Abstract
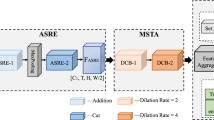
Gait recognition plays a crucial role in long-distance, unconstrained identity verification. Silhouette-based methods are widely recognized for their accuracy but often utilize single-stage temporal compression techniques, such as global pooling, to condense sequence temporal information into fixed-length features. However, this approach restricts their ability to fully capture the dynamic temporal characteristics inherent in gait sequences. To address this, we introduce SF-Gait, a novel framework employing two-stage compression-leveraging a 3D CNN for micro-motion and a 2D CNN for gait cycle features. It then anchors dense short-term micro-motion features to representative 2D contour features, forming sparse sequences as the initial stage of temporal compression. A subsequent global temporal pooling method, akin to other approaches, serves as the second stage of compression, thereby yielding more representative temporal features. Our Spatio-Temporal Downsampling (ST-D) and Dual-stream Fusion Encoder (DFE) enhance gait modeling capabilities, achieving state-of-the-art performance on CASIA-B, OU-MVLP, and Gait3D datasets.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant 62371350 and 62171324.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benedek, C., Gálai, B., Nagy, B., Jankó, Z.: Lidar-based gait analysis and activity recognition in a 4d surveillance system. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol. 28(1), 101–113 (2016)
Chao, H., He, Y., Zhang, J., Feng, J.: Gaitset: regarding gait as a set for cross-view gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 8126–8133 (2019)
Del Din, S., Elshehabi, M., Galna, B., Hobert, M.A., Warmerdam, E., Suenkel, U., Brockmann, K., Metzger, F., Hansen, C., Berg, D., et al.: Gait analysis with wearables predicts conversion to Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 86(3), 357–367 (2019)
Dou, H., Zhang, P., Su, W., Yu, Y., Li, X.: Metagait: learning to learn an Omni sample adaptive representation for gait recognition. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 357–374. Springer (2022)
Dou, H., Zhang, P., Su, W., Yu, Y., Lin, Y., Li, X.: Gaitgci: generative counterfactual intervention for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5578–5588 (2023)
Fan, C., Hou, S., Huang, Y., Yu, S.: Exploring deep models for practical gait recognition (2023). arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.03301
Fan, C., Liang, J., Shen, C., Hou, S., Huang, Y., Yu, S.: Opengait: revisiting gait recognition towards better practicality. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9707–9716 (2023)
Fan, C., Peng, Y., Cao, C., Liu, X., Hou, S., Chi, J., Huang, Y., Li, Q., He, Z.: Gaitpart: temporal part-based model for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14225–14233 (2020)
Feichtenhofer, C., Fan, H., Malik, J., He, K.: Slowfast networks for video recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6202–6211 (2019)
Gálai, B., Benedek, C.: Feature selection for Lidar-based gait recognition. In: 2015 International Workshop on Computational Intelligence for Multimedia Understanding (IWCIM), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2015)
Gupta, J.P., Singh, N., Dixit, P., Semwal, V.B., Dubey, S.R.: Human activity recognition using gait pattern. Int. J. Comput. Vis. Image Process. (IJCVIP) 3(3), 31–53 (2013)
Han, J., Bhanu, B.: Individual recognition using gait energy image. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(2), 316–322 (2005)
Hou, S., Cao, C., Liu, X., Huang, Y.: Gait lateral network: learning discriminative and compact representations for gait recognition. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 382–398. Springer (2020)
Huang, X., Zhu, D., Wang, H., Wang, X., Yang, B., He, B., Liu, W., Feng, B.: Context-sensitive temporal feature learning for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 12909–12918 (2021)
Huang, Z., Xue, D., Shen, X., Tian, X., Li, H., Huang, J., Hua, X.S.: 3d local convolutional neural networks for gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 14920–14929 (2021)
Islam, M.A., Jia, S., Bruce, N.D.: How much position information do convolutional neural networks encode? In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2019)
Lin, B., Zhang, S., Yu, X.: Gait recognition via effective global-local feature representation and local temporal aggregation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 14648–14656 (2021)
Liu, R., Lehman, J., Molino, P., Petroski Such, F., Frank, E., Sergeev, A., Yosinski, J.: An intriguing failing of convolutional neural networks and the coordconv solution. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 31 (2018)
Luo, H., Gu, Y., Liao, X., Lai, S., Jiang, W.: Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 0–0 (2019)
Radenović, F., Tolias, G., Chum, O.: Fine-tuning CNN image retrieval with no human annotation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(7), 1655–1668 (2018)
Takemura, N., Makihara, Y., Muramatsu, D., Echigo, T., Yagi, Y.: Multi-view large population gait dataset and its performance evaluation for cross-view gait recognition. IPSJ Trans. Comput. Vis. Appl. 10, 1–14 (2018)
Teepe, T., Gilg, J., Herzog, F., Hörmann, S., Rigoll, G.: Towards a deeper understanding of skeleton-based gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1569–1577 (2022)
Teepe, T., Khan, A., Gilg, J., Herzog, F., Hörmann, S., Rigoll, G.: Gaitgraph: Graph convolutional network for skeleton-based gait recognition. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2314–2318. IEEE (2021)
Wang, L., Liu, B., Liang, F., Wang, B.: Hierarchical spatio-temporal representation learning for gait recognition. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 19582–19592. IEEE (2023)
Wang, M., Guo, X., Lin, B., Yang, T., Zhu, Z., Li, L., Zhang, S., Yu, X.: DyGait: exploiting dynamic representations for high-performance gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13424–13433 (2023)
Wang, W., Liu, A.X., Shahzad, M.: Gait recognition using WiFi signals. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 363–373 (2016)
Wolf, T., Babaee, M., Rigoll, G.: Multi-view gait recognition using 3d convolutional neural networks. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 4165–4169. IEEE (2016)
Yan, S., Xiong, Y., Lin, D.: Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32 (2018)
Ye, M., Shen, J., Lin, G., Xiang, T., Shao, L., Hoi, S.C.: Deep learning for person re-identification: a survey and outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(6), 2872–2893 (2021)
Yu, S., Tan, D., Tan, T.: A framework for evaluating the effect of view angle, clothing and carrying condition on gait recognition. In: 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), vol. 4, pp. 441–444. IEEE (2006)
Yue, Y., Zou, Q., Yu, H., Wang, Q., Wang, Z., Wang, S.: An end-to-end network for co-saliency detection in one single image. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 66(11), 210101 (2023)
Zheng, J., Liu, X., Liu, W., He, L., Yan, C., Mei, T.: Gait recognition in the wild with dense 3d representations and a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 20228–20237 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yue, Y., Wang, Y., Shi, L., Wang, Z., Zou, Q. (2025). SF-Gait: Two-Stage Temporal Compression Network for Learning Gait Micro-Motions and Cycle Patterns. In: Lin, Z., et al. Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. PRCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15045. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-8499-8_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-8499-8_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-8498-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-8499-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)