Abstract
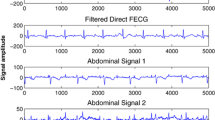
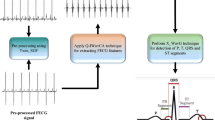
Extraction of fetal ECG (fECG) signal is essential for monitoring the health of fetus during pregnancy and helps in early diagnosis of heart abnormalities, which leads to increased infant mortality rate and post-natal complications. In real scenarios, extraction of clear fECG is challenging due to maternal ECG (mECG) and other contaminated noise (such as: baseline wander and high frequency noise). This paper is focused on design, implementation, and verification of a robust approach for fECG extraction, recorded by non-invasive procedure from the pregnant women, using empirical mode decomposition (EMD), independent component analysis (ICA), and FIR filtering. The combined EMD and ICA approach are found suitable for effective extraction in real and synthetic data. EMD separates the non-stationary and non-linear time varying signals like ECG into various modes, having high to low frequencies using signal itself as a basis. The coefficients obtained during this decomposition are called intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) representing various frequency components. Different number of IMFs are combined with the residuals to create the data matrix (or mixed signals), which are fed to the ICA (extended efficient Fast-ICA and multi-combi ICA) for separating the independent components (ICs) due to their strength in separating the combination of various distribution signals. These extracted ICs (such as: thorax ECG, fECG, and noises etc.,) are subjected to FIR filtering to obtain the fECG and its corresponding heart rate (HR). This technique is validated on simulated signals for separation, prior to applying on fECG synthetic-data and aECG-data collected from PhysioBank ATM. The performance of ICA algorithm is evaluated by API.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Zaben, A., Al-Smadi, A.: Extraction of foetal ECG by combination of singular value decomposition and neuro-fuzzy inference system. Phys. Med. Biol. 51(1), 137–143 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/51/1/010
Anbalagan, T., Nath, M.K., Vijayalakshmi, D., Anbalagan, A.: Analysis of various techniques for ECG signal in healthcare, past, present, and future. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 6(1–28), 100,089 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bea.2023.100089
Assaleh, K.: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems for extracting fetal electrocardiogram, pp. 122–126. IEEE (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSPIT.2006.270782
Basak, P., et al.: A novel deep learning technique for morphology preserved fetal ECG extraction from mother ECG using 1D-CycleGAN. Expert Syst. Appl. 235, 1–17 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121196
Dhas, D.E., Suchetha, M.: Extraction of fetal ECG from abdominal and thorax ECG using a non-causal adaptive filter architecture. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circ. Syst. 16(5), 981–990 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2022.3204993
Gao, Y., Ge, G., Sheng, Z., Sang, E.: Analysis and solution to the mode mixing phenomenon in EMD. In: 2008 Congress on Image and Signal Processing, vol. 5, pp. 223–237 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/CISP.2008.193
Goldberger, A.L., et al.: PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circ. Electron. Pages 101(23), 215–220 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.23.e215
Gupta, V., Mittal, M.: A comparison of ECG signal pre-processing using FrFT, FrWT and IPCA for improved analysis. IRBM 40(3), 145–156 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irbm.2019.04.003
Gupta, V., Mittal, M., Mittal, V.: R-peak detection based chaos analysis of ECG signal. Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Process 102, 479–490 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01556-1
Hasan, M.A., Reaz, M.B.I.: Hardware prototyping of neural network based fetal electrocardiogram extraction. Meas. Sci. Rev. 12, 52–55 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/v10048-012-0007-8
Huang, N.E., et al.: The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. R. Soc. 454, 903–995 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1998.0193
James, C.J., Hesse, C.W.: Independent component analysis for biomedical signals. Physiol. Meas. 26(1), R15–R39 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0967-3334/26/1/R02
Jezewski, J., Matonia, A., Kupka, T., Roj, D., Czabanski, R.: Determination of the fetal heart rate from abdominal signals: evaluation of beat-to-beat accuracy in relation to the direct fetal electrocardiogram. Biomed. Eng./Biomedizinische Technik 57, 383–394 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1515/bmt-2011-0130
Jia, W., Yang, C., Zhong, G., Zhou, M., Wu, S.: Fetal ECG extraction based on adaptive linear neural network. IEEE 2, 899–902 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/BMEI.2010.5639886
Kanjilal, P.P., Saha, G.: Fetal ECG extraction from single channel maternal ECG using SVD and SVR spectrum. IEEE 1, 187–188 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.1995.575063
Koldovsky, Z., Tichavsky, P., Oja, E.: Efficient variant of algorithm FastICA for independent component analysis attaining the CramÉr-Rao lower bound. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 17, 1265–1277 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2006.875991
de Lathauwer, L., de Moor, B., Vandewalle, J.: Fetal electrocardiogram extraction by blind source subspace separation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 47(5), 567–572 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/10.841326
Martinek, R., et al.: Comparative effectiveness of ICA and PCA in extraction of fetal ECG from abdominal signals: Toward non-invasive fetal monitoring. Front. Physiol. 9, 1–25 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00648
Martín-Clemente, R., Olivares, J.L.C., Hornillo-Mellado, S., Elena, M., Román, I.: Fast technique for noninvasive fetal ECG extraction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58(2), 227–230 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2010.2059703
Mohebbian, M.R., Vedaei, S.S., Wahid, K.A., Dinh, A., Marateb, H.R., Tavakolian, K.: Fetal ECG extraction from maternal ECG using attention-based CycleGAN. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 26(2), 515–526 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2021.3111873
Naik, G.R., Kumar, D.K.: An overview of independent component analysis and its applications. Informatica (Slovenia) 35, 63–81 (2011). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:15353908
Nath, M.K., Sahambi, J.: Independent component analysis of functional MRI data. In: TENCON 2008–2008 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Hyderabad, India, pp. 1–6 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TENCON.2008.4766666
Sarafan, S., Le, T., Lau, M.P.H., Hameed, A., Ghirmai, T., Cao, H.: Fetal electrocardiogram extraction from the mother’s abdominal signal using the ensemble Kalman filter. Sensors (Basel) 22(7), 2788 (1–14) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/s22072788
Taralunga, D., Ungureanu, M., Strungaru, R., Wolf, W.: Performance comparison of four ICA algorithms applied for fECG extraction from transabdominal recordings. In: ISSCS 2011 - International Symposium on Signals, Circuits and Systems Proceedings, pp. 1–4 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSCS.2011.5978768
Tichavský, P., Koldovský, Z., Doron, E., Yeredor, A., Gómez-Herrero, G.: Blind signal separation by combining two ICA algorithms: HOS-based EFICA and time structure-based WASOBI. In: 14th European Signal Processing Conference, pp. 1–5 (2006). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:14611445
Wei, Z., Hongxing, L., Aijun, H., Xinbao, N., Jianchun, C.: Single-lead fetal electrocardiogram estimation by means of combining R-peak detection, resampling and comb filter. Med. Eng. Phys. 32(7), 708–719 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2010.04.012
Wei, Z., Hongxing, L., Jianchun, C.: Adaptive filtering in phase space for foetal electrocardiogram estimation from an abdominal electrocardiogram signal and a thoracic electrocardiogram signal. IET Signal Process. 6, 171–177 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-spr.2010.0263
Wei, Z., Xueyun, W., Jian, Z.J., Hongxing, L.: Noninvasive fetal ECG estimation using adaptive comb filter. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 112(1), 125–134 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.07.015
Widrow, B., et al.: Adaptive noise cancelling: principles and applications. Proc. IEEE 63(12), 1692–1716 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1975.10036
Wu, S., Shen, Y., Zhou, Z., Lin, L., Zeng, Y., Gao, X.: Research of fetal ECG extraction using wavelet analysis and adaptive filtering. Comput. Biol. Med. 43(10), 1622–1627 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2013.07.028
Wu, Z., Huang, N.E.: Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1(1), 1–41 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536909000047
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dash, S.S., Nath, M.K., Anbalagan, T. (2024). Identification of FECG from AECG Recordings using ICA over EMD. In: Su, R., Zhang, YD., Frangi, A.F. (eds) Proceedings of 2023 International Conference on Medical Imaging and Computer-Aided Diagnosis (MICAD 2023). MICAD 2023. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1166. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1335-6_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1335-6_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-1334-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-1335-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)