Abstract
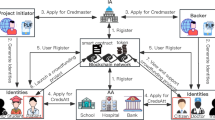
Charity crowdfunding is a technique for raising funds that involves collecting modest contributions from a vast number of individuals or groups via established crowdfunding platforms or other digital avenues. The objective is to provide support for charitable organizations, social welfare initiatives, or personal requirements. The widespread adoption of the Internet and the rapid advancement of digital technology have facilitated the global dissemination and promotion of charity crowdfunding. However, crowdfunding platforms have recently experienced a decline in credibility due to various factors such as fraudulent donations, inadequate fund management, and other forms of disorder. The blockchain’s decentralization and anti-tampering features exhibit a high degree of compatibility with the requirements of a crowdfunding platform. Most current state-of-the-art techniques do not ensure the non-linkability of user identities in the face of sybil attacks, nor do they offer a streamlined auditing mechanism for crowdsourcing modest donations that simultaneously preserves transactional privacy. This paper presents a novel crowdfunding system called CFChain based on blockchain technology. Initially, the distributed identity and BLS signature are employed to establish a user authentication mechanism, enabling CFChain to withstand sybil attacks while preserving the non-linkability of user identities. Subsequently, a crowdfunding mechanism is constructed utilizing zero-knowledge proofs to facilitate streamlined auditing procedures while safeguarding donations’ confidentiality. Additionally, a security analysis of CFChain is presented. The system prototype is subsequently implemented on the Hyperledger Fabric. Empirical evidence indicates that the efficiency of CFChain is viable.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yahoo. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/crowdfunding-market-reach-42-93-150700017.html. Accessed 29 Jun 2022
Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1078273/global-crowdfunding-market-size/. Accessed 22 Aug 2022
Zcash “sapling” cryptography. https://github.com/zcash-hackworks/sapling-crypto. Accessed 28 Feb 2020
Weidentity: Digital identity for data sharing on open consortium chain (2022). Software available, https://fintech.webank.com/en/weidentity/
Androulaki, E., et al.: Hyperledger fabric: a distributed operating system for permissioned blockchains. In: Proceedings of the Thirteenth EuroSys Conference, pp. 1–15 (2018)
Biçer, O., Küpçü, A.: Anonymous, attribute based, decentralized, secure, and fair e-donation. Cryptology ePrint Archive (2020)
Boneh, D., Gentry, C., Lynn, B., Shacham, H.: Aggregate and verifiably encrypted signatures from bilinear maps. In: Biham, E. (ed.) EUROCRYPT 2003. LNCS, vol. 2656, pp. 416–432. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-39200-9_26
Béres, F., et al.: Blockchain is watching you: profiling and deanonymizing Ethereum users. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Decentralized Applications and Infrastructures (DAPPS), pp. 69–78 (2021)
Chaum, D., Pedersen, T.P.: Wallet databases with observers. In: Brickell, E.F. (ed.) CRYPTO 1992. LNCS, vol. 740, pp. 89–105. Springer, Heidelberg (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-48071-4_7
Constantinides, K., et al.: BulletProof: a defect-tolerant CMP switch architecture, pp. 5–16. IEEE (2006)
Douceur, J.R.: The Sybil attack. In: Druschel, P., Kaashoek, F., Rowstron, A. (eds.) IPTPS 2002, Revised Paper. LNCS, vol. 2429, pp. 251–260. Springer, Heidelberg (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45748-8_24
Farooq, M.S., Khan, M., Abid, A.: A framework to make charity collection transparent and auditable using blockchain technology. Comput. Electr. Eng. 83, 106588 (2020)
Fiege, U., et al.: Zero knowledge proofs of identity. In: Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 210–217 (1987)
Hossain, M., Oparaocha, G.O.: Crowdfunding: motives, definitions, typology and ethical challenges. Entrep. Res. J. 7, 1–14 (2017)
Kang, H., et al.: FabZK: supporting privacy-preserving, auditable smart contracts in hyperledger fabric. In: 2019 49th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks (DSN), pp. 543–555. IEEE (2019)
Lundkvist, C., et al.: uPort: a platform for self-sovereign identity (2017). https://whitepaper.uport.me/uPort_whitepaper_DRAFT20170221.pdf
Manda, V.K., Prasada Rao, S.S., Prasadarao, S.S.: Blockchain technology for the mutual fund industry. In: National Seminar on Paradigm Shifts in Commerce and Management, pp. 12–17 (2018)
Maram, D., et al.: CanDID: can-do decentralized identity with legacy compatibility, Sybil-resistance, and accountability. In: 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), pp. 1348–1366. IEEE (2021)
Mehra, A., et al.: Vishrambh: trusted philanthropy with end-to-end transparency. In: HCI for Blockchain: a CHI 2018 Workshop on Studying, Critiquing, Designing and Envisioning Distributed Ledger Technologies, Montreal, QC, Canada (2018)
Nakamoto, S.: Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Decentralized business review, p. 21260 (2008)
Narula, N., et al.: zkLedger: privacy-preserving auditing for distributed ledgers. In: 15th \(\{\)USENIX\(\}\) Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (\(\{\)NSDI\(\}\) 18), pp. 65–80 (2018)
Patel, V.: New Jersey man gets 5 years in prison in GoFundMe fraud case. The Times (2022). https://www.nytimes.com/2022/08/07/nyregion/gofundme-scam-mark-damico-sentenced.html
Pedersen, T.P.: Non-interactive and information-theoretic secure verifiable secret sharing. In: Feigenbaum, J. (ed.) CRYPTO 1991. LNCS, vol. 576, pp. 129–140. Springer, Heidelberg (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-46766-1_9
Picard, C.: Scammers hijack crowdfunding campaign for 6-year-old with leukemia (2016). https://www.goodhousekeeping.com/life/news/a39792/leukemia-patient-gofundme-hacked/
Renat, G., et al.: Karma-blockchain based charity foundation platform. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC), pp. 1–2. IEEE (2021)
Sahana, S.C., Bhuyan, B.: A provable secure short signature scheme based on bilinear pairing over elliptic curve. Int. J. Netw. Secur. 21, 145–152 (2019)
Saleh, H., et al.: Platform for tracking donations of charitable foundations based on blockchain technology. In: 2019 Actual Problems of Systems and Software Engineering (APSSE), pp. 182–187 (2019)
Sasson, E.B., et al.: Zerocash: decentralized anonymous payments from bitcoin. In: 2014 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, pp. 459–474. IEEE (2014)
Singh, A., et al.: Aid, charity and donation tracking system using blockchain. In: 2020 4th International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI) (48184), pp. 457–462. IEEE (2020)
Wood, G., et al.: Ethereum: a secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger. Ethereum project yellow paper 151(2014), 1–32 (2014)
Yin, J., et al.: SmartDID: a novel privacy-preserving identity based on blockchain for IoT. IEEE IoT J. 10, 6718–6732 (2022)
Yuen, T.H.: PAChain: private, authenticated & auditable consortium blockchain and its implementation. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 112, 913–929 (2020)
Zhang, R., et al.: Security and privacy on blockchain. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 52, 1–34 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by JST SPRING (Grant No. JPMJSP2136), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 30106220482).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, Y., Chen, J., Inoue, K. (2024). CFChain: A Crowdfunding Platform that Supports Identity Authentication, Privacy Protection, and Efficient Audit. In: Tari, Z., Li, K., Wu, H. (eds) Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing. ICA3PP 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14493. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0862-8_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0862-8_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-0861-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-0862-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)