Abstract
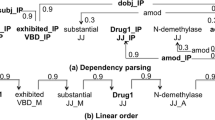
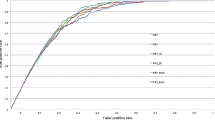
The explosive growth of biomedical literature has produced a large amount of information on drug-drug interactions (DDI). How to effectively extract DDI from biomedical literature is of great significance for constructing biomedical knowledge and discovering new biomedical knowledge. Drug entity names are mostly nouns in specific fields. Most of the existing models can’t make full use of the importance of drug entity information and syntax information for DDI extraction. In this paper, we propose a model that can reasonably use domain knowledge and syntactic information to extract DDI, which makes full use of domain knowledge to obtain an enhanced representation of entities and can learn sentence sequence information and long-distance grammatical relation. We conducted comparative experiments and ablation studies on the DDI extraction 2013 dataset. The experimental results show that our method can effectively integrate domain knowledge and syntactic information to improve the performance of DDI extraction compared with the existing methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roblek, T., Vaupotic, T., Mrhar, A., et al.: Drug-drug interaction software in clinical practice: a systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 71(2), 131–142 (2015)
Zhang, T., Leng, J., Liu, Y.: Deep learning for drug–drug interaction extraction from the literature: a review. Brief. Bioinform. 21(5), 1609–1627 (2020)
Zhang, Y., Lin, H., Yang, Z., et al.: Neural network-based approaches for biomedical relation classification: a review. J. Biomed. Inform. 99, 103294 (2019)
Hong, L., Lin, J., Li, S., et al.: A novel machine learning framework for automated biomedical relation extraction from large-scale literature repositories. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2(6), 347–355 (2020)
Zhao, S., Su, C., Lu, Z., et al.: Recent advances in biomedical literature mining. Briefings Bioinform. 22(3), bbaa057 (2021)
Segura-Bedmar, I., Martínez, P., de Pablo-Sánchez, C.: A linguistic rule-based approach to extract drug-drug interactions from pharmacological documents. BMC Bioinform. BioMed Central 12(2), 1–11 (2011)
Chowdhury, M., Lavelli, A.: FBK-irst: a multi-phase kernel based approach for drug-drug interaction detection and classification that exploits linguistic information. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, pp. 351–355 (2013)
Kim, S., Liu, H., Yeganova, L., Wilbur, W.J.: Extracting drug–drug interactions from literature using a rich feature-based linear kernel approach. J. Biomed. Inf. 55, 23–30 (2015)
Liu, S., Tang, B., Chen, Q., et al.: Drug-drug interaction extraction via convolutional neural networks. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2016, 6918381 (2016)
Zhao, Z., Yang, Z., Luo, L., et al.: Drug drug interaction extraction from biomedical literature using syntax convolutional neural network. Bioinformatics 32(22), 3444–3453 (2016)
Liu, S., Chen, K., Chen, Q., et al.: Dependency-based convolutional neural network for drug-drug interaction extraction. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 1074–1080. IEEE (2016)
Asada, M., Miwa, M., Sasaki, Y.: Extracting drug–drug interactions with attention CNNs. BioNLP 2017, 9–18 (2017)
Kavuluru, R., Rios, A., Tran, T.: Extracting drug-drug interactions with word and character-level recurrent neural networks. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), pp. 5–12. IEEE (2017)
Wang, W., Yang, X., Yang, C., et al.: Dependency-based long short term memory network for drug-drug interaction extraction. BMC Bioinform. 18(16), 99–109 (2017)
Sahu, S.K., Anand, A.: Drug-drug interaction extraction from biomedical texts using long short-term memory network. J. Biomed. Inform. 86, 15–24 (2018)
Huang, D., Jiang, Z., Zou, L., et al.: Drug–drug interaction extraction from biomedical literature using support vector machine and long short term memory networks. Inf. Sci. 415, 100–109 (2017)
Zheng, W., Lin, H., Luo, L., et al.: An attention-based effective neural model for drug-drug interactions extraction. BMC Bioinform. 18(1), 445 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Zheng, W., Lin, H., et al.: Drug–drug interaction extraction via hierarchical RNNs on sequence and shortest dependency paths. Bioinformatics 34(5), 828–835 (2018)
Park, C., Park, J., Park, S.: AGCN: attention-based graph convolutional net-works for drug-drug interaction extraction. Expert Syst. Appl. 159, 113538 (2020)
Peng, Y., Yan, S., Lu, Z.: Transfer learning in biomedical natural language processing: an evaluation of BERT and ELMo on ten benchmarking datasets. BioNLP 2019, 58 (2019)
Lee, J., Yoon, W., Kim, S., et al.: BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics 36(4), 1234–1240 (2020)
Wu, S., He, Y.: Enriching pre-trained language model with entity information for relation classification. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 2361–2364 (2019)
Herrero-Zazo, M., Segura-Bedmar, I., Martínez, P., et al.: The DDI corpus: an annotated corpus with pharmacological substances and drug–drug interactions. J. Biomed. Inform. 46(5), 914–920 (2013)
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by grant from the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62072070 and 62106034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Du, W., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., Liu, D., Liu, X. (2022). KGSG: Knowledge Guided Syntactic Graph Model for Drug-Drug Interaction Extraction. In: Sun, M., et al. Knowledge Graph and Semantic Computing: Knowledge Graph Empowers the Digital Economy. CCKS 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1669. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7596-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7596-7_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-7595-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-7596-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)