Abstract
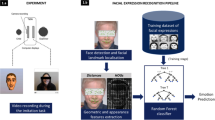
Understanding expressions is vital for deciphering human behavior, and nowadays, end-to-end trained black box models achieve high performance. Due to the black-box nature of these models, it is unclear how they behave when applied out-of-distribution. Specifically, these models show decreased performance for unilateral facial palsy patients. We hypothesize that one crucial factor guiding the internal decision rules is facial symmetry. In this work, we use insights from causal reasoning to investigate the hypothesis. After deriving a structural causal model, we develop a synthetic interventional framework. This approach allows us to analyze how facial symmetry impacts a network’s output behavior while keeping other factors fixed. All 17 investigated expression classifiers significantly lower their output activations for reduced symmetry. This result is congruent with observed behavior on real-world data from healthy subjects and facial palsy patients. As such, our investigation serves as a case study for identifying causal factors that influence the behavior of black-box models.
T. Büchner and N. Penzel—These authors contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltrušaitis, T., Robinson, P., Morency, L.: OpenFace: An open source facial behavior analysis toolkit. In: 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). pp. 1–10 (Mar 2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2016.7477553
Baltrusaitis, T., Zadeh, A., Lim, Y.C., Morency, L.P.: OpenFace 2.0: Facial behavior analysis toolkit. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018). pp. 59–66 (2018https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2018.00019
Banks, C.A., Bhama, P.K., Park, J., Hadlock, C.R., Hadlock, T.A.: Clinician-Graded Electronic Facial Paralysis Assessment: The eFACE. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 136(2), 223e (2015). https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000001447
Bareinboim, E., Correa, J.D., Ibeling, D., Icard, T.F.: On pearl’s hierarchy and the foundations of causal inference. Probabilistic and Causal Inference (2022)
Blanz, V., Vetter, T.: A morphable model for the synthesis of 3D faces. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques - SIGGRAPH ’99. pp. 187–194. ACM Press, Not Known (1999https://doi.org/10.1145/311535.311556
Büchner, T., Guntinas-Lichius, O., Denzler, J.: Improved obstructed facial feature reconstruction for emotion recognition with minimal change cyclegans. In: Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems (Acivs). pp. 262–274. SpringerNature (august 2023https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45382-3_22
Büchner, T., Sickert, S., Volk, G.F., Anders, C., Guntinas-Lichius, O., Denzler, J.: Let’s get the facs straight - reconstructing obstructed facial features. In: International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP). SciTePress (march 202https://doi.org/10.5220/0011619900003417
Büchner, T., Sickert, S., Volk, G.F., Guntinas-Lichius, O., Denzler, J.: From Faces to Volumes - Measuring Volumetric Asymmetry in 3D Facial Palsy Scans. In: Advances in Visual Computing. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer Nature Switzerland (2023https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47969-4_10
Büchner, T., Penzel, N., Guntinas-Lichius, O., Denzler, J.: The power of properties: Uncovering the influential factors in emotion classification. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence (ICPRAI) (2024), https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.07867, (accepted)
Büchner, T., Sickert, S., Graßme, R., Anders, C., Guntinas-Lichius, O., Denzler, J.: Using 2d and 3d face representations to generate comprehensive facial electromyography intensity maps. In: International Symposium on Visual Computing (ISVC). pp. 136–147 (202https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47966-3_11,
Chalupka, K., Perona, P., Eberhardt, F.: Fast conditional independence test for vector variables with large sample sizes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02747 (2018)
Chen, Y., Li, J., Shan, S., Wang, M., Hong, R.: From Static to Dynamic: Adapting Landmark-Aware Image Models for Facial Expression Recognition in Videos (Dec 2023)
Chen, Y., Li, W., Chen, X., Gool, L.V.: Learning semantic segmentation from synthetic data: A geometrically guided input-output adaptation approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 1841–1850 (2019)
Choi, Y., Choi, M., Kim, M., Ha, J.W., Kim, S., Choo, J.: Stargan: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 8789–8797 (2018)
Choithwani, M., Almeida, S., Egger, B.: PoseBias: On Dataset Bias and Task Difficulty - Is there an Optimal Camera Position for Facial Image Analysis? In: 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW). pp. 3088–3096. IEEE, Paris, France (Oct 2023https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW60793.2023.00334
Cootes, T.F., Edwards, G.J., Taylor, C.J.: Active appearance models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23(6), 681–685 (2001)
Danečěk, R., Black, M.J., Bolkart, T.: EMOCA: Emotion Driven Monocular Face Capture and Animation. CVPR p. 12 (2022)
Demeco, A., Marotta, N., Moggio, L., Pino, I., Marinaro, C., Barletta, M., Petraroli, A., Palumbo, A., Ammendolia, A.: Quantitative analysis of movements in facial nerve palsy with surface electromyography and kinematic analysis. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 56, 102485 (Feb 2021https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2020.102485
Deng, Y., Yang, J., Chen, D., Wen, F., Tong, X.: Disentangled and controllable face image generation via 3d imitative-contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 5154–5163 (2020)
Dumitru, Goodfellow, I., Cukierski, W., Bengio, Y.: Challenges in representation learning: Facial expression recognition challenge (2013), https://kaggle.com/competitions/challenges-in-representation-learning-facial-expression-recognition-challenge
Egger, B., Smith, W.A.P., Tewari, A., Wuhrer, S., Zollhoefer, M., Beeler, T., Bernard, F., Bolkart, T., Kortylewski, A., Romdhani, S., Theobalt, C., Blanz, V., Vetter, T.: 3D Morphable Face Models-Past, Present, and Future. ACM Transactions on Graphics 39(5), 157:1–157:38 (Jun 2020https://doi.org/10.1145/3395208
Egger, B., Sutherland, S., Medin, S.C., Tenenbaum, J.: Identity-Expression Ambiguity in 3D Morphable Face Models. In: 2021 16th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2021). pp. 1–7. IEEE Press, Jodhpur, India (Dec 2021https://doi.org/10.1109/FG52635.2021.9667002
Ekman, P.: An argument for basic emotions. Cogn. Emot. 6(3–4), 169–200 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1080/02699939208411068
El Boudouri, Y., Bohi, A.: Emonext: an adapted convnext for facial emotion recognition. In: 2023 IEEE 25th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP). pp. 1–6 (2023https://doi.org/10.1109/MMSP59012.2023.10337732
Feng, Y., Feng, H., Black, M.J., Bolkart, T.: Learning an animatable detailed 3D face model from in-the-wild images. ACM Transactions on Graphics 40(4), 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3450626.3459936
Fornberg, B.: Generation of finite difference formulas on arbitrarily spaced grids. Mathematics of Computation 51, 699–706 (1988), https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:119513587
Fukumizu, K., Gretton, A., Sun, X., Schölkopf, B.: Kernel measures of conditional dependence. Advances in neural information processing systems 20 (2007)
Gao, X., Su, Y., Li, X., Tao, D.: A review of active appearance models. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews) 40(2), 145–158 (2010)
Gerig, T., Morel-Forster, A., Blumer, C., Egger, B., Luthi, M., Schoenborn, S., Vetter, T.: Morphable Face Models - An Open Framework. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018). pp. 75–82. IEEE, Xi’an (May 2018https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2018.00021
Good, P.: Permutation Tests: A Practical Guide to Resampling Methods for Testing Hypotheses. Springer Series in Statistics, Springer New York (2013), https://books.google.de/books?id=pK3hBwAAQBAJ
Guntinas-Lichius, O., Trentzsch, V., Mueller, N., Heinrich, M., Kuttenreich, A.M., Dobel, C., et al.: High-resolution surface electromyographic activities of facial muscles during the six basic emotional expressions in healthy adults: a prospective observational study. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 19214 (2023)
Guo, J., Zhu, X., Yang, Y., Yang, F., Lei, Z., Li, S.Z.: Towards fast, accurate and stable 3D dense face alignment. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2020)
Haase, D., Rodner, E., Denzler, J.: Instance-weighted transfer learning of active appearance models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 1426–1433 (2014)
...Harris, C.R., Millman, K.J., van der Walt, S.J., Gommers, R., Virtanen, P., Cournapeau, D., Wieser, E., Taylor, J., Berg, S., Smith, N.J., Kern, R., Picus, M., Hoyer, S., van Kerkwijk, M.H., Brett, M., Haldane, A., del Río, J.F., Wiebe, M., Peterson, P., Gérard-Marchant, P., Sheppard, K., Reddy, T., Weckesser, W., Abbasi, H., Gohlke, C., Oliphant, T.E.: Array programming with NumPy. Nature 585(7825), 357–362 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2649-2
Holm, S.: A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 6(2), 65–70 (1979), http://www.jstor.org/stable/4615733
Hu, Y.T., Wang, J., Yeh, R.A., Schwing, A.G.: Sail-vos 3d: A synthetic dataset and baselines for object detection and 3d mesh reconstruction from video data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 1418–1428 (2021)
Josifovski, J., Kerzel, M., Pregizer, C., Posniak, L., Wermter, S.: Object detection and pose estimation based on convolutional neural networks trained with synthetic data. In: 2018 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS). pp. 6269–6276. IEEE (2018)
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aila, T.: A Style-Based Generator Architecture for Generative Adversarial Networks (Mar 2019https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1812.04948
Katsumi, S., Esaki, S., Hattori, K., Yamano, K., Umezaki, T., Murakami, S.: Quantitative analysis of facial palsy using a three-dimensional facial motion measurement system. Auris Nasus Larynx 42(4), 275–283 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2015.01.002
Kim, B., Wattenberg, M., Gilmer, J., Cai, C., Wexler, J., Viegas, F., et al.: Interpretability beyond feature attribution: Quantitative testing with concept activation vectors (tcav). In: International conference on machine learning. pp. 2668–2677. PMLR (2018)
Knoedler, L., Baecher, H., Kauke-Navarro, M., Prantl, L., Machens, H.G., Scheuermann, P., Palm, C., Baumann, R., Kehrer, A., Panayi, A.C., Knoedler, S.: Towards a Reliable and Rapid Automated Grading System in Facial Palsy Patients: Facial Palsy Surgery Meets Computer Science. J. Clin. Med. 11(17), 4998 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11174998
Kortylewski, A., Egger, B., Schneider, A., Gerig, T., Morel-Forster, A., Vetter, T.: Empirically Analyzing the Effect of Dataset Biases on Deep Face Recognition Systems. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). pp. 2174–217409. IEEE, Salt Lake City, UT, USA (Jun 2018https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2018.00283
Lapuschkin, S., Wäldchen, S., Binder, A., Montavon, G., Samek, W., Müller, K.R.: Unmasking clever hans predictors and assessing what machines really learn. Nat. Commun. 10(1), 1096 (2019)
Lewis, J.P., Cordner, M., Fong, N.: Pose space deformation: A unified approach to shape interpolation and skeleton-driven deformation. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. pp. 165–172. Siggraph ’00, ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., USA (2000https://doi.org/10.1145/344779.344862
Li, S., Deng, W.: Reliable crowdsourcing and deep locality-preserving learning for unconstrained facial expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(1), 356–370 (2019)
Li, S., Deng, W., Du, J.: Reliable crowdsourcing and deep locality-preserving learning for expression recognition in the wild. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp. 2584–2593. IEEE (2017)
Li, T., Bolkart, T., Black, M.J., Li, H., Romero, J.: Learning a model of facial shape and expression from 4D scans. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36(6), 1–17 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3130800.3130813
Lin, C.Z., Nagano, K., Kautz, J., Chan, E.R., Iqbal, U., Guibas, L., Wetzstein, G., Khamis, S.: Single-Shot Implicit Morphable Faces with Consistent Texture Parameterization. In: Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Conference Conference Proceedings. pp. 1–12 (Jul 2023https://doi.org/10.1145/3588432.3591494
Mao, J., Xu, R., Yin, X., Chang, Y., Nie, B., Huang, A.: POSTER++: A simpler and stronger facial expression recognition network (Feb 2023)
Matthews, I., Baker, S.: Active appearance models revisited. Int. J. Comput. Vision 60, 135–164 (2004)
Medin, S.C., Egger, B., Cherian, A., Wang, Y., Tenenbaum, J.B., Liu, X., Marks, T.K.: MOST-GAN: 3D Morphable StyleGAN for Disentangled Face Image Manipulation. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 36(2), 1962–1971 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v36i2.20091
Mollahosseini, A., Hasani, B., Mahoor, M.H.: Affectnet: A database for facial expression, valence, and arousal computing in the wild. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 10(1), 18–31 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2017.2740923
Nachbar, F., Stolz, W., Merkle, T., Cognetta, A.B., Vogt, T., Landthaler, M., Bilek, P., Braun-Falco, O., Plewig, G.: The abcd rule of dermatoscopy. high prospective value in the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 30 4, 551–9 (1994), https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:4860343
Neumann, T., Lorenz, A., Volk, G., Hamzei, F., Schulz, S., Guntinas-Lichius, O.: Validierung einer Deutschen Version des Sunnybrook Facial Grading Systems. Laryngorhinootologie 96(03), 168–174 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-111512
Nowruzi, F.E., Kapoor, P., Kolhatkar, D., Hassanat, F.A., Laganiere, R., Rebut, J.: How much real data do we actually need: Analyzing object detection performance using synthetic and real data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.07061 (2019)
Özsoy, U., Uysal, H., Hizay, A., Sekerci, R., Yildirim, Y.: Three-dimensional objective evaluation of facial palsy and follow-up of recovery with a handheld scanner. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery p. S1748681521002552 (Jun 2021https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2021.05.003
Patel, A., Islam, S.M.S., Murray, K., Goonewardene, M.S.: Facial asymmetry assessment in adults using three-dimensional surface imaging. Prog. Orthod. 16(1), 36 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40510-015-0106-9
Paysan, P., Knothe, R., Amberg, B., Romdhani, S., Vetter, T.: A 3D Face Model for Pose and Illumination Invariant Face Recognition. In: 2009 Sixth IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance. pp. 296–301. IEEE, Genova, Italy (Sep 2009https://doi.org/10.1109/AVSS.2009.58
Pearl, J.: Causality. Cambridge university press (2009)
Penzel, N., Kierdorf, J., Roscher, R., Denzler, J.: Analyzing the behavior of cauliflower harvest-readiness models by investigating feature relevances. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW). pp. 572–581. IEEE (2023)
Penzel, N., Reimers, C., Bodesheim, P., Denzler, J.: Investigating neural network training on a feature level using conditional independence. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 383–399. Springer (2022)
Perarnau, G., Van De Weijer, J., Raducanu, B., Álvarez, J.M.: Invertible conditional gans for image editing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.06355 (2016)
Peters, J., Janzing, D., Schlkopf, B.: Elements of Causal Inference: Foundations and Learning Algorithms. The MIT Press (2017)
Pham, L., Vu, T.H., Tran, T.A.: Facial expression recognition using residual masking network. In: 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). pp. 4513–4519 (2021https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR48806.2021.9411919
Piao, J., Sun, K., Wang, Q., Lin, K.Y., Li, H.: Inverting generative adversarial renderer for face reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 15619–15628 (2021)
Pumarola, A., Agudo, A., Martinez, A.M., Sanfeliu, A., Moreno-Noguer, F.: GANimation: Anatomically-aware facial animation from a single image. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision - ECCV 2018, pp. 835–851. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2018)
Pumarola, A., Agudo, A., Sanfeliu, A., Moreno-Noguer, F.: Unsupervised person image synthesis in arbitrary poses. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 8620–8628 (2018)
Qiu, Z., Li, Y., He, D., Zhang, Q., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Xu, L., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Yu, J.: SCULPTOR: Skeleton-Consistent Face Creation Using a Learned Parametric Generator. ACM Transactions on Graphics 41(6), 213:1–213:17 (Nov 2022https://doi.org/10.1145/3550454.3555462
Reichenbach, H.: The direction of time, vol. 65. Univ of California Press (1956)
Reimers, C., Bodesheim, P., Runge, J., Denzler, J.: Conditional adversarial debiasing: Towards learning unbiased classifiers from biased data. In: DAGM German Conference on Pattern Recognition. pp. 48–62. Springer (2021)
Reimers, C., Penzel, N., Bodesheim, P., Runge, J., Denzler, J.: Conditional dependence tests reveal the usage of abcd rule features and bias variables in automatic skin lesion classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 1810–1819 (2021)
Reimers, C., Runge, J., Denzler, J.: Determining the relevance of features for deep neural networks. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer (2020)
Ribeiro, M.T., Singh, S., Guestrin, C.: “why should i trust you?”: Explaining the predictions of any classifier. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (2016), https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:13029170
Richardson, E., Sela, M., Kimmel, R.: 3d face reconstruction by learning from synthetic data. In: 2016 fourth international conference on 3D vision (3DV). pp. 460–469. IEEE (2016)
Roberts, W., Strayer, J.: Empathy, emotional expressiveness, and prosocial behavior. Child Dev. 67(2), 449–470 (1996)
Ros, G., Sellart, L., Materzynska, J., Vazquez, D., Lopez, A.M.: The synthia dataset: A large collection of synthetic images for semantic segmentation of urban scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3234–3243 (2016)
Ross, B.G., Fradet, G., Nedzelski, J.M.: Development of a Sensitive Clinical Facial Grading System. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery 114(3), 380–386 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0194-59989670206-1
Runge, J.: Conditional independence testing based on a nearest-neighbor estimator of conditional mutual information. In: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. PMLR (2018)
Saleh, F.S., Aliakbarian, M.S., Salzmann, M., Petersson, L., Alvarez, J.M.: Effective use of synthetic data for urban scene semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). pp. 84–100 (2018)
Sankaranarayanan, S., Balaji, Y., Jain, A., Lim, S.N., Chellappa, R.: Learning from synthetic data: Addressing domain shift for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3752–3761 (2018)
Savchenko, A.: Facial expression recognition with adaptive frame rate based on multiple testing correction. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. vol. 202. PMLR (2023), https://proceedings.mlr.press/v202/savchenko23a.html
Savchenko, A.V.: Video-based frame-level facial analysis of affective behavior on mobile devices using EfficientNets. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops. pp. 2359–2366 (Jun 2022)
Savchenko, A.V., Savchenko, L.V., Makarov, I.: Classifying emotions and engagement in online learning based on a single facial expression recognition neural network. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing (2022)
Selvaraju, R.R., Das, A., Vedantam, R., Cogswell, M., Parikh, D., Batra, D.: Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. International Journal of Computer Vision 128, 336 – 359 (2016), https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:15019293
Smilkov, D., Thorat, N., Kim, B., Viégas, F.B., Wattenberg, M.: Smoothgrad: removing noise by adding noise. ArXiv abs/1706.03825 (2017), https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:11695878
Springenberg, J.T., Dosovitskiy, A., Brox, T., Riedmiller, M.A.: Striving for simplicity: The all convolutional net. CoRR abs/1412.6806 (2014), https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:12998557
Storn, R., Price, K.: Differential Evolution - A Simple and Efficient Heuristic for global Optimization over Continuous Spaces. J. Global Optim. 11(4), 341–359 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008202821328
Sundararajan, M., Taly, A., Yan, Q.: Axiomatic attribution for deep networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (2017), https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:16747630
Sutton, R.: The bitter lesson (2019)
Takmaz, A., Schult, J., Kaftan, I., Akçay, M., Leibe, B., Sumner, R., Engelmann, F., Tang, S.: 3d segmentation of humans in point clouds with synthetic data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 1292–1304 (2023)
Tewari, A., Elgharib, M., Bharaj, G., Bernard, F., Seidel, H.P., Pérez, P., Zöllhofer, M., Theobalt, C.: StyleRig: Rigging StyleGAN for 3D control over portrait images, CVPR 2020. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE (Jun 2020)
Thalhammer, S., Patten, T., Vincze, M.: Sydpose: Object detection and pose estimation in cluttered real-world depth images trained using only synthetic data. In: 2019 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). pp. 106–115. IEEE (2019)
Thompson, R.A.: Empathy and emotional understanding: The early development of empathy. Empathy and its development 119, 145 (1987)
Tremblay, J., To, T., Birchfield, S.: Falling things: A synthetic dataset for 3d object detection and pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. pp. 2038–2041 (2018)
Vanherle, B., Moonen, S., Van Reeth, F., Michiels, N.: Analysis of training object detection models with synthetic data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.16066 (2022)
Vignesh, S., Savithadevi, M., Sridevi, M., Sridhar, R.: A novel facial emotion recognition model using segmentation VGG-19 architecture. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 15(4), 1777–1787 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-023-01184-z
Wagner, N., Botsch, M., Schwanecke, U.: SoftDECA: Computationally Efficient Physics-Based Facial Animations. In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Motion, Interaction and Games. pp. 1–11. MIG ’23, Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA (Nov 2023https://doi.org/10.1145/3623264.3624439
Wasi, A.T., Šerbetar, K., Islam, R., Rafi, T.H., Chae, D.K.: ARBEx: Attentive Feature Extraction with Reliability Balancing for Robust Facial Expression Learning (Jul 2023)
Weiherer, M., Klein, F., Egger, B.: Approximating Intersections and Differences Between Linear Statistical Shape Models Using Markov Chain Monte Carlo. In: 2024 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). pp. 6352–6361. IEEE, Waikoloa, HI, USA (Jan 2024https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV57701.2024.00624
Wen, Z., Lin, W., Wang, T., Xu, G.: Distract Your Attention: Multi-head Cross Attention Network for Facial Expression Recognition. Biomimetics 8(2), 199 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020199
Wu, Z., Wang, L., Wang, W., Shi, T., Chen, C., Hao, A., Li, S.: Synthetic data supervised salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM international conference on multimedia. pp. 5557–5565 (2022)
Yang, H., Zhu, H., Wang, Y., Huang, M., Shen, Q., Yang, R., Cao, X.: FaceScape: A large-scale high quality 3D face dataset and detailed riggable 3D face prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2020)
Yang, L., Zoss, G., Chandran, P., Gross, M., Solenthaler, B., Sifakis, E., Bradley, D.: Learning a Generalized Physical Face Model From Data (Feb 2024)
Yang, Y., Zhang, H., Katabi, D., Ghassemi, M.: Change is hard: A closer look at subpopulation shift. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.12254 (2023)
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A., Shechtman, E., Wang, O.: The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Apr 2018https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1801.03924
Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Song, Z.: A Dual-Direction Attention Mixed Feature Network for Facial Expression Recognition. Electronics 12(17), 3595 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173595
Zhou, H., Meng, D., Zhang, Y., Peng, X., Du, J., Wang, K., Qiao, Y.: Exploring Emotion Features and Fusion Strategies for Audio-Video Emotion Recognition. In: 2019 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction. pp. 562–566 (Oct 2019https://doi.org/10.1145/3340555.3355713
Zhu, H., Yang, H., Guo, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Huang, M., Wu, Menghua and Shen, Q., Yang, R., Cao, X.: FaceScape: 3D facial dataset and benchmark for single-view 3D face reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) (2023)
Acknowledgment
Partially supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG - German Research Foundation) project 427899908 BRIDGING THE GAP: MIMICS AND MUSCLES (DE 735/15-1 and GU 463/12-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Written consent was obtained from all participants. The Jena University Hospital ethics committee approved the study (No. 2019-1539).
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Büchner, T., Penzel, N., Guntinas-Lichius, O., Denzler, J. (2025). Facing Asymmetry - Uncovering the Causal Link Between Facial Symmetry and Expression Classifiers Using Synthetic Interventions. In: Cho, M., Laptev, I., Tran, D., Yao, A., Zha, H. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2024. ACCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15475. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0911-6_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-0911-6_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-96-0910-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-96-0911-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)