Abstract
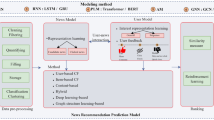
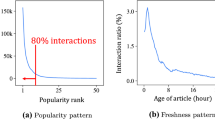
Personalized news recommendation is essential for helping users efficiently discover content aligned with their interests. Current methods primarily treat it as a sequential task, focusing on statistical correlations within news content, which hinders the inference of causal patterns in user behaviors. Unlike conventional sequential recommendation, users’ browsing behaviors are generally driven by diverse and evolving interests, leading to dissimilar adjacent news selections. Uncovering causal relationships among user interests can reveal the underlying behavioral patterns. For instance, users are more likely to browse lighter content after reading serious political news. Ignoring such causal patterns can result in recommendations that overly emphasize similar content. To address this, we propose Causal Behavior Pattern Inference (CBPI), a framework that models user behavior from a causal perspective. CBPI infers multiple latent interests and uncovers their causal structures, while dynamically adapting to changes in user preferences. By mapping interest-level causal relations to news-level interactions, CBPI offers a more accurate understanding of user preferences. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show that CBPI outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
An, M., Wu, F., Wu, C., Zhang, K., Liu, Z., Xie, X.: Neural news recommendation with long-and short-term user representations. In: ACL, pp. 336–345 (2019)
Gao, S., et al.: Generative news recommendation. In: WWW, pp. 3444–3453 (2024)
He, Y., et al.: CausPref: causal preference learning for out-of-distribution recommendation. In: WWW, pp. 410–421 (2022)
Jiang, H., Li, C., Cai, J., Wang, J.: RCENR: a reinforced and contrastive heterogeneous network reasoning model for explainable news recommendation. In: SIGIR, pp. 1710–1720 (2023)
Kyono, T., Zhang, Y., van der Schaar, M.: Castle: regularization via auxiliary causal graph discovery. In: NeurIPS, vol. 33, pp. 1501–1512 (2020)
Li, J., Zhu, J., Bi, Q., Cai, G., Shang, L., et al.: Miner: multi-interest matching network for news recommendation. In: ACL, pp. 343–352 (2022)
Löwe, S., Madras, D., Zemel, R., et al.: Amortized causal discovery: learning to infer causal graphs from time-series data. In: CLeaR, pp. 509–525. PMLR (2022)
Mao, Z., Zeng, X., Wong, K.: Neural news recommendation with collaborative news encoding and structural user encoding. In: EMNLP, pp. 46–55 (2021)
Perry, R., Von Kügelgen, J., et al.: Causal discovery in heterogeneous environments under the sparse mechanism shift hypothesis. NeurIPS 35, 10904–10917 (2022)
Shen, J., Zhen, X., Worring, M., Shao, L.: Variational multi-task learning with gumbel-softmax priors. In: NeurIPS, vol. 34, pp. 21031–21042 (2021)
Velickovic, P., et al.: Graph attention networks. stat 1050(20), 10–48550 (2017)
Wang, H., Zhang, F., Xie, X., Guo, M.: DKN: deep knowledge-aware network for news recommendation. In: WWW, pp. 1835–1844 (2018)
Wang, R., Wang, S., Lu, W., Peng, X., Zhang, W., et al.: Intention-aware user modeling for personalized news recommendation. In: DASFAA, pp. 179–194 (2023)
Wang, S., Guo, S., Wang, L., Liu, T., Xu, H.: HDNR: a hyperbolic-based debiased approach for personalized news recommendation. In: SIGIR, pp. 259–268 (2023)
Wang, Z., Chen, X., Zhou, R., Dai, Q., Dong, Z., Wen, J.: Sequential recommendation with user causal behavior discovery. In: ICDE, pp. 28–40 (2023)
Wang, Z., He, Y., Liu, J., Zou, W., Yu, P.S., Cui, P.: Invariant preference learning for general debiasing in recommendation. In: KDD, pp. 1969–1978 (2022)
Wu, C., Wu, F., An, M., Huang, J., Huang, Y., Xie, X.: Neural news recommendation with attentive multi-view learning. In: IJCAI, pp. 3863–3869 (2019)
Wu, C., Wu, F., An, M., Huang, J., Huang, Y., Xie, X.: NPA: neural news recommendation with personalized attention. In: KDD, pp. 2576–2584 (2019)
Wu, C., Wu, F., Ge, S., Qi, T., Huang, Y., Xie, X.: Neural news recommendation with multi-head self-attention. In: EMNLP-IJCNLP, pp. 6389–6394 (2019)
Wu, C., Wu, F., Qi, T., Huang, Y.: Empowering news recommendation with pre-trained language models. In: SIGIR, pp. 1652–1656 (2021)
Zhang, W., Gui, L., Procter, R., He, Y.: Multi-layer ranking with large language models for news source recommendation. In: SIGIR (2024)
Zheng, X., Aragam, B., Ravikumar, P.K., Xing, E.P.: Dags with no tears: continuous optimization for structure learning. In: NeurIPS, vol. 31 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, X., Fan, W., Li, Q. (2025). Causal Behavior Pattern Inference for News Recommendation Through Multi-interest Matching. In: Barhamgi, M., Wang, H., Wang, X. (eds) Web Information Systems Engineering – WISE 2024. WISE 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15438. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0570-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0570-5_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-96-0569-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-96-0570-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)