Abstract
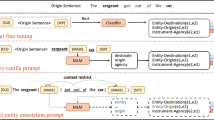
This study introduces a novel hybrid approach to text annotation that combines rule-based regular expressions with the pretrained neural network model DistilBERT. Given limited task-specific labeled data, regular expressions are first leveraged to efficiently annotate sentences, providing a cost-effective alternative to manual labeling. The annotated dataset then serves as training data for DistilBERT, enabling the model to learn nuanced linguistic patterns and improve upon the rule-based annotations. Results demonstrate that this pretraining strategy significantly enhances performance, achieving state-of-the-art models performance, notably those reliant solely on prompt engineering, such as the biggest large language model GPT-4. This study underscores the efficacy of integrating data-driven strategies with modern pretrained models, particularly for tasks where annotated data is scarce. The proposed method presents a promising direction for building robust and adaptable sentence annotation pipelines across diverse and resource-constrained natural language processing applications. By capitalizing on both manually crafted rules and learned representations, this hybrid approach can potentially generalize better compared to relying solely on either technique alone.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan, J., Ahmad, N., Khalid, S., Ali, F., Lee, Y.: Sentiment and context-aware hybrid DNN with attention for text sentiment classification. IEEE Access 11, 28162–28179 (2023)
Liu, C., Xu, X.: AMFF: a new attention-based multi-feature fusion method for intention recognition. Knowl.-Based Syst. 233, 107525 (2021)
Wagh, R., Punde, P.: Survey on sentiment analysis using Twitter dataset. In: 2018 Second International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), pp. 208–211. IEEE, March 2018
Li, Q., et al.: A survey on text classification: from traditional to deep learning. ACM Trans. Intell. Systems and Technology (TIST) 13(2), 1–41 (2022)
Meng, Y., et al.: Text classification using label names only: a language model self-training approach. Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 9006–9017 (2020)
Jánez-Martino, F., Fidalgo, E., Gonzá-Martínez, S., Velasco-Mata, J.: Classification of spam emails through hierarchical clustering and supervised learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.08773 (2020)
Sanh, V., Debut, L., Chaumond, J., Wolf, T.: DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.01108 (2019)
Shetty, J., Adibi, J.: The Enron email dataset database schema and brief statistical report. Inf. Sci. Inst. Tech. Rep. Univ. Southern Calif. 4(1), 120–128 (2004)
Neves, M., Ševa, J.: An extensive review of tools for manual annotation of documents. Brief. Bioinform. 22(1), 146–163 (2021)
van Gompel, M., Reynaert, M.: FoLiA: a practical XML format for linguistic annotation - a descriptive and comparative study. Comput. Linguist. Netherlands J. 3, 63–81 (2013)
Islamaj, R., Kwon, D., Kim, S., Lu, Z.: TeamTat: a collaborative text annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 48(W1), W5–W11 (2020)
Zhang, Z., Strubell, E., Hovy, E.: A survey of active learning for natural language processing. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 6166–6190 (2022)
Cejuela, J.M., et al.: tagtog: Interactive and text-mining-assisted annotation of gene mentions in PLOS full-text articles. Database, bau033 (2014)
Schroder, C., Niekler, A., Potthast, M.: Revisiting uncertainty-based query strategies for active learning with transformers. Findings Assoc. Comput. Linguist. (ACL), pp. 2194–2203 (2022)
Liu, X., et al.: Developing multi-labelled corpus of twitter short texts: a semi-automatic method. Systems 11(8), 390 (2023)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL) (2019)
Karim, A., Azam, S., Shanmugam, B., Kannoorpatti, K.: Efficient clustering of emails into spam and ham: the foundational study of a comprehensive unsupervised framework. IEEE Access 8, 154759–154788 (2020)
Wendy, W., Will Bridewell, C., Hanbury, P., Cooper, G.F., Buchanan, B.G.: A simple algorithm for identifying negated findings and diseases in discharge summaries. J. Biomed. Inform. 34(5), 301–310 (2001)
Smit, A., Jain, S., Rajpurkar, P., Pareek, A., Ng, A.Y., Lungren, M.P.: CheXBERT: combining automatic labelers and expert annotations for accurate radiology report labeling using BERT. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.09167 (2020)
Yogish, D., Manjunath, T.N., Hegadi, R.S.: Review on natural language processing trends and techniques using NLTK. In: Santosh, K.C., Hegadi, R.S. (eds.) RTIP2R 2018. CCIS, vol. 1037, pp. 589–606. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9187-3_53
Sbei, A., ElBedoui, K., Barhoumi, W., Maktouf, C.: Adaptive feature selection in PET scans based on shared information and multi-label learning. Vis. Comput. 1–21 (2022)
Hu, E.J., et al.: Lora: low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.09685 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sbei, A., ElBedoui, K., Barhoumi, W. (2024). Synergistic Text Annotation Based on Rule-Based Expressions and DistilBERT. In: Nguyen, N.T., et al. Intelligent Information and Database Systems. ACIIDS 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14796. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-4985-0_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-4985-0_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-4984-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-4985-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)