Abstract
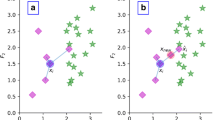
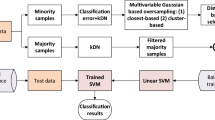
Imbalanced data classification has become one of the hot topics in the field of data mining and machine learning. Oversampling is one of the mainstream methods to solve the imbalance problem by synthesizing new samples to balance the data distribution. However, due to the limited sample local information, the data synthetic process is risky in deteriorating the class overlap phenomenon, showing a vulnerable robustness with respect to data noise. In this paper, we propose a noise robust gaussian distribution based imbalanced oversampling (NGOS). NGOS first determines the neighborhood radius based on the global information, and then assigns sampling weights to minority class samples based on the density and the distance information within each of the neighborhoods. Finally, NGOS generates new samples with a Gaussian distribution model. We validate the effectiveness of our proposed method on the 38 KEEL datasets, DT classifier and eleven comparison methods. Experimental results show that our method outperforms the other compared methods in terms of Fmeasure, AUC, Gmean. The codes of NGOS are released in https://github.com/ytyancp/NGOS.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62376002.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barua, S., Islam, M.M., Yao, X., Murase, K.: MWMOTE-majority weighted minority oversampling technique for imbalanced data set learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 26(2), 405–425 (2012)
Batista, G.E., Prati, R.C., Monard, M.C.: A study of the behavior of several methods for balancing machine learning training data. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 6(1), 20–29 (2004)
Bunkhumpornpat, C., Sinapiromsaran, K., Lursinsap, C.: Safe-Level-SMOTE: safe-level-synthetic minority over-sampling technique for handling the class imbalanced problem. In: Theeramunkong, T., Kijsirikul, B., Cercone, N., Ho, T.-B. (eds.) PAKDD 2009. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 5476, pp. 475–482. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01307-2_43
Chawla, N.V., Bowyer, K.W., Hall, L.O., Kegelmeyer, W.P.: SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 16, 321–357 (2002)
Chen, Y., Wu, K., Chen, X., Tang, C., Zhu, Q.: An entropy-based uncertainty measurement approach in neighborhood systems. Inf. Sci. 279, 239–250 (2014)
Folino, G., Pisani, F.S., Sabatino, P.: An incremental ensemble evolved by using genetic programming to efficiently detect drifts in cyber security datasets. In: Proceedings of the 2016 on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion, pp. 1103–1110 (2016)
García, V., Sánchez, J.S., Marqués, A., Florencia, R., Rivera, G.: Understanding the apparent superiority of over-sampling through an analysis of local information for class-imbalanced data. Exp. Syst. Appl. 158, 113026 (2020)
Haixiang, G., Yijing, L., Shang, J., Mingyun, G., Yuanyue, H., Bing, G.: Learning from class-imbalanced data: review of methods and applications. Exp. Syst. Appl. 73, 220–239 (2017)
Han, H., Wang, W.-Y., Mao, B.-H.: Borderline-SMOTE: a new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning. In: Huang, D.-S., Zhang, X.-P., Huang, G.-B. (eds.) ICIC 2005, Part I 1. LNCS, vol. 3644, pp. 878–887. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/11538059_91
He, H., Bai, Y., Garcia, E.A., Li, S.: ADASYN: adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In: 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), pp. 1322–1328. IEEE (2008)
Ivan, T.: Two modifications of CNN. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Commun. (SMC) 6, 769–772 (1976)
Jurgovsky, J., et al.: Sequence classification for credit-card fraud detection. Exp. Syst. Appl. 100, 234–245 (2018)
Koziarski, M.: Radial-based undersampling for imbalanced data classification. Pattern Recogn. 102, 107262 (2020)
Krawczyk, B., Koziarski, M., Woźniak, M.: Radial-based oversampling for multiclass imbalanced data classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(8), 2818–2831 (2019)
Lin, W.C., Tsai, C.F., Hu, Y.H., Jhang, J.S.: Clustering-based undersampling in class-imbalanced data. Inf. Sci. 409, 17–26 (2017)
López, V., Fernández, A., García, S., Palade, V., Herrera, F.: An insight into classification with imbalanced data: empirical results and current trends on using data intrinsic characteristics. Inf. Sci. 250, 113–141 (2013)
Rodriguez, D., Herraiz, I., Harrison, R., Dolado, J., Riquelme, J.C.: Preliminary comparison of techniques for dealing with imbalance in software defect prediction. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering, pp. 1–10 (2014)
Vuttipittayamongkol, P., Elyan, E., Petrovski, A.: On the class overlap problem in imbalanced data classification. Knowl. Based Syst. 212, 106631 (2021)
Wilson, D.L.: Asymptotic properties of nearest neighbor rules using edited data. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 3, 408–421 (1972)
Xie, Y., Qiu, M., Zhang, H., Peng, L., Chen, Z.: Gaussian distribution based oversampling for imbalanced data classification. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 34(2), 667–679 (2022)
Yan, Y., Jiang, Y., Zheng, Z., Yu, C., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y.: LDAS: local density-based adaptive sampling for imbalanced data classification. Exp. Syst. Appl. 191, 116213 (2022)
Yan, Y., Zhu, Y., Liu, R., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L.: Spatial distribution-based imbalanced undersampling. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 35, 6376–6391 (2023)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shao, X., Yan, Y. (2024). Noise-Robust Gaussian Distribution Based Imbalanced Oversampling. In: Tari, Z., Li, K., Wu, H. (eds) Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing. ICA3PP 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14488. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0801-7_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0801-7_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-0800-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-0801-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)