaptive IIR notch filter: simulation and implementation. In: International conference on neural networks & signal processing, vol 1, pp 848–851
Deepak S (2008) Feedback cancellation in a sound system, US
Van Waterschoot T, Rombouts G, Moonen M (2004) On the performance of decorrelation by prefiltering for adaptive feedback cancellation in Public Address systems. In: Proceedings of the 4th IEEE benelux signal processing symposium, pp 167–170
Schmidt G, Haulick T (2006) Signal processing for in-car communication systems. Signal Process 86(6):1307–1326
Waterschoot TV (2004) Instrumental variable methods for acoustic feedback cancellation. Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium
Estermann P, Kaelin A (1994) Feedback cancellation in hearing aids: results from using frequency-domain adaptive filters. In: IEEE international symposium on circuits & systems (ISCAS), vol 2, pp 257–260
Wu S, Qiu X (2009) A windowing frequency domain adaptive filter for acoustic echo cancellation. IEICE Trans Fundam Electron Commun Comput Sci 10:2626–2628
Williamson DS, Wang Y, Wang DL (2017) Complex ratio masking for monaural speech separation. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 24(3):483–492
Taal CH, Hendriks RC, Heusdens R, Jensen J (2011) An algorithm for intelligibility prediction of time-frequency weighted noisy speech. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 19(7):2125–2136
Rix AW, Beerends JG, Hollier MP, Hekstra AP (2001) Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)-a new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In: 2001 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, vol 2, pp 749–752
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gan, H., Luo, G., Luo, Y., Luo, W. (2022). Howling Noise Cancellation in Time–Frequency Domain by Deep Neural Networks. In: Yang, XS., Sherratt, S., Dey, N., Joshi, A. (eds) Proceedings of Sixth International Congress on Information and Communication Technology. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 236. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2380-6_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2380-6_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-2379-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-2380-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)