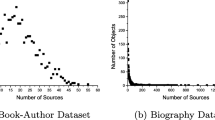
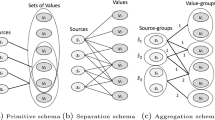
Abstract
In the era of big data, obtaining large amounts of data from different sources has become increasingly easy. However, conflicts may arise among the information provided by these sources. Therefore, various truth discovery methods have been proposed to solve this problem. In practical applications, information may be generated in chronological order, such as daily or hourly updates on weather conditions in a particular location. As a result, the truth of an object and the reliability of sources may dynamically change over time. Besides, there may be dependencies among data sources and the dependencies are stable in the short term. However, existing truth discovery methods for dynamic scenarios ignore the continuity of source dependencies in the short term. To address this issue, we study the source dependency detection and the problem of data sparsity caused by removing dependent sources in dynamic scenarios, and propose an incremental model based on source dependency detection, namely SDPTD, which can dynamically update object truth values and source weights and detect source dependencies when new data arrive. Experiments on two real-world datasets and synthetic datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong, X.L., Berti-Equille, L., Srivastava, D.: Integrating conflicting data: the role of source dependence. VLDB 2(1), 550–561 (2009)
Dong, X.L., Berti-Equille, L., Srivastava, D.: Truth discovery and copying detection in a dynamic world. VLDB 2(1), 562–573 (2009)
Galland, A., Abiteboul, S., Marian, A., Senellart, P.: Corroborating information from disagreeing views. In: WSDM, pp. 131–140 (2010)
Jiang, L., Niu, X., Xu, J., Yang, D., Xu, L.: Incentivizing the workers for truth discovery in crowdsourcing with copiers. In: ICDCS, pp. 1286–1295. IEEE (2019)
Li, Q., Li, Y., Gao, J., Zhao, B., Fan, W., Han, J.: Resolving conflicts in heterogeneous data by truth discovery and source reliability estimation. In: SIGMOD, pp. 1187–1198 (2014)
Li, T., Gu, Y., Zhou, X., Ma, Q., Yu, G.: An effective and efficient truth discovery framework over data streams. In: EDBT, pp. 180–191. Springer (2017)
Li, Y., et al.: A survey on truth discovery. In: SIGKDD, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 1–16 (2016)
Li, Y., et al.: On the discovery of evolving truth. In: SIGKDD, pp. 675–684 (2015)
Li, Y., Sun, H., Wang, W.H.: Towards fair truth discovery from biased crowdsourced answers. In: SIGKDD, pp. 599–607 (2020)
Ma, L., Tay, W.P., Xiao, G.: Iterative expectation maximization for reliable social sensing with information flows. Inf. Sci. 501, 621–634 (2019)
Pasternack, J., Roth, D.: Knowing what to believe (when you already know something). In: Coling 2010, pp. 877–885 (2010)
Wang, X., Sheng, Q.Z., Fang, X.S., Yao, L., Xu, X., Li, X.: An integrated Bayesian approach for effective multi-truth discovery. In: CIKM, pp. 493–502 (2015)
Wang, Y., Wang, K., Miao, C.: Truth discovery against strategic Sybil attack in crowdsourcing. In: SIGKDD, pp. 95–104 (2020)
Yang, J., Tay, W.P.: An unsupervised Bayesian neural network for truth discovery in social networks. TKDE 34(11), 5182–5195 (2021)
Yang, Y., Bai, Q., Liu, Q.: A probabilistic model for truth discovery with object correlations. KBS 165, 360–373 (2019)
Yao, L., et al.: Online truth discovery on time series data. In: SDM, pp. 162–170. SIAM (2018)
Yin, X., Han, J., Yu, P.S.: Truth discovery with multiple conflicting information providers on the web. In: SIGKDD, pp. 1048–1052 (2007)
Zhang, H., et al.: Influence-aware truth discovery. In: CIKM, pp. 851–860 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 23D111204, 22D111210), Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (No. 22YF1401100), and National Science Fund for Young Scholars (No. 62202095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fang, X., Shen, C., Sun, G., Chen, H., Tang, Y. (2024). Truth Discovery of Source Dependency Perception in Dynamic Scenarios. In: Song, X., Feng, R., Chen, Y., Li, J., Min, G. (eds) Web and Big Data. APWeb-WAIM 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14333. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-2387-4_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-2387-4_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-2386-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-2387-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)