Abstract
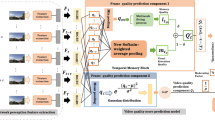
Due to the lack of reference videos and complex distortions, video quality assessment (VQA) for user-generated content (UGC) has become a highly challenging task. Previous studies have fully demonstrated the effectiveness of deep learning models in UGC VQA, but most methods only use a single CNN or Transformer to extract features, without fully integrating the advantages of them. In this paper, we propose a no-reference video quality assessment method based on Conformer, which utilizes convolutional neural networks and self-attention mechanisms in parallel to obtain features more suitable for UGC video quality. A Feature Attention (FA) module is further proposed to help the model focus on important parts of the video. The experimental results show that the proposed model achieves good performance on mainstream subjective UGC video quality databases, indicating the effectiveness on UGC VQA.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gulati, A., et al.: Conformer: convolution-augmented transformer for speech recognition. arXiv abs/2005.08100 (2020)
Feichtenhofer, C., et al.: SlowFast networks for video recognition. In: IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 6201–6210 (2018)
Korhonen, J.: Two-level approach for no-reference consumer video quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28, 5923–5938 (2019)
Tu, Z., et al.: UGC-VQA: benchmarking blind video quality assessment for user generated content. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 4449–4464 (2020)
Li, D., et al.: Quality assessment of in-the-wild videos. In: ACM International Conference on Multimedia (2019)
Sun, W., et al.: A deep learning based no-reference quality assessment model for UGC videos. In: ACM International Conference on Multimedia (2022)
Wu, H., et al.: DisCoVQA: temporal distortion-content transformers for video quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33, 4840–4854 (2022)
Wu, H., et al.: FAST-VQA: efficient end-to-end video quality assessment with fragment sampling. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13666, pp. 538–554. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20068-7_31
Li, J., et al.: SCConv: spatial and channel reconstruction convolution for feature redundancy. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6153–6162 (2023)
Ying, Z., et al.: Patch-VQ: ‘patching up’ the video quality problem. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 14014–14024 (2020)
Hosu, V., et al.: The Konstanz natural video database (KoNViD-1k). In: Ninth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), pp. 1–6 (2017)
Sinno, Z., Bovik, A.C.: Large-scale study of perceptual video quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28, 612–627 (2018)
Min, X., et al.: Perceptual video quality assessment: a survey. arXiv abs/2402.03413 (2024)
Mittal, A., et al.: No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21, 4695–4708 (2012)
Lin, T.Y., et al.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 740–755. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Kay, W., et al.: The kinetics human action video dataset. arXiv abs/1705.06950 (2017)
Zhang, Z., et al.: MD-VQA: multi-dimensional quality assessment for UGC live videos. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1746–1755 (2023)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yang, Z., Zhang, Y., Si, Z. (2024). Conformer Based No-Reference Quality Assessment for UGC Video. In: Huang, DS., Si, Z., Guo, J. (eds) Advanced Intelligent Computing Technology and Applications. ICIC 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14867. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-5597-4_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-5597-4_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-5596-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-5597-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)