Abstract
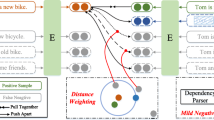
Contrastive Learning, a transformative approach to the embedding of unsupervised sentences, fundamentally works to amplify similarity within positive samples and suppress it amongst negative ones. However, an obscure issue associated with Contrastive Learning is the occurrence of False Negatives, which treat similar samples as negative samples that will hurt the semantics of the sentence embedding. To address it, we propose a framework called FNC (False Negative Calibration) to alleviate the influence of false negatives. Our approach has two strategies to amplify the effect, i.e. false negative elimination and reuse. Specifically, in the training process, our method eliminates false negatives by clustering and comparing the semantic similarity. Next, we reuse those eliminated false negatives to reconstruct new positive pairs to boost contrastive learning performance. Our experiments on seven semantic textual similarity tasks demonstrate that our approach is more effective than competitive baselines.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agirre, E., et al.: SemEval-2015 task 2: semantic textual similarity, English, Spanish and pilot on interpretability. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2015), pp. 252–263. Association for Computational Linguistics, Denver, Colorado (2015). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/S15-2045, https://aclanthology.org/S15-2045
Agirre, E., et al.: SemEval-2014 task 10: multilingual semantic textual similarity. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2014), pp. 81–91. Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland (2014). https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/S14-2010, https://aclanthology.org/S14-2010
Agirre, E., et al.: SemEval-2016 task 1: semantic textual similarity, monolingual and cross-lingual evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2016), pp. 497–511. Association for Computational Linguistics, San Diego, California (2016). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/S16-1081, https://aclanthology.org/S16-1081
Agirre, E., Cer, D., Diab, M., Gonzalez-Agirre, A.: SemEval-2012 task 6: a pilot on semantic textual similarity. In: *SEM 2012: The First Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics – Volume 1: Proceedings of the Main Conference and the Shared Task, and Volume 2: Proceedings of the Sixth International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2012), pp. 385–393. Association for Computational Linguistics, Montréal, Canada (2012). https://aclanthology.org/S12-1051
Agirre, E., Cer, D., Diab, M., Gonzalez-Agirre, A., Guo, W.: *SEM 2013 shared task: semantic textual similarity. In: Second Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics (*SEM), Volume 1: Proceedings of the Main Conference and the Shared Task: Semantic Textual Similarity, pp. 32–43. Association for Computational Linguistics, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (2013). https://aclanthology.org/S13-1004
Cer, D., Diab, M., Agirre, E., Lopez-Gazpio, I., Specia, L.: SemEval-2017 task 1: semantic textual similarity multilingual and crosslingual focused evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2017), pp. 1–14. Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, Canada (2017). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/S17-2001, https://aclanthology.org/S17-2001
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: III, H.D., Singh, A. (eds.) Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 119, pp. 1597–1607. PMLR (2020)
Chen, T.S., Hung, W.C., Tseng, H.Y., Chien, S.Y., Yang, M.H.: Incremental false negative detection for contrastive learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.03719 (2021)
Chuang, Y.S., et al.: DiffCSE: difference-based contrastive learning for sentence embeddings. In: Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL) (2022)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pp. 4171–4186. Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, Minnesota (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/N19-1423, https://aclanthology.org/N19-1423
Gao, T., Yao, X., Chen, D.: SimCSE: simple contrastive learning of sentence embeddings. In: Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) (2021)
Hadsell, R., Chopra, S., LeCun, Y.: Dimensionality reduction by learning an invariant mapping. In: 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2006), vol. 2, pp. 1735–1742 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2006.100
Jiang, T., et al.: PromptBERT: improving BERT sentence embeddings with prompts. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 8826–8837. Association for Computational Linguistics, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates (2022). https://aclanthology.org/2022.emnlp-main.603
Kiros, R., et al.: Skip-thought vectors. In: Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Lee, D., Sugiyama, M., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 28. Curran Associates, Inc. (2015). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2015/file/f442d33fa06832082290ad8544a8da27-Paper.pdf
Li, B., Zhou, H., He, J., Wang, M., Yang, Y., Li, L.: On the sentence embeddings from pre-trained language models. In: Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 9119–9130. Association for Computational Linguistics (2020). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-main.733, https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-main.733
Liu, Y., et al.: Roberta: a robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692 (2019)
Logeswaran, L., Lee, H.: An efficient framework for learning sentence representations. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2018). https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJvJXZb0W
Marelli, M., Menini, S., Baroni, M., Bentivogli, L., Bernardi, R., Zamparelli, R.: A SICK cure for the evaluation of compositional distributional semantic models. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2014), pp. 216–223. European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Reykjavik, Iceland (2014). http://www.lrec-conf.org/proceedings/lrec2014/pdf/$363_Paper$.pdf
Pennington, J., Socher, R., Manning, C.: GloVe: global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 1532–1543. Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar (2014). https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/D14-1162, https://aclanthology.org/D14-1162
Phan, X.H., Nguyen, L.M., Horiguchi, S.: Learning to classify short and sparse text & web with hidden topics from large-scale data collections. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on World Wide Web, pp. 91–100 (2008)
Reimers, N., Gurevych, I.: Sentence-BERT: sentence embeddings using Siamese BERT-networks. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pp. 3982–3992. Association for Computational Linguistics, Hong Kong, China (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D19-1410, https://aclanthology.org/D19-1410
Su, J., Cao, J., Liu, W., Ou, Y.: Whitening sentence representations for better semantics and faster retrieval. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.15316 (2021)
Williams, A., Nangia, N., Bowman, S.: A broad-coverage challenge corpus for sentence understanding through inference. In: Walker, M., Ji, H., Stent, A. (eds.) Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers), pp. 1112–1122. Association for Computational Linguistics, New Orleans, Louisiana (2018). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/N18-1101, https://aclanthology.org/N18-1101
Wu, Z., Wang, S., Gu, J., Khabsa, M., Sun, F., Ma, H.: Clear: contrastive learning for sentence representation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.15466 (2020)
Xu, J., et al.: Self-taught convolutional neural networks for short text clustering. Neural Networks 88, 22–31 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2016.12.008, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0893608016301976
Yan, Y., Li, R., Wang, S., Zhang, F., Wu, W., Xu, W.: ConSERT: a contrastive framework for self-supervised sentence representation transfer. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 5065–5075. Association for Computational Linguistics (2021). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.393, https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-long.393
Yin, J., Wang, J.: A model-based approach for text clustering with outlier detection. In: 2016 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), pp. 625–636 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2016.7498276
Zhang, D., et al.: Pairwise supervised contrastive learning of sentence representations. In: Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 5786–5798. Association for Computational Linguistics, Online and Punta Cana, Dominican Republic (2021). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.emnlp-main.467, https://aclanthology.org/2021.emnlp-main.467
Zhang, X., LeCun, Y.: Text understanding from scratch. arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.01710 (2015)
Zhou, K., Zhang, B., Zhao, W.X., Wen, J.R.: Debiased contrastive learning of unsupervised sentence representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.00656 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by Qualcomm through a Taiwan University Research Collaboration Project NAT-487842.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chiu, CM., Lin, YJ., Kao, HY. (2024). Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Sentence Embedding with False Negative Calibration. In: Yang, DN., Xie, X., Tseng, V.S., Pei, J., Huang, JW., Lin, J.CW. (eds) Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. PAKDD 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14647. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-2259-4_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-2259-4_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-2261-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-2259-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)