Abstract
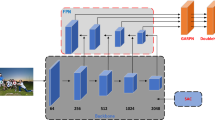
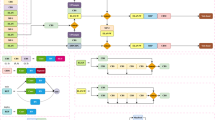
Complex backgrounds, scale and occlusion variance have long limited the accuracy of pedestrian detection. In this paper, we propose a pedestrian detector named Convergence and Divergence (CADNet). In “Convergence” network, we propose a cross-scale semantic alignment block (CSAB). CSAB effectively mitigates the background interference and resolves scale variance through multi-scale global contexts aggregation, without extensive computational overhead. In “Divergence” network, we propose a receptive field differentiation block (RFDB) to tackle the challenges of scale and occlusion variance. RFDB generates discriminative features with varying receptive fields, effectively capturing pedestrians across different scales and occlusion conditions. Due to the effectiveness of the proposed components, CADNet achieves an excellent performance of 8.47% and 2.16% MR−2 on a Reasonable subset of CityPersons and Caltech, respectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate the robustness and efficiency of CADNet, ensuring its superior performance in various scenarios.
Y. Zhu, H. Huang and S. Yue—Contribute equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, C.F.R., Fan, Q., Panda, R.: Crossvit: cross-attention multi-scale vision transformer for image classification. In: ICCV, pp. 347–356 (2021)
Chen, W., et al.: Beyond appearance: a semantic controllable self-supervised learning frame work for human-centric visual tasks. In: CVPR, pp. 15050–15061 (2023)
Dollár, P., Wojek, C., Schiele, B., et al.: Pedestrian detection: an evaluation of the state of the art. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(4), 743–761 (2012)
Hsu, W.Y., Chen, P.C.: Pedestrian detection using stationary wavelet dilated residual super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71, 1–11 (2022)
Huang, Z., et al.: Ccnet: criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In: ICCV, pp. 603–612 (2019)
Jiang, H., Liao, S., Li, J., et al.: Urban scene based semantical modulation for pedestrian detection. Neurocomputing 474, 1–12 (2022)
Li, C., Zhou, A., Yao, A.: Omni-dimensional dynamic convolution. In: ICLR (2022)
Li, J., et al.: Box guided convolution for pedestrian detection. In: ACM MM, pp. 1615–1624 (2020)
Li, Q., Su, Y., Gao, Y., et al.: Oaf-net: an occlusion-aware anchor-free network for pedestrian detection in a crowd. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23(11), 21291–21300 (2022)
Li, X., et al.: Selective kernel networks. In: CVPR, pp. 510–519 (2019)
Liu, M., et al.: Vlpd: context-aware pedestrian detection via vision-language semantic self-supervision. In: CVPR, pp. 6662–6671 (2023)
Liu, S., Huang, D., Wang, Y.: Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11215, pp. 404–419. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01252-6_24
Liu, W., Liao, S., Weidong, H., Liang, X., Chen, X.: Learning efficient single-stage pedestrian detectors by asymptotic localization fitting. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018: 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, September 8–14, 2018, Proceedings, Part XIV, pp. 643–659. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_38
Liu, W., et al.: High-level semantic feature detection: a new perspective for pedestrian detection. In: CVPR, pp. 5182–5191 (2019)
Mei, Y., et al.: Image super-resolution with cross-scale non-local attention and exhaustive self-exemplars mining. In: CVPR, pp. 5689–5698 (2020)
Song, T., Sun, L., Xie, D., Sun, H., Shiliang, P.: Small-Scale Pedestrian Detection Based on Topological Line Localization and Temporal Feature Aggregation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018: 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, September 8–14, 2018, Proceedings, Part VII, pp. 554–569. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_33
Tan, Y., et al.: Prf-ped: multi-scale pedestrian detector with prior-based receptive field. In: ICPR, pp. 6059–6064 (2020)
Wang, J., Sun, K., Cheng, T., et al.: Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43, 3349–3364 (2021)
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: CVPR, pp. 7794–7803 (2018)
Yuan, J., Panagiotis, B., Stathaki, T.: Effectiveness of vision transformer for fast and accurate single-stage pedestrian detection. In: NIPS. (2022)
Zhang, J., Lin, L., Zhu, J., et al.: Attribute-aware pedestrian detection in a crowd. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 23, 3085–3097 (2021)
Zhang, S., Benenson, R., Schiele, B.: Citypersons: a diverse dataset for pedestrian detection. In: CVPR, pp. 4457–4465 (2017)
Zhang, S., Wen, L., Bian, X., Lei, Z., Li, S.Z.: Occlusion-aware R-CNN: detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018: 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, September 8–14, 2018, Proceedings, Part III, pp. 657–674. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_39
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant 2022YFF0904300.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhu, Y., Huang, H., Yue, S., Zhang, S., Chen, A. (2024). Convergence and Divergence: A New Paradigm for Pedestrian Detection. In: Huang, DS., Zhang, C., Zhang, Q. (eds) Advanced Intelligent Computing Technology and Applications. ICIC 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14868. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-5600-1_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-5600-1_36
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-5599-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-5600-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)