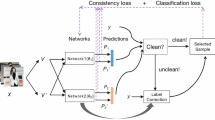
Abstract
The remarkable success of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in image classification can be attributed large clean training datasets. However, real-world data is often far from noise-free, impacting the performance of resulting deep neural network (DNN) models. Existing literature focuses on noisy label detection, often drawing a clear line between noisy and clean label samples. Nevertheless, each sample contributes differently to the final model performance; some noisy-label samples may still be valuable to a certain level, while certain clean-label samples might not significantly enhance the model. In this work, assuming that a small clean-label dataset may be available, we aim to learn a sample weight for each training sample. This weight is gradually updated as the model is training to indicate the usefulness of a particular sample in minimizing loss with respect to the clean-label dataset. Consequently, our method prioritizes high-quality data samples, minimizing the impact of harmful or unhelpful ones by assigning close-to-zero weights in a weighted loss function. We empirically demonstrate that our method is not dependent on noise type and can work well for both real-world and synthetic noise. Our method can achieve state-of-the-art performance in terms of the classification accuracy on clean test sets.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
We note that as MW-Net [16] aims to minimized the impact of noisy samples, and the authors do not provide a way to separate clean and noisy samples. Hence, we only report AUC for MW-Net.
- 2.
As authors of MW-Net [16] does not provide a way to separate clean and noisy samples, we assume that the noise rate is available to estimate the number of noisy samples (lowest weights) and eliminate them.
- 3.
They use 40% of CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets as clean data.
References
Bahri, D., Jiang, H., Gupta, M.: Deep k-NN for noisy labels. In: ICML. vol. 119, pp. 540–550 (13–18 Jul 2020)
Bai, Y., Yang, E., Han, B., Yang, Y., Li, J., Mao, Y., Niu, G., Liu, T.: Understanding and improving early stopping for learning with noisy labels. In: NeurIPS (2021)
Cheng, H., Zhu, Z., Li, X., Gong, Y., Sun, X., Liu, Y.: Learning with instance-dependent label noise: A sample sieve approach. In: ICLR (2021)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical Image Database. In: CVPR (2009)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Hendrycks, D., Mazeika, M., Wilson, D., Gimpel, K.: Using trusted data to train deep networks on labels corrupted by severe noise. In: Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Grauman, K., Cesa-Bianchi, N., Garnett, R. (eds.) NIPS. vol. 31 (2018)
Jiang, L., Zhou, Z., Leung, T., Li, L.J., Fei-Fei, L.: MentorNet: Learning data-driven curriculum for very deep neural networks on corrupted labels. In: ICML. pp. 2304–2313 (10–15 Jul 2018)
Kim, Y., Yim, J., Yun, J., Kim., J.: Nlnl: Negative learning for noisy labels. In: ICCV (2019)
Kong, S., Li, Y., Wang, J., Rezaei, A., Zhou, H.: Knn-enhanced deep learning against noisy labels. CoRR abs/2012.04224 (2020)
Krizhevsky, A.: Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. University of Toronto, Tech. rep. (2009)
Li, J., Socher, R., Hoi, S.C.: Dividemix: Learning with noisy labels as semi-supervised learning. In: ICLR (2020)
Li, Y., Yang, J., Song, Y., Cao, L., Luo, J., Li, L.J.: Learning from noisy labels with distillation. In: ICCV. pp. 1928–1936 (2017)
Patrini, G., Rozza, A., Menon, A.K., Nock, R., Qu, L.: Making deep neural networks robust to label noise: A loss correction approach. In: CVPR. pp. 2233–2241 (2017)
Pfister, T., Zhang, Z.: Learning fast sample re-weighting without reward data. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (2021)
Ren, M., Zeng, W., Yang, B., Urtasun, R.: Learning to reweight examples for robust deep learning. In: ICML (2018)
Shu, J., Xie, Q., Yi, L., Zhao, Q., Zhou, S., Xu, Z., Meng, D.: Meta-weight-net: learning an explicit mapping for sample weighting (2019)
Vahdat, A.: Toward robustness against label noise in training deep discriminative neural networks. In: NIPS. p. 5601–5610 (2017)
Xia, X., Liu, T., Han, B., Wang, N., Gong, M., Liu, H., Niu, G., Tao, D., Sugiyama, M.: Part-dependent label noise: Towards instance-dependent label noise. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Xia, X., Liu, T., Wang, N., Han, B., Gong, C., Niu, G., Sugiyama, M.: Are anchor points really indispensable in label-noise learning? In: NeurIPS. vol. 32 (2019)
Xiao, T., Xia, T., Yang, Y., Huang, C., Wang, X.: Learning from massive noisy labeled data for image classification. In: CVPR (2015)
Yao, Y., Liu, T., Han, B., Gong, M., Deng, J., Niu, G., Sugiyama, M.: Dual t: reducing estimation error for transition matrix in label-noise learning. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Yu, C., Ma, X., Liu, W.: Delving into noisy label detection with clean data. In: ICML (2023)
Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., Arik, S.O., Lee, H., Pfister, T.: Distilling effective supervision from severe label noise. In: CVPR. pp. 9291–9300 (2020)
Zhu, Z., Dong, Z., , Liu, Y.: Detecting corrupted labels without training a model to predict. In: ICML (2022)
Zhu, Z., Song, Y., Liu, Y.: Clusterability as an alternative to anchor points when learning with noisy labels. In: ICML. pp. 12912–12923 (18–24 Jul 2021)
Acknowledgement
This research was partially supported by the Australian Government through the Australian Research Council’s Discovery Projects funding scheme (project DP210102798). The views expressed herein are those of the authors and are not necessarily those of the Australian Government or Australian Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hoang, T., Tran, H., Rana, S., Gupta, S., Venkatesh, S. (2025). Revisiting Sample Weights Based Method for Noisy-Label Detection and Classification. In: Cho, M., Laptev, I., Tran, D., Yao, A., Zha, H. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2024. ACCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15472. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0885-0_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0885-0_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-96-0884-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-96-0885-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)