Abstract
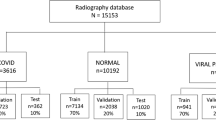
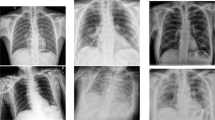
The medical community is working harder to develop quick and accurate methods of diagnosing the virus in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The speed and efficiency of image-based COVID-19 diagnosis are its benefits, but it also carries a risk of error and necessitates the involvement of numerous skilled radiologists. In this paper, a novel convolutional neural network architecture called AlexNet is presented. It has the capacity to automatically learn features in a hierarchy and recognize complex patterns and improves the model’s recognition of disease-related features. In addition, AlexNet’s adaptability and generalization capabilities contribute to its effectiveness in processing various imaging datasets. AlexNet therefore has great potential to identify complex patterns associated with COVID-19-related lung abnormalities. Nevertheless, it also has certain limitations, including the need for a large amount of processing power, the possibility of overfitting, the lack of sufficient interpretability, and the need for further development in order to make it more applicable to particular diagnostic tasks. In summary, collaborative efforts between the AI research community and healthcare professionals will continue to seek accurate, efficient, and ethical solutions for image-based COVID-19 diagnosis.
Y. Peng—Contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, X.-W., et al.: A novel method based on multi-molecular infrared (MM-IR) AlexNet for rapid detection of trace harmful substances in flour. Food Bioprocess Technol. 16(3) (2023)
Luo, X., Wen, W., Wang, J., Xu, S., Gao, Y., Huang, J.: Health classification of Meibomian gland images using keratography 5M based on AlexNet model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 219 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106742
Hosny, K.M., Kassem, M.A., Fouad, M.M.: Classification of skin lesions into seven classes using transfer learning with AlexNet. J. Digit. Imaging 33, 1325–1334 (2020)
Badawi, A.A., et al.: Towards the AlexNet moment for homomorphic encryption: HCNN, the first homomorphic CNN on encrypted data with GPUs. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 9(3), 1330–1343 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tetc.2020.3014636
Shen, Z., Yang, H., Zhang, S.: Optimal approximation rate of ReLU networks in terms of width and depth. J. de mathematiques pures et appliquees 157 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpur.2021.07.009
Liang, X., Xu, J.: Biased ReLU neural networks. Neurocomputing 423, 71–79 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.09.050
Xu, Y., Wang, Y., Razmjooy, N.: Lung cancer diagnosis in CT images based on Alexnet optimized by modified Bowerbird optimization algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 77, 103791 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103791
Zhuang, J., et al.: Evaluation of different deep convolutional neural networks for detection of broadleaf weed seedlings in wheat. Pest Manag. Sci. 78(2) (2022).https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6656
Xie, J., et al.: Advanced dropout: a model-free methodology for Bayesian dropout optimization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(9), 4605–4625 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2021.3083089
Salehinejad, H., Valaee, S.: EDropout: energy-based dropout and pruning of deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33(10), 5279–5292 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2021.3069970
Cheng, J., Huang, W., Lam, H.-K., Cao, J., Zhang, Y.: Fuzzy-model-based control for singularly perturbed systems with nonhomogeneous Markov switching: a dropout compensation strategy. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30(2), 530–541 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tfuzz.2020.3041588
Pandey, M., et al.: The transformational role of GPU computing and deep learning in drug discovery. Nat. Mach. Intell. 4(3), 211–221 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-022-00463-x
Yidi, W., Kaihao, M., Xiao, Y., Zhi, L., James, C.: Elastic deep learning in multi-tenant GPU clusters. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 33(1), 144–158 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpds.2021.3064966
Sun, S., et al.: Fault diagnosis of conventional circuit breaker contact system based on time-frequency analysis and improved Alexnet. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2020.3045798
Gu, R., et al.: Liquid: intelligent resource estimation and network-efficient scheduling for deep learning jobs on distributed GPU clusters. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 33(11), 2808–2820 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpds.2021.3138825
Lu, T., Yu, F., Xue, C., Han, B.: Identification, classification, and quantification of three physical mechanisms in oil-in-water emulsions using AlexNet with transfer learning. J. Food Eng. 288 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110220
Robinson, P.C., et al.: COVID-19 therapeutics: challenges and directions for the future. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119(15), e2119893119 (2022)
Díaz, A., Esparcia, C., López, R.: The diversifying role of socially responsible investments during the COVID-19 crisis: a risk management and portfolio performance analysis. Econ. Anal. Policy 75, 39–60 (2022)
Yuan, Y., Jiao, B., Qu, L., Yang, D., Liu, R.: The development of COVID-19 treatment. Front. Immunol. 14, 1125246 (2023)
Mueller, Y.M., et al.: Stratification of hospitalized COVID-19 patients into clinical severity progression groups by immuno-phenotyping and machine learning. Nat. Commun. 13(1), 915 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28621-0
Qorib, M., Oladunni, T., Denis, M., Ososanya, E., Cotae, P.: Covid-19 vaccine hesitancy: text mining, sentiment analysis and machine learning on COVID-19 vaccination Twitter dataset. Expert Syst. Appl. 212, 118715 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118715
Aslan, M.F., Sabanci, K., Durdu, A., Unlersen, M.F.: COVID-19 diagnosis using state-of-the-art CNN architecture features and Bayesian optimization. Comput. Biol. Med. 142, 105244 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105244
Basu, A., Sheikh, K.H., Cuevas, E., Sarkar, R.: COVID-19 detection from CT scans using a two-stage framework. Expert Syst. Appl. 193, 116377 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.116377
Bernal, A.J., et al.: Molnupiravir for oral treatment of covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 386(6) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Watson, O.J., Barnsley, G., Toor, J., Hogan, A.B., Winskill, P., Ghani, A.C.: Global impact of the first year of COVID-19 vaccination: a mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22(9), 1293–1302 (2022)
Bhatele, K.R., et al.: COVID-19 detection: a systematic review of machine and deep learning-based approaches utilizing chest X-rays and CT scans. Cognit. Comput., 1–38 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-022-10076-6
Farhangnia, P., et al.: Recent advances in passive immunotherapies for COVID-19: the evidence-Based approaches and clinical trials. Int. Immunopharmacol. 109, 108786 (2022)
Jiang, D., Wang, X., Zhao, R.: Analysis on the economic recovery in the post-COVID-19 era: evidence from China. Front. Public Health 9, 787190 (2022)
Attallah, O., Samir, A.: A wavelet-based deep learning pipeline for efficient COVID-19 diagnosis via CT slices. Appl. Soft Comput. 128, 109401 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109401
Jadhav, S., Deng, G., Zawin, M., Kaufman, A.E.: COVID -view: diagnosis of COVID-19 using chest CT. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 28(1), 227–237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tvcg.2021.3114851
Bhattacharyya, A., Bhaik, D., Kumar, S., Thakur, P., Sharma, R., Pachori, R.B.: A deep learning based approach for automatic detection of COVID-19 cases using chest X-ray images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 71(Part), 103182 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103182
Goel, T., Murugan, R., Mirjalili, S., Chakrabartty, D.K.: Multi-COVID-net: multi-objective optimized network for COVID-19 diagnosis from chest X-ray images. Appl. Soft Comput. 115, 108250 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.108250
Ieracitano, C., et al.: A fuzzy-enhanced deep learning approach for early detection of Covid-19 pneumonia from portable chest X-ray images. Neurocomputing 481, 202–215 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.01.055
Kumar, A., Tripathi, A.R., Satapathy, S.C., Zhang, Y.D.: SARS-Net: COVID-19 detection from chest X-rays by combining graph convolutional network and convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit. 122(1), 108255 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108255
Aslan, M.F., Unlersen, M.F., Sabanci, K., Durdu, A.: CNN-based transfer learning-BiLSTM network: a novel approach for Covid-19 infection detection. Appl. Soft Comput. 98, 106912 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106912
Muhammad, U., Hoque, M.Z., Oussalah, M., Keskinarkaus, A., Seppänen, T., Sarder, P.: SAM: Self-augmentation mechanism for COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images. Knowl. Based Syst. 241, 108207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108207
Xu, X., Tian, H., Zhang, X., Qi, L., He, Q., Dou, W.: DisCOV: distributed COVID-19 detection on X-ray images with edge-cloud collaboration. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 15(3), 1206–1219 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tsc.2022.3142265
Mahbub, M.K., Biswas, M., Gaur, L., Alenezi, F., Santosh, K.C.: Deep features to detect pulmonary abnormalities in chest X-rays due to infectious diseaseX: Covid-19, pneumonia, and tuberculosis. Inf. Sci. 592, 389–401 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.01.062
Malhotra, A., et al.: Multi-task driven explainable diagnosis of COVID-19 using chest X-ray images. Pattern Recognit. 122(1), 108243 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108243
Hashimoto, H., et al.: A swallowing decoder based on deep transfer learning: AlexNet classification of the intracranial electrocorticogram. Int. J. Neural Syst. 31(11), 2050056 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065720500562
Davari, N., Akbarizadeh, G., Mashhour, E.: Corona detection and power equipment classification based on GoogleNet-AlexNet: an accurate and intelligent defect detection model based on deep learning for power distribution lines. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 37(4), 2766–2774 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpwrd.2021.3116489
Daubechies, I., DeVore, R., Foucart, S., Hanin, B., Petrova, G.: Nonlinear Approximation and (Deep) ReLU Networks. Constr. Approx. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00365-021-09548-z
Opschoor, J.A.A., Schwab, C., Zech, J.: Exponential ReLU DNN expression of holomorphic maps in high dimension. Constr. Approx. 55(1) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00365-021-09542-5
He, M., Zhao, X., Lu, Y., Hu, Y.: An improved AlexNet model for automated skeletal maturity assessment using hand X-ray images. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. Int. J. Esci. 121, 106–113 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.03.018
Dhar, P., Dutta, S., Mukherjee, V.: Cross-wavelet assisted convolution neural network (Alexnet) approach for phonocardiogram signals classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 63, 102142 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102142
Chen, J., et al.: Medical image segmentation and reconstruction of prostate tumor based on 3D AlexNet. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 200, 105878 (2021)
Zarini, H., Khalili, A., Tabassum, H., Rasti, M., Saad, W.: AlexNet classifier and support vector regressor for scheduling and power control in multimedia heterogeneous networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 22 (01) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tmc.2021.3123200
Sabitha, P., Meeragandhi, G.: A dual stage AlexNet-HHO-DrpXLM archetype for an effective feature extraction, classification and prediction of liver cancer based on histopathology images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 77, 103833 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103833
Alencastre-Miranda, M., Johnson, R.R., Krebs, H.I.: Convolutional neural networks and transfer learning for quality inspection of different sugarcane varieties. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 17(2), 787–794 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tii.2020.2992229
Chen, T., Zhang, X., You, M., Zheng, G., Lambotharan, S.: A GNN-based supervised learning framework for resource allocation in wireless IoT networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 9(3), 1712–1724 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2021.3091551
Li, X., Liu, H., Wang, W., Zheng, Y., Lv, H., Lv, Z.: Big data analysis of the internet of things in the digital twins of smart city based on deep learning. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 128, 167–177 (2022)
Portilla, L., et al.: Wirelessly powered large-area electronics for the Internet of Things. Nat. Electron. 6(1), 10–17 (2023)
Chen, H.-C., et al.: AlexNet convolutional neural network for disease detection and classification of tomato leaf. Electronics 11(6), 951 (2022)
Ibrahim, R., Shafiq, M.O.: Augmented Score-CAM: high resolution visual interpretations for deep neural networks. Knowl. Based Syst. 252, 109287 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109287
Zhang, B., Dong, Z., Zhang, J., Lin, H.: Functional network: a novel framework for interpretability of deep neural networks. Neurocomputing 519, 94–103 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.11.035
Salahuddin, Z., Woodruff, H.C., Chatterjee, A., Lambin, P.: Transparency of deep neural networks for medical image analysis: a review of interpretability methods. Comput. Biol. Med. 140, 105111 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.105111
Acknowledgments
The research work was supported by the open project of State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves (Grant No. K202218).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest regarding this paper.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tang, M., Peng, Y., Wang, S., Chen, S., Zhang, Y. (2024). AlexNet for Image-Based COVID-19 Diagnosis. In: Su, R., Zhang, YD., Frangi, A.F. (eds) Proceedings of 2023 International Conference on Medical Imaging and Computer-Aided Diagnosis (MICAD 2023). MICAD 2023. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1166. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1335-6_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1335-6_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-1334-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-1335-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)