Abstract
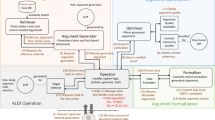
This paper delves into the application of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of legal task processing with a specific focus on the emerging capabilities these models have demonstrated in complex reasoning and zero-shot learning (ZSL). By introducing a multi-intelligence framework based on Large Scale Legal Language Modeling, the research aims to improve the efficiency and performance of the models across a wide range of functions including legal review, consultation, and judicial decision-making. The framework utilizes function-specific legal chains of thoughts and specialized agents to guide the LLMs to handle legal tasks, optimize response behaviors, and enhance reasoning capabilities. The study also incorporates an information retrieval module to address the common hallucination problem of LLMs, thereby improving response reliability and enhancing the model's ability to tackle complex legal issues. The evaluation of the LegalGPT model shows that it indeed outperforms the existing legal LLMs in terms of accuracy, completeness, and linguistic quality in several Chinese legal domains.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, T., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 1877–1901 (2020)
Black, S., et al.: GPT-NeoX-20B: an open-source autoregressive language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.06745 (2022)
Zhang, S., et al.: OPT: open pre-trained transformer Language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.01068 (2022)
Smith, S., et al.: Using deepspeed and megatron to train megatron-turing NLG 530b, a large-scale generative language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.11990 (2022)
OpenAI: GPT-4 Technical report. arXiv abs/2303.08774 (2023)
Penedo, G., et al.: The RefinedWeb dataset for Falcon LLM: outperforming curated corpora with web data, and web data only. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.01116 (2023)
Anil, R., et al.: PaLM 2 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10403 (2023)
Araci, D.: FinBERT: financial sentiment analysis with pre-trained language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.10063 (2019)
Huang, K., Altosaar, J., Ranganath, R.: ClinicalBERT: modeling clinical notes and predicting hospital readmission. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.05342 (2019)
Wu, S., et al.: BloombergGPT: a large language model for finance. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17564 (2023)
Driess, D., et al.: PaLM-E: an embodied multimodal language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.03378 (2023)
Huang, S., et al.: Instruct2ACT: mapping multi-modality instructions to robotic actions with large language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11176 (2023)
Wei, J., et al.: Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 24824–24837 (2022)
Wang, X., et al.: Self-consistency improves chain of thought reasoning in language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.11171 (2022)
Kıcıman, E., et al.: Causal reasoning and large language models: opening a new frontier for causality. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.00050 (2023)
Kojima, T., et al.: Large language models are zero-shot reasoners. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 22199–22213 (2022)
Wan, X., et al.: Better zero-shot reasoning with self-adaptive prompting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14106 (2023)
Yao, S., et al.: ReAct: synergizing reasoning and acting in language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.03629 (2022)
Shinn, N., et al.: Reflexion: language agents with verbal reinforcement learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 36 (2024)
Park, J.S., et al.: Generative agents: interactive simulacra of human behavior. In: Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (2023)
Wang, L., et al.: A survey on large language model based autonomous agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.11432 (2023)
Xi, Z., et al.: The rise and potential of large language model based agents: a survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07864 (2023)
Wang, L., et al.: Plan-and-solve prompting: improving zero-shot chain-of-thought reasoning by large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.04091 (2023)
Liu, P., et al.: Pre-train, prompt, and predict: a systematic survey of prompting methods in natural language processing. ACM Comput. Surv. 55(9), 1–35 (2023)
Sartor, G.: Legal reasoning. Treatise Legal Philos. Gen. Jurisprud. 5 (2005)
Jansen, B.J., et al.: The illusion of data validity: why numbers about people are likely wrong. Data Inf. Manage. 6(4), 100020 (2022)
Chen, J., et al.: S-Agents: self-organizing agents in open-ended environment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.04578 (2024)
Zhuge, M., et al.: Mindstorms in natural language-based societies of mind. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17066 (2023)
Hao, R., et al.: ChatLLM network: More brains, more intelligence. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.12998 (2023)
Liu, R., et al.: Training socially aligned language models in simulated human society. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16960 (2023)
Cai, T., et al.: Large language models as tool makers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17126 (2023)
Yu, F., Quartey, L., Schilder, F.: Legal prompting: teaching a language model to think like a lawyer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.01326 (2022)
Jiang, C., Yang, X.: Legal syllogism prompting: teaching large language models for legal judgment prediction. In: Proceedings of the Nineteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Law (2023)
Zhong, H., et al.: JEC-QA: a legal-domain question answering dataset. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2020)
Duan, X., et al.: CJRC: a reliable human-annotated benchmark dataset for chinese judicial reading comprehension. In: Sun, M., HUANG, X., Ji, H., Liu, Z., Liu, Y. (eds.) CCL 111112019. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 11856, pp. 439–451. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32381-3_36
Huang, Q., et al.: Lawyer llama technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15062 (2023)
Nguyen, H.-T.: A brief report on lawGPT 1.0: a virtual legal assistant based on GPT-3. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.05729 (2023)
Hassanzadeh, T., Meybodi, M.R.: A new hybrid approach for data clustering using firefly algorithm and K-means. In: Proceedings of the 16th CSI International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence and Signal Processing (AISP 2012). IEEE (2012)
Yue, S., et al.: DISC-LawLLM: fine-tuning large language models for intelligent legal services. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.11325 (2023)
Lu, J., et al.: Ziya-VL: bilingual large vision-language model via multi-task instruction tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.08166 (2023)
Du, Z., et al.: GLM: general language model pretraining with autoregressive blank infilling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.10360 (2021)
Yang, A., et al.: Baichuan 2: open large-scale language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.10305 (2023)
Dai, Y., et al.: LAiW: a Chinese legal large language models benchmark (a technical report). arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.05620 (2023)
Cui, J., et al.: ChatLaw: open-source legal large language model with integrated external knowledge bases. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.16092 (2023)
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFC3300500); This work is also supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant U20B2047, U20B2053, U19B2044.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shi, J., Guo, Q., Liao, Y., Liang, S. (2024). LegalGPT: Legal Chain of Thought for the Legal Large Language Model Multi-agent Framework. In: Huang, DS., Si, Z., Chen, W. (eds) Advanced Intelligent Computing Technology and Applications. ICIC 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14880. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-5678-0_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-5678-0_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-5677-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-5678-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)