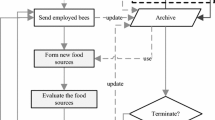
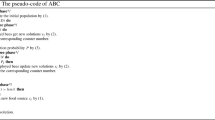
Abstract
Artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm shows good performance on many optimization problems. However, most ABC variants focus on single objective optimization problems. In this paper, an improved bare-bones multi-objective artificial bee colony (called BMOABC) algorithm is proposed to solve multi-objective optimization problems (MOPs). Fast non-dominated sorting is used to select non-dominated solutions. The crowded-comparison operator is employed to maintain population diversity. To enhance the search ability, an improved bare-bones strategy is utilized. The fitness function is modified to handle multiple objective values. Then, a novel probability selection model is designed for the onlooker bees. To verify the effectiveness of BMOABC, five benchmark MOPs are employed in the experiment. Experimental results show that BMOABC is superior to three other multi-objective algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karaboga, D.: An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization. Technical report-TR06, Erciyes University, Engineering Faculty, Computer Engineering Department (2005)
Wang, H., Wu, Z.J., Rahnamayan, S., Sun, H., Liu, Y., Pan, J.: Multi-strategy ensemble artificial bee colony algorithm. Inf. Sci. 27, 587–603 (2014)
Wang, H., Wang, W.: A new multi-strategy ensemble artificial bee colony algorithm for water demand prediction. In: Peng, H., Deng, C., Wu, Z., Liu, Y. (eds.) ISICA 2018. CCIS, vol. 986, pp. 63–70. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6473-0_6
Wang, H., et al.: Multi-strategy and dimension perturbation ensemble of artificial bee colony. In: IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC 2019), pp. 697–704 (2019)
Wang, H., Wang, W.J., Xiao, S.Y., Cui, Z.H., Xu, M.Y., Zhou, X.Y.: Improving artifificial Bee colony algorithm using a new neighborhood selection mechanism. Inf. Sci. 527, 227–240 (2020)
Xiao, S., Wang, H., Wang, W., Huang, Z., Zhou, X., Xu, M.: Artificial bee colony algorithm based on adaptive neighborhood search and Gaussian perturbation. Appl. Soft Comput. 100, 106955 (2021)
Ye, T., Zeng, T., Zhang, L., Xu, M., Wang, H., Hu, M.: Artificial bee colony algorithm with an adaptive search manner. In: Zhang, H., Yang, Z., Zhang, Z., Wu, Z., Hao, T. (eds.) NCAA 2021. CCIS, vol. 1449, pp. 486–497. Springer, Singapore (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5188-5_35
Zeng, T., Ye, T., Zhang, L., Xu, M., Wang, H., Hu, M.: Population diversity guided dimension perturbation for artificial bee colony algorithm. In: Zhang, H., Yang, Z., Zhang, Z., Wu, Z., Hao, T. (eds.) NCAA 2021. CCIS, vol. 1449, pp. 473–485. Springer, Singapore (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5188-5_34
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., Meyarivan, T.: A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6(2), 182–197 (2002)
Huo, Y., Zhuang, Y., Gu, J.J., Ni, S.R.: Elite-guided multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 32, 199–210 (2015)
Xiang, Y., Zhou, Y.R.: A dynamic multi-colony artificial bee colony algorithm for multi-objective optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 35, 766–785 (2015)
Xiang, Y., Zhou, Y.R., Liu, H.L.: An elitism based multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 245(1), 168–193 (2015)
Hu, Z.Y., Yang, J.M., Sun, H., Wei, L.X., Zhao, Z.W.: An improved multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on environmental and history information. Neurocomputing 222, 170–182 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Gong, D.W., Ding, Z.H.: A bare-bones multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm for environmental/economic dispatch. Inf. Sci. 192, 213–227 (2012)
Zhang, M., Wang, H., Cui, Z., Chen, J.: Hybrid multi-objective cuckoo search with dynamical local search. Memetic Comput. 10(2), 199–208 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-017-0237-2
Schott, J.: Fault tolerant design using single and multicriteria genetic algorithm optimization. Cell. Immunol. 37(1), 1–13 (1995)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62166027), and Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 20212ACB212004 and 20212BAB202023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ye, T., Wang, H., Wang, W., Zeng, T., Zhang, L. (2022). An Improved Bare-Bones Multi-objective Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. In: Pan, L., Cui, Z., Cai, J., Li, L. (eds) Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications. BIC-TA 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1565. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1256-6_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1256-6_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-1255-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-1256-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)