Abstract
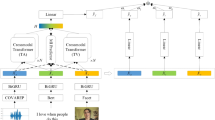
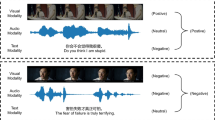
Multimodal sentiment analysis(MSA) aims to recognize human emotions by integrating information from multiple modalities. Previous approaches to modality decomposition for obtaining common and private representations often overlooked the fact that the interactions between modalities are actually independent, leading to inaccurate decomposed representations. To address this issue, we propose a method called Inter-Modal Shifting and Intra- Adaptation (ISIA) for the MSA task. Firstly, inter-modal shifting sequentially identifies a primary modality from all modalities and calculates the shifting magnitude relative to the other modalities within independent feature spaces, obtaining accurate common representations for each modality. Secondly, a gated attention mechanism, combined with the common representations, adaptively extracts private representation from the original modality representation. ISIA enables a more precise decomposition of modalities, enhancing the quality of both common and private representations. Experiments on two public benchmarks demonstrate that our ISIA outperforms state-of-the-art methods, confirming the model’s effectiveness. Our code is available at https://github.com/AnleKer/ISIA.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, J., Zhang, C., Hui, Y., Leng, D., Niu, Y., Song, Y., Gai, K.: Pepnet: Parameter and embedding personalized network for infusing with personalized prior information. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 3795–3804 (2023)
Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K.M., Rasch, M.J., Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.: A kernel two-sample test. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13(1), 723–773 (2012)
Hazarika, D., Zimmermann, R., Poria, S.: Misa: Modality-invariant and-specific representations for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1122–1131 (2020)
Kenton, J.D.M.W.C., Toutanova, L.K.: Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of naacL-HLT. vol. 1, p. 2 (2019)
Lin, R., Hu, H.: Multimodal contrastive learning via uni-modal coding and cross-modal prediction for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2022, pp. 511–523 (2022)
Lin, Z., Liang, B., Long, Y., Dang, Y., Yang, M., Zhang, M., Xu, R.: Modeling intra-and inter-modal relations: Hierarchical graph contrastive learning for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. vol. 29, pp. 7124–7135. Association for Computational Linguistics (2022)
Liu, Z., Shen, Y., Lakshminarasimhan, V.B., Liang, P.P., Zadeh, A.B., Morency, L.P.: Efficient low-rank multimodal fusion with modality-specific factors. In: Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 2247–2256 (2018)
Van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-sne. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(11) (2008)
MacQueen, J., et al.: Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In: Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability. vol. 1, pp. 281–297. Oakland, CA, USA (1967)
Parzen, E.: On estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 33(3), 1065–1076 (1962)
Rahman, W., Hasan, M.K., Lee, S., Zadeh, A., Mao, C., Morency, L.P., Hoque, E.: Integrating multimodal information in large pretrained transformers. In: Proceedings of the Conference. Association for Computational Linguistics. Meeting. vol. 2020, p. 2359. NIH Public Access (2020)
Sun, T., Ni, J., Wang, W., Jing, L., Wei, Y., Nie, L.: General debiasing for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 5861–5869 (2023)
Swietojanski, P., Li, J., Renals, S.: Learning hidden unit contributions for unsupervised acoustic model adaptation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 24(8), 1450–1463 (2016)
Tsai, Y.H.H., Bai, S., Liang, P.P., Kolter, J.Z., Morency, L.P., Salakhutdinov, R.: Multimodal transformer for unaligned multimodal language sequences. In: Proceedings of the Conference. Association for Computational Linguistics. Meeting. vol. 2019, p. 6558. NIH Public Access (2019)
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Wang, Y., Shen, Y., Liu, Z., Liang, P.P., Zadeh, A., Morency, L.P.: Words can shift: Dynamically adjusting word representations using nonverbal behaviors. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. vol. 33, pp. 7216–7223 (2019)
Wu, Y., Lin, Z., Zhao, Y., Qin, B., Zhu, L.N.: A text-centered shared-private framework via cross-modal prediction for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021, pp. 4730–4738 (2021)
Yang, D., Huang, S., Kuang, H., Du, Y., Zhang, L.: Disentangled representation learning for multimodal emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1642–1651 (2022)
Yang, J., Yu, Y., Niu, D., Guo, W., Xu, Y.: Confede: Contrastive feature decomposition for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 7617–7630 (2023)
Yu, W., Xu, H., Yuan, Z., Wu, J.: Learning modality-specific representations with self-supervised multi-task learning for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. vol. 35, pp. 10790–10797 (2021)
Zadeh, A., Chen, M., Poria, S., Cambria, E., Morency, L.P.: Tensor fusion network for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 1103–1114 (2017)
Zadeh, A., Liang, P.P., Mazumder, N., Poria, S., Cambria, E., Morency, L.P.: Memory fusion network for multi-view sequential learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. vol. 32 (2018)
Zadeh, A., Zellers, R., Pincus, E., Morency, L.P.: Mosi: multimodal corpus of sentiment intensity and subjectivity analysis in online opinion videos. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.06259 (2016)
Zadeh, A.B., Liang, P.P., Poria, S., Cambria, E., Morency, L.P.: Multimodal language analysis in the wild: Cmu-mosei dataset and interpretable dynamic fusion graph. In: Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 2236–2246 (2018)
Zhao, D., Han, D., Yuan, Y., Ning, B., Mengxiang, L., He, Z., Song, S.: Autograph: Enabling visual context via graph alignment in open domain multi-modal dialogue generation. In: ACM Multimedia 2024 (2024), https://openreview.net/forum?id=hZYk17jJaf
Zhao, D., Han, D., Yuan, Y., Wang, C., Song, S.: Muse: A multi-scale emotional flow graph model for empathetic dialogue generation. In: Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, pp. 491–507. Springer (2023)
Zhu, L., Zhu, Z., Zhang, C., Xu, Y., Kong, X.: Multimodal sentiment analysis based on fusion methods: A survey. Inform. Fusion 95, 306–325 (2023)
Zhu, Y., Zhuang, F., Wang, D.: Aligning domain-specific distribution and classifier for cross-domain classification from multiple sources. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. vol. 33, pp. 5989–5996 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, K., Han, D., Zhao, D., Li, J., Qiao, B., Wu, G. (2025). Inter-Modal Shifting and Intra Adaptation for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. In: Sheng, Q.Z., et al. Advanced Data Mining and Applications. ADMA 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 15391. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0847-8_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0847-8_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-96-0846-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-96-0847-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)