Abstract
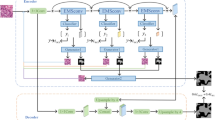
Cytopathologists analyse images captured at different magnifications to detect the malignancies in effusions. They identify the malignant cell clusters from the lower magnification, and the identified area is zoomed in to study cell level details in high magnification. The automatic segmentation of low magnification images saves scanning time and storage requirements. This work predicts the malignancy in the effusion cytology images at low magnification levels such as \(10{\times }\) and 4\(\times \). However, the biggest challenge is the difficulty in annotating the low magnification images, especially the 4\(\times \) data. We extend a semi-supervised learning (SSL) semantic model to train unlabelled 4\(\times \) data with the labelled 10\(\times \) data. The benign F-score on the predictions of 4\(\times \) data using the SSL model is improved 15% compared with the predictions of 4\(\times \) data on the semantic 10\(\times \) model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboobacker, S., Vijayasenan, D., David, S.S., Suresh, P.K., Sreeram, S.: A deep learning model for the automatic detection of malignancy in effusion cytology. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), pp. 1–5
Barwad, A., Dey, P., Susheilia, S.: Artificial neural network in diagnosis of metastatic carcinoma in effusion cytology. Cytometry Part B Clin. Cytometry 82(2), 107–111 (2012)
Belsare, A., Mushrif, M.: Histopathological image analysis using image processing techniques: an overview. Signal Image Process. 3(4), 23 (2012)
Berthelot, D., Carlini, N., Goodfellow, I., Papernot, N., Oliver, A., Raffel, C.A.: Mixmatch: a holistic approach to semi-supervised learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32 (2019)
Gurcan, M.N., Boucheron, L.E., Can, A., Madabhushi, A., Rajpoot, N.M., Yener, B.: Histopathological image analysis: a review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2, 147–171 (2009)
Higgins, C.: Applications and challenges of digital pathology and whole slide imaging. Biotech. Histochem. 90(5), 341–347 (2015)
Howard, A.G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D., Wang, W., Weyand, T., Andreetto, M., Adam, H.: Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861 (2017)
Jha, D., Smedsrud, P.H., Riegler, M.A., Johansen, D., De Lange, T., Halvorsen, P., Johansen, H.D.: Resunet++: an advanced architecture for medical image segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), pp. 225–2255. IEEE (2019)
Lee, D.H., et al.: Pseudo-label: The simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. In: Workshop Challenges Representation Learn., ICML. vol. 3, p. 896 (2013)
Miyato, T., Maeda, S.i., Koyama, M., Ishii, S.: Virtual adversarial training: a regularization method for supervised and semi-supervised learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(8), 1979–1993 (2018)
Samuli, L., Timo, A.: Temporal ensembling for semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), vol. 4, p. 6 (2017)
Sohn, K., Berthelot, D., Carlini, N., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., Raffel, C.A., Cubuk, E.D., Kurakin, A., Li, C.L.: Fixmatch: simplifying semi-supervised learning with consistency and confidence. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 596–608 (2020)
Spanhol, F.A., Oliveira, L.S., Petitjean, C., Heutte, L.: A dataset for breast cancer histopathological image classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63(7), 1455–1462 (2015)
Ta, V.T., Lezoray, O., Elmoataz, A., Schüpp, S.: Graph-based tools for microscopic cellular image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 42(6), 1113–1125 (2009)
Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Mean teachers are better role models: weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Teramoto, A., Yamada, A., Kiriyama, Y., Tsukamoto, T., Yan, K., Zhang, L., Imaizumi, K., Saito, K., Fujita, H.: Automated classification of benign and malignant cells from lung cytological images using deep convolutional neural network. Inform. Med. Unlocked 16, 100205 (2019)
Van Engelen, J.E., Hoos, H.H.: A survey on semi-supervised learning. Mach. Learn. 109(2), 373–440 (2020)
Win, K., Choomchuay, S., Hamamoto, K., Raveesunthornkiat, M.: Detection and classification of overlapping cell nuclei in cytology effusion images using a double-strategy random forest. Appl. Sci. 8(9), 1608 (2018)
Win, K.Y., Choomchuay, S., Hamamoto, K., Raveesunthornkiat, M., Rangsirattanakul, L., Pongsawat, S.: Computer aided diagnosis system for detection of cancer cells on cytological pleural effusion images. BioMed. Res. Int. (2018)
Xie, Q., Luong, M.T., Hovy, E., Le, Q.V.: Self-training with noisy student improves imagenet classification. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10687–10698 (2020)
Zeiser, F.A., da Costa, C.A., de Oliveira Ramos, G., Bohn, H.C., Santos, I., Roehe, A.V.: Deepbatch: a hybrid deep learning model for interpretable diagnosis of breast cancer in whole-slide images. Exp. Syst. Appl. 185, 115586 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Aboobacker, S., Vijayasenan, D., David, S.S., Suresh, P.K., Sreeram, S. (2023). Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation for Effusion Cytology Images. In: Tistarelli, M., Dubey, S.R., Singh, S.K., Jiang, X. (eds) Computer Vision and Machine Intelligence. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 586. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7867-8_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7867-8_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-7866-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-7867-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)