Abstract
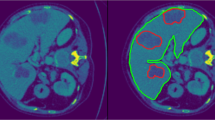
In this paper, we introduce PB-FELTuCS, a hierarchical deep neural network architecture which first performs enhanced 3D liver segmentation and subsequently employs a 3D patch-based filtering algorithm over the 3D liver segments to achieve 3D liver tumor classification and segmentation on LiTS dataset [1]. Despite the simplicity of our liver segmentation network, it surpasses recent benchmarks by achieving an impressive Dice score of 0.98, facilitated by our proposed weighted version of Exponential Logarithmic Dice (ELDice) loss [20]. Furthermore, we propose a filtering approach to extract meaningful 3D patches from the segmented liver, which are then used (as opposed to full volumes) during training of our tumor classification and segmentation networks. This approach enables simpler networks to obtain an accuracy of 89.1% in tumor classification and a 0.747 Dice score for tumor segmentation, highlighting the importance of effective training strategies as an alternative to complex neural network architectures, in enhancing the precision of volumetric medical assessments. Code is available at https://github.com/BheeshmSharma/PBFELTuCS_MICAD2023.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilic, P., et al.: The liver tumor segmentation benchmark (LiTS). arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.04056 (2019)
Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., Lienkamp, S.S., Brox, T., Ronneberger, O.: 3D U-net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9901, pp. 424–432. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
Chen, Y., Hu, F., Wang, Y., Zheng, C.: Hybrid-attention densely connected U-Net with GAP for extracting livers from CT volumes. Med. Phys. 49(1), 1015–1033 (2022)
Chen, Y., et al.: MS-FANet: multi-scale feature attention network for liver tumor segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 163, 107208 (2023)
Chen, Y., et al.: A deep residual attention-based U-Net with a biplane joint method for liver segmentation from CT scans. Comput. Biol. Med. 152, 106421 (2023)
Chi, J., Han, X., Wu, C., Wang, H., Ji, P.: X-net: multi-branch UNet-like network for liver and tumor segmentation from 3D abdominal CT scans. Neurocomputing 459(C), 81–96 (2021)
Dickson, J., Linsely, A., Nineta, R.J.A.: An integrated 3D-sparse deep belief network with enriched seagull optimization algorithm for liver segmentation. Multim. Syst. 29(3), 1315–1334 (2023)
Isensee, F., Jaeger, P.F., Kohl, S.A.A., Petersen, J., Maier-Hein, K.: nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 18, 203–211 (2020)
Hatamizadeh, A., et al.: Unetr: transformers for 3d medical image segmentation. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 1748–1758. IEEE Computer Society (2022)
Karimijafarbigloo, S., Azad, R., Kazerouni, A., Merhof, D.: MS-former: multi-scale self-guided transformer for medical image segmentation. In: Med. Imaging Deep Learn. (2023)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Kushnure, D.T., Tyagi, S., Talbar, S.N.: LiM-net: llightweight multi-level multiscale network with deep residual learning for automatic liver segmentation in CT images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 80, 104305 (2023)
Lei, T., Wang, R., Zhang, Y., Wan, Y., Liu, C., Nandi, A.K.: DefED-net: deformable encoder-decoder network for liver and liver tumor segmentation. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 6, 68–78 (2021)
Liu, H., et al.: GCHA-net: global context and hybrid attention network for automatic liver segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 152, 10635 (2023)
Ma, J., Xia, M., Ma, Z., Jiu, Z.: MDAU-Net: a liver and liver tumor segmentation method combining an attention mechanism and multi-scale features. Appl. Sci. 13(18), 10443 (2023)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Song, L., Wang, H., Wang, Z.J.: Bridging the gap between 2D and 3D contexts in CT volume for liver and tumor segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 25(9), 3450–3459 (2021)
Wang, C., et al.: Automatic liver segmentation using multi-plane integrated fully convolutional neural networks. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 1–6 (2018)
Wang, X., Wang, S., Zhang, Z., Yin, X., Wang, T., Li, N.: CPAD-net: contextual parallel attention and dilated network for liver tumor segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 79, 104258 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104258
Wong, K.C.L., Moradi, M., Tang, H., Syeda-Mahmood, T.F.: 3D segmentation with exponential logarithmic loss for highly unbalanced object sizes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.00076 (2018)
Zhou, Z., Siddiquee, R., Mahfuzur, M., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: a nested U-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) DLMIA 2018. LNC, vol. 11045, pp. 3–11. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1
Acknowledgments
We thank Technocraft Centre of Applied Artificial Intelligence (TCA2I), IIT Bombay, for their generous funding support towards this project. We acknowledge Viplove Kanaujia for his help with experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sharma, B., Balamurugan, P. (2024). PB-FELTuCS: Patch-Based Filtering for Enhanced Liver Tumor Classification and Segmentation. In: Su, R., Zhang, YD., Frangi, A.F. (eds) Proceedings of 2023 International Conference on Medical Imaging and Computer-Aided Diagnosis (MICAD 2023). MICAD 2023. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1166. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1335-6_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1335-6_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-1334-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-1335-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)