Abstract
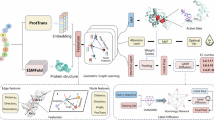
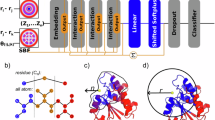
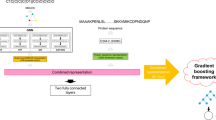
Protein function prediction has long been a widely discussed task in the field of synthetic biology, and it is of paramount importance for gaining a deeper understanding of the roles and interactions of proteins within living organisms. Since the 3D structure data of proteins obtained experimentally are far less in quantity than the corresponding protein sequence data, most experiments related to protein function prediction currently rely on using protein sequences as training data, although 3D protein structures contain much more information. Here, an enzyme turnover number prediction model (PSKcat) is proposed based on 3D protein structures. PSKcat takes protein PDB files as input, represents proteins using a modified pre-trained model called GearNet-Edge for 3D protein structures, and combines graph neural network to characterize the substrates involved in enzyme reactions. In order to verify the effectiveness of the model, several enzyme reaction datasets were constructed, and multiple groups of comparative experiments were conducted. The experimental results demonstrate the feasibility of using 3D protein structures for enzyme function prediction, which opens up avenues for further exploration of the applications of 3D protein structures in the future.
Y. He and Y. Wang—Contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, S., An, J., Li, Y., et al.: Automated high-throughput genome editing platform with an AI learning in situ prediction model. Nat. Commun. 13(1), 7386 (2022)
Zelezniak, A., Vowinckel, J., Capuano, F., et al.: Machine learning predicts the yeast metabolome from the quantitative proteome of kinase knockouts. Cell Syst. 7(3), 269–283.e6 (2018)
Kim, G.B., Kim, W.J., Kim, H.U., et al.: Machine learning applications in systems metabolic engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 64, 1–9 (2020)
Doudna, J.A., Charpentier, E.: The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science 346(6213), 1258096 (2014)
Radivojević, T., Costello, Z., Workman, K., et al.: A machine learning automated recommendation tool for synthetic biology. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 4879 (2020)
Li, G., Rabe, K.S., Nielsen, J., et al.: Machine learning applied to predicting microorganism growth temperatures and enzyme catalytic optima. ACS Synth. Biol. 8(6), 1411–1420 (2019)
Limbu, S., Dakshanamurthy, S.: A new hybrid neural network deep learning method for protein-ligand binding affinity prediction and de novo drug design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23(22), 13912 (2022)
Tsubaki, M., Tomii, K., Sese, J.: Compound–protein interaction prediction with end-to-end learning of neural networks for graphs and sequences. Bioinformatics 35(2), 309–318 (2019)
Li, F., Yuan, L., Lu, H., et al.: Deep learning-based k cat prediction enables improved enzyme-constrained model reconstruction. Nat. Catal. 5(8), 662–672 (2022)
Kroll, A., Rousset, Y., Hu, X.P., et al.: Turnover number predictions for kinetically uncharacterized enzymes using machine and deep learning. Nat. Commun. 14(1), 4139 (2023)
Hermosilla, P., Ropinski, T.: Contrastive representation learning for 3d protein structures. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.15675 (2022)
Zhang, Z., Xu, M., Jamasb, A., et al.: Protein representation learning by geometric structures pretraining. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.06125 (2022)
Aslam, B., Basit, M., Nisar, M.A., et al.: Proteomics: technologies and their applications. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1–15 (2016)
Zhao, J., Yan, W., Yang, Y.: DeepTP: a deep learning model for thermophilic protein prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24(3), 2217 (2023)
Hu, T.M., Hayton, W.L.: Architecture of the drug–drug interaction network. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 36(2), 135–143 (2011)
Wang, Z., Masoomi, A., Xu, Z., et al.: Improved prediction of smoking status via isoform-aware RNA-seq deep learning models. PLoS Comput. Biol. 17(10), e1009433 (2021)
Paysan-Lafosse, T., Blum, M., Chuguransky, S., et al.: InterPro in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 51(D1), D418–D427 (2023)
Jumper, J., Evans, R., Pritzel, A., et al.: Highly accurate protein structures prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596(7873), 583–589 (2021)
Zaidi, S., Schaarschmidt, M., Martens, J., et al.: Pre-training via denoising for molecular property prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.00133 (2022)
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., et al.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1597–1607. PMLR (2020)
Berman, H.M., et al.: The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 28(1), 235–242 (2000)
Ye, J., McGinnis, S., Madden, T.L.: BLAST: improvements for better sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 34(suppl_2), W6–W9 (2006)
Landrum, G., et al.: RDKit: open-source cheminformatics (2006). http://www.rdkit.org
Kipf, T.N., Welling, M.: Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02907 (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., et al.: Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) Computer Vision–ECCV 2016, Part IV, pp. 630–645. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_38
Shervashidze, N., Schweitzer, P., Van Leeuwen, E.J., et al.: Weisfeiler-lehman graph kernels. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12(9) (2011)
Harary, F., Norman, R.Z.: Some properties of line digraphs. Rendiconti del circolo matematico di palermo 9, 161–168 (1960)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China (2022YFA0911800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y., Cheng, L., Alghazzawi, D. (2024). Enzyme Turnover Number Prediction Based on Protein 3D Structures. In: Huang, DS., Premaratne, P., Yuan, C. (eds) Applied Intelligence. ICAI 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 2014. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0903-8_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0903-8_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-0902-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-0903-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)