Abstract
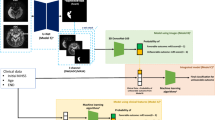
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common cause of ischemic stroke, accounting for up to one-third of all cases. Untreated AF can increase the risk of stroke by up to five times and make stroke recurrence more likely. Anticoagulation has proven beneficial in reducing stroke risk. However, AF is often paroxysmal and asymptomatic, remaining undetected and undiagnosed in up to 30% of cases. The current methods for AF detection are usually lengthy (cardiac monitoring), expensive (smart devices), or invasive (implantable cardiac monitors), limiting their routine use. We present a novel method to screen for AF by analyzing infarct patterns of stroke patients from brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. We propose EDAF, a novel method based on the segment anything model (SAM) that leverages the power of a foundational deep learning model to efficiently analyze brain MRI and identify whether the underlying stroke etiology is AF. EDAF is trained and validated using a retrospectively acquired dataset of 235 post-stroke patients, achieving an area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) of \(83.08\% \pm 2.96\% \) in identifying the presence of AF. EDAF can achieve optimal solutions with minimal training, highlighting its potential for use in low-resource settings. As MRI is readily available in stroke centers and routinely performed on many patients after a stroke, either during their admission or as an outpatient, the proposed method can effectively identify patients for further AF investigation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams Jr, H.P., Bendixen, B.H., Kappelle, L.J., Biller, J., Love, B.B., Gordon, D.L., Marsh 3rd, E.: Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. toast. trial of org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. stroke 24(1), 35–41 (1993)
Amarenco, P., Bogousslavsky, J., Caplan, L., Donnan, G., Hennerici, M.: New approach to stroke subtyping: the asco (phenotypic) classification of stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 27(5), 502–508 (2009)
Arsava, E.M., Helenius, J., Avery, R., Sorgun, M.H., Kim, G.M., Pontes-Neto, O.M., Park, K.Y., Rosand, J., Vangel, M., Ay, H.: Assessment of the predictive validity of etiologic stroke classification. JAMA Neurol. 74(4), 419–426 (2017)
Ay, H., Benner, T., Murat Arsava, E., Furie, K.L., Singhal, A.B., Jensen, M.B., Ayata, C., Towfighi, A., Smith, E.E., Chong, J.Y., et al.: A computerized algorithm for etiologic classification of ischemic stroke: the causative classification of stroke system. Stroke 38(11), 2979–2984 (2007)
Bang, O.Y., Lee, P.H., Joo, S.Y., Lee, J.S., Joo, I.S., Huh, K.: Frequency and mechanisms of stroke recurrence after cryptogenic stroke. Ann. Neurol. 54(2), 227–234 (2003)
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Fukamizu, S., Hojo, R., Kitamura, T., Kawamura, I., Miyazawa, S., Karashima, J., Nakamura, S., Takeda, K., Yamaoka, K., Arai, T., et al.: Recurrent ischemic stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation ablation and prior stroke: a study based on etiological classification. Journal of Arrhythmia 36(1), 95–104 (2020)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 770–778 (2016)
He, S., Bao, R., Li, J., Grant, P.E., Ou, Y.: Accuracy of segment-anything model (sam) in medical image segmentation tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.09324 (2023)
Huang, Y., Yang, X., Liu, L., Zhou, H., Chang, A., Zhou, X., Chen, R., Yu, J., Chen, J., Chen, C., et al.: Segment anything model for medical images? Med. Image Anal. 92, 103061 (2024)
Kalarus, Z., Mairesse, G.H., Sokal, A., Boriani, G., Średniawa, B., Casado-Arroyo, R., Wachter, R., Frommeyer, G., Traykov, V., Dagres, N., et al.: Searching for atrial fibrillation: looking harder, looking longer, and in increasingly sophisticated ways. an ehra position paper. Europace 25(1), 185–198 (2023)
Kim, B.K., Park, S., Han, M.K., Hong, J.H., Lee, D.I., Yum, K.S.: Deep learning for prediction of mechanism in acute ischemic stroke using brain diffusion magnetic resonance image. Journal of Neurocritical Care 16(2), 85–93 (2023)
Kirillov, A., Mintun, E., Ravi, N., Mao, H., Rolland, C., Gustafson, L., Xiao, T., Whitehead, S., Berg, A.C., Lo, W.Y., et al.: Segment anything. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.02643 (2023)
Ko, Y., Lee, S., Chung, J.W., Han, M.K., Park, J.M., Kang, K., Park, T.H., Park, S.S., Cho, Y.J., Hong, K.S., et al.: Mri-based algorithm for acute ischemic stroke subtype classification. Journal of stroke 16(3), 161 (2014)
Lee, K.J., Jung, K.H., Byun, J.I., Kim, J.M., Roh, J.K.: Infarct pattern and clinical outcome in acute ischemic stroke following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 38(1), 31–38 (2014)
Liu, Z., Mao, H., Wu, C.Y., Feichtenhofer, C., Darrell, T., Xie, S.: A convnet for the 2020s. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 11976–11986 (2022)
Ma, J., He, Y., Li, F., Han, L., You, C., Wang, B.: Segment anything in medical images. Nat. Commun. 15(1), 654 (2024)
Mazurowski, M.A., Dong, H., Gu, H., Yang, J., Konz, N., Zhang, Y.: Segment anything model for medical image analysis: an experimental study. Med. Image Anal. 89, 102918 (2023)
McGrath, E.R., Kapral, M.K., Fang, J., Eikelboom, J.W., O’Conghaile, A., Canavan, M., O’Donnell, M.J., of the Ontario Stroke Registry, I., et al.: Association of atrial fibrillation with mortality and disability after ischemic stroke. Neurology 81(9), 825–832 (2013)
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J., Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N., Antiga, L., et al.: Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Advances in neural information processing systems 32 (2019)
Penado, S., Cano, M., Acha, O., Hernández, J.L., Riancho, J.A.: Atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for stroke recurrence. Am. J. Med. 114(3), 206–210 (2003)
Roy, S., Wald, T., Koehler, G., Rokuss, M.R., Disch, N., Holzschuh, J., Zimmerer, D., Maier-Hein, K.H.: Sam. md: Zero-shot medical image segmentation capabilities of the segment anything model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.05396 (2023)
Singhal, A.B., Topcuoglu, M.A., Buonanno, F.S.: Acute ischemic stroke patterns in infective and nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis: a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke 33(5), 1267–1273 (2002)
Sposato, L.A., Andrade, J.: Prolonged cardiac monitoring for atrial fibrillation detection after stroke: in search of the elusive sweet spot (2022)
Tang, W., Zhang, H., Yu, P., Kang, H., Zhang, R.: Mmmna-net for overall survival time prediction of brain tumor patients. In: 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). pp. 3805–3808. IEEE (2022)
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017)
Wu, J., Fu, R., Fang, H., Liu, Y., Wang, Z., Xu, Y., Jin, Y., Arbel, T.: Medical sam adapter: Adapting segment anything model for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.12620 (2023)
Zhang, K., Liu, D.: Customized segment anything model for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.13785 (2023)
Zhang, Y., Shen, Z., Jiao, R.: Segment anything model for medical image segmentation: Current applications and future directions. Computers in Biology and Medicine p. 108238 (2024)
Zhang, Z., Lin, K., Wang, J., Ding, L., Sun, Y., Fu, C., Qian, D., Li, J., Huang, D.: Searching for underlying atrial fibrillation using artificial intelligence-assisted mri images from ischemic stroke patients. European Heart Journal 43(Supplement_2), ehac544–543 (2022)
Zhou, T., Fu, H., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Lu, X., Shen, J., Shao, L.: M\(^2\) net m 2 net: Multi-modal multi-channel network for overall survival time prediction of brain tumor patients. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, October 4–8, 2020, Proceedings, Part II 23. pp. 221–231. Springer (2020)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by The University of Melbourne’s Research Computing Services and the Petascale Campus Initiative.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Interests
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shokri, M.J., Desai, N., Rao, A.S., Sharobeam, A., Yan, B., Palaniswami, M. (2025). EDAF: Early Detection of Atrial Fibrillation from Post-stroke Brain MRI. In: Cho, M., Laptev, I., Tran, D., Yao, A., Zha, H. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2024. ACCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15473. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0901-7_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0901-7_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-96-0900-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-96-0901-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)