Abstract
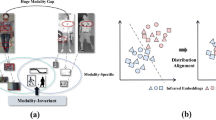
Cross-modality person re-identification, particularly between daytime RGB images and nighttime infrared (IR) images, is one of the challenges in image retrieval tasks on the visual database. Cross-modality feature alignment is one typical solution in current works. However, the significant difference between RGB and IR modalities makes it difficult to align the two features directly. To reduce the modality gap, we introduce an intermediate modality, a grayscale image, which can be generated from RGB with the same label. The grayscale image retains the structural information of the RGB modality and exhibits a visual style similar to the IR image. To improve the performance of Re-ID in visible-infrared cross-modality tasks, we propose a Tri-modality Collaborative Learning model (TCL). There are two modules in TCL, the tri-modality joint feature extraction module and the modality-specific mean teaching classifier module. In the feature extraction module, multiple channels with different modalities are trained to learn modality-independent high-dimensional shared features. The classifier module is designed to ignore modality-specific information. We evaluate the effectiveness of TCL in the public dataset.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhong, X., Lu, T., Huang, W., Yuan, J., Liu, W., Lin, C.-W.: Visible-infrared person re-identification via colorization-based Siamese generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, pp. 421–427 (2020)
Zhong, X., Lu, T., Huang, W., Ye, M., Jia, X., Lin, C.-W.: Grayscale enhancement colorization network for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(3), 1418–1430 (2021)
Kniaz, V.V., Knyaz, V.A., Hladuvka, J., Kropatsch, W.G., Mizginov, V.: Thermalgan: multimodal color-to-thermal image translation for person re-identification in multispectral dataset. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops (2018)
Wang, G., Zhang, T., Cheng, J., Liu, S., Yang, Y., Hou, Z.: RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3623–3632 (2019)
Liu, H., Ma, S., Xia, D., Li, S.: Sfanet: a spectrum-aware feature augmentation network for visible-infrared person reidentification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 34(4), 1958–1971 (2021)
Feng, Z., Lai, J., Xie, X.: Learning modality-specific representations for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 579–590 (2019)
Lu, Y., et al.: Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13379–13389 (2020)
Ye, M., Lan, X., Leng, Q., Shen, J.: Cross-modality person re-identification via modality-aware collaborative ensemble learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 9387–9399 (2020)
Wei, X., Li, D., Hong, X., Ke, W., Gong, Y.: Co-attentive lifting for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1028–1037 (2020)
Wang, H., Zhao, J., Zhou, Y., Yao, R., Chen, Y., Chen, S.: AMC-net: attentive modality-consistent network for visible-infrared person re-identification. Neurocomputing 463, 226–236 (2021)
Sun, X., Liu, B., Ai, L., Liu, D., Meng, Q., Cao, J.: In your eyes: modality disentangling for personality analysis in short video. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 10(3), 982–993 (2022)
Ye, M., Lan, X., Wang, Z., Yuen, P.C.: Bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking for visible thermal person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Security 15, 407–419 (2019)
Ye, M., Lan, X., Li, J., Yuen, P.: Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32 (2018)
Ye, M., Shen, J., Crandall, D.J., Shao, L., Luo, J.: Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020, Proceedings, Part XVII 16, pp. 229–247. Springer (2020)
Ye, M., Shen, J., Lin, G., Xiang, T., Shao, L., Hoi, S.C.H.: Deep learning for person re-identification: a survey and outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(6), 2872–2893 (2021)
Wu, A., Zheng, W.-S., Yu, H.-X., Gong, S., Lai, J.: RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5380–5389 (2017)
Dai, P., Ji, R., Wang, H., Wu, Q., Huang, Y.: Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training. In: IJCAI, vol. 1, p. 6 (2018)
Ye, M., Shen, J., Shao, L.: Visible-infrared person re-identification via homogeneous augmented tri-modal learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 16, 728–739 (2020)
Li, D., Wei, X., Hong, X., Gong, Y.: Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 4610–4617 (2020)
Park, H., Lee, S, Lee, J., Ham, B.: Learning by aligning: visible-infrared person re-identification using cross-modal correspondences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 12046–12055 (2021)
Fu, X., Liu, S., Li, C., Sun, J.: Mclnet: an multidimensional convolutional lightweight network for gastric histopathology image classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 80, 104319 (2023)
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the corresponding author Dongyue Chen and other authors for their contributions. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62202087, 62206043), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation 2024A1515010244, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N2404008, N2404011, N2304020), and the 111 Project (B16009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Deng, S., Yang, Q., Yang, Z., Chen, D., Yang, Y., Wang, H. (2025). Tri-modality Collaborative Learning for Person Re-identification. In: Chen, T., Cao, Y., Nguyen, Q.V.H., Nguyen, T.T. (eds) Databases Theory and Applications. ADC 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15449. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-1242-0_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-1242-0_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-96-1241-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-96-1242-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)