Abstract
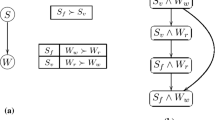
This paper deals with a type of decision-making that pairwise comparisons specify which alternative is better concerning two criteria and that chosen alternative selects one of the criteria. Solutions to the decision-making are regarded as equilibria of a normal form game of two players. The equilibria are sought by drawing directed graphs that consist of nodes, arrows, and undirected edges. Each node of the graphs is a pair of a criterion and an alternative. An arrow represents which one prefers to another between two nodes. Weights, how better nodes are, can be put on arrows. An undirected edge connects indifferent two nodes. Throughout two examples of decision-making in this paper, how to seek the equilibria, pure and mixed, from the graphs are explained. In one of them, votes create weights on the arrows of the graphs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nisan, N., Roughgarden, T., Tardos, E., Vazirani, V.V.: Algorithmic Game Theory. Cambridge University Press (2007)
Nash, J.: Equilibrium points in n-person games. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 36(1), 48–49 (1950)
Saaty, T.L.: The Analytic Hierarchy Process. McGraw Hill, New York (1980)
Kinoshita, E., Nakanishi, M.: Proposal of new AHP model in light of dominant relationship among alternatives. J. Oper. Res. Soc. Jpn. 42(2), 180–197 (1999)
Kinoshita, E., Nakanishi, M.: A proposal of CCM as a processing technique for additional data in the dominant AHP. J. Infrastructure Planning Manage. IV-42-611, 13–19 (1999)
Mizuno, T.: A diagram for finding nash equilibria in two-players strategic form games. In: Czarnowski, I., Howlett, R., Jain, L. (eds.) Intelligent Decision Technologies, IDT 2020, Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol. 193. Springer, Singapore (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mizuno, T. (2021). Equilibria Between Two Sets of Pairwise Comparisons as Solutions of Decision-Making with Orthogonal Criteria. In: Czarnowski, I., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C. (eds) Intelligent Decision Technologies. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 238. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2765-1_51
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2765-1_51
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-2764-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-2765-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)