Abstract
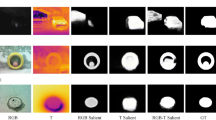
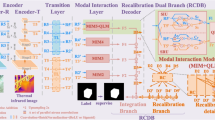
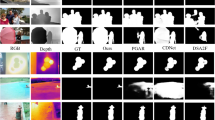
RGB-Thermal Salient Object Detection(SOD) aims to identify common salient regions or objects from both the visible and thermal infrared modalities. Existing methods usually based on the hierarchical interactions within the same modality or between different modalities at the same level. However, this approach may lead to a situation where one modality or one level of features dominates the fusion result during the fusion process, failing to fully utilize the complementary information of the two modalities. Additionally, these methods usually overlooking the potential for the network to extract specific information in each modality. To address these issues, we propose a Bidirectional Alternating Fusion Network (BAFNet) consisting of three modules for RGB-T salient object detection. In particular, we design a Global Information Enhancement Module(GIEM) for improving the information representation of high-level features. Then we propose a novel bidirectional alternating fusion strategy which is applied during decoding, and we design a Multi-modal Multi-level Fusion Module(MMFM) for collaborating mulit-modal mulit-level information. Furthermore, we embed the proposed Modal Erase Module (MEM) into both GIEM and MMFM to extract the inherent specific information in each modality. Our extensive experiments on three public benchmark datasets show that our method achieves outstanding performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
This work was supported by the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province under Grant No.GXXT-2022-014, in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.62376005.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, E., Zhou, W., Qian X.: MGCNet: multilevel gated collaborative network for RGB-D semantic segmentation of indoor scene. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 29, 2567–2571 (2022)
Xu, J., Xiong, Z.: PIDNet: a real-time semantic segmentation network inspired by PID controllers. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 19529–19539
Ying, X., Chuah., M.C.: UCTNet: uncertainty-aware cross-modal transformer network for indoor RGB-D semantic segmentation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, vol. 13690. Springer, Heidelberg (2022). ISBN:978-3-031-20055-7
Xinyi, W., Yuan, X.: RGB-D road segmentation based on geometric prior information. In: Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision: 6th Chinese Conference, PRCV,: Xiamen, China, 13–15 Oct 2023, Proceedings, Part I. Springer, Heidelberg, pp. 434–445 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8429-935
Xiao, Y., Yang, M.: Attribute-based progressive fusion network for RGBT tracking. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 2831–2838. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v36i3.20187
Tang, Z., Xu, T.: Exploring fusion strategies for accurate RGBT visual object tracking. Inf. Fusion 99, 101881 (2023). ISSN:1566-2535
Loghmani, M.R., Robbiano, L.: Unsupervised domain adaptation through inter-modal rotation for RGB-D object recognition. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5(4), 6631–6638 (2020). Oct
Song, Z., Qin, P.: EdgeFusion: infrared and visible image fusion algorithm in low light. In: Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision: 6th Chinese Conference, PRCV,: Xiamen, China, 13–15 Oct 2023, Proceedings, pp. 259–270. Part I. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg (2023)
Jiang, S., Xu, Y.: Multi-scale fusion for RGB-D indoor semantic segmentation. Sci. Rep. 20305, 2045–2322 (2022)
Zhang, T., Li, H.: MGT: modality-guided transformer for infrared and visible image fusion. In: Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision: 6th Chinese Conference, PRCV,: Xiamen, China, 13–15 Oct 2023, Proceedings, Part I. Springer, Heidelberg, pp. 321–332 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8429-926
Wang, C., Xu, C.: Cross-modal pattern-propagation for RGB-T tracking. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, pp. 7062–7071 (2020)
Wang, D., Liu, J.: An interactively reinforced paradigm for joint infrared-visible image fusion and saliency object detection. Inf. Fusion 98, 101828 (2023). (Elsevier)
Lee, M., Park, C.: SPSN: superpixel prototype sampling network for rgb-d salient object detection. In: Computer Vision-ECCV: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 Oct 2022, Proceedings, pp. 630–647. Part XXIX. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg (2022)
Fushuo, H., Xuegui, Z.: Efficient context-guided stacked refinement network for RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(5), 3111–3124 (2022). May
Wang, Y., Dong, F.: Interactive context-aware network for RGB-T salient object detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 1–22 (2024). (Springer)
Ma, S., Song, K.: Modal complementary fusion network for RGB-T salient object detection. Appl. Intell. 53(8), 9038–9055 (2023). (Springer)
Wujie, Z., Qinling, G.: ECFFNet: effective and consistent feature fusion network for RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(3), 1224–1235 (2022). March
Guibiao, L., Wei, G.: Cross-collaborative fusion-encoder network for robust RGB-thermal salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(11), 7646–7661 (2022). Nov.
Wang, J., Song, K.: CGFNet: cross-guided fusion network for RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(5), 2949–2961 (2022). May
Tu, Z., Li, Z.: Multi-interactive dual-decoder for RGB-thermal salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 5678–5691 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3087412
Hou, R., Chang, H.: Temporal complementary learning for video person re-identification. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 Aug 2020, Proceedings, Part XXV 16, pp. 388–405. Springer (2020)
Zhao, X., Pang, Y.: Suppress and balance: a simple gated network for salient object detection. In: Computer Vision-ECCV,: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, pp. 35–51. Part II. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg (2020)
Tian, X., Zhang, J.: Modeling the distributional uncertainty for salient object detection models. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2023, pp. 19660–19670 (2023)
Pang, Y., Zhao, X.: Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 2020, pp. 9410–9419 (2020)
Wu, Z., Wang, L.: Pixel is all you need: adversarial trajectory-ensemble active learning for salient object detection. In: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 2883–2891 (2023)
Liu, J.-J., Hou, Q.: PoolNet+: exploring the potential of pooling for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(1), 887–904 (1 Jan 2023)
Ma, M., Xia, C.: Boosting broader receptive fields for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 32, 1026–1038 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3232209
Tu, Z., Xia, T.: RGB-T image saliency detection via collaborative graph learning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 22(1), 160–173 (Jan 2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2019.2924578
Gao, W., Liao, G.: Unified information fusion network for multi-modal RGB-D and RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(4), 2091–2106 (April 2022)
Tu, Z., Ma, Y.: RGBT salient object detection: a large-scale dataset and benchmark. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 25, pp. 4163–4176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3171688
Dai, J., Qi, H.: Deformable convolutional networks. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 764–773
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N.: Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’17). Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook, NY, USA, pp. 6000–6010
Tolstikhin, I.O., Houlsby, N.: Mlp-mixer: an all-mlp architecture for vision. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 24261–24272 (2021)
Nair, V., Hinton, G.E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), pp. 807–814 (2010)
Godard, C, Mac Aodha, O.: Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6602–6611
Milletari, F.: V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 2016, pp. 565–571 (2016)
Tang, J., Fan, D.: RGBT Salient Object Detection: Benchmark and A Novel Cooperative Ranking Approach, vol. 30, no. 12, pp. 4421–4433 (2020)
Liu, Z., Tan, Y.: SwinNet: swin transformer drives edge-aware RGB-D and RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(7), 4486–4497 (2022)
Huo, F., Zhu, X.: Real-time one-stream semantic-guided refinement network for RGB-thermal salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71, 1–12 (2022)
Cong, R., Zhang, K.: Does thermal really always matter for RGB-T salient object detection? IEEE Trans. Multimed. 25, 6971–6982 (2023)
Tu, Z., Li, Z.: Weakly alignment-free RGBT salient object detection with deep correlation network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 3752–3764 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3176540
Zhou, W., Zhu, Y.: LSNet: lightweight spatial boosting network for detecting salient objects in RGB-thermal images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 32, 1329–1340 (2023)
Tang, B, Liu, Z.: HRTransNet: HRFormer-driven two-modality salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33(2), 728–742 (2023)
Pang, Y., Zhao, X.: CAVER: cross-modal view-mixed transformer for bi-modal salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 32, 892–904 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2023.3234702
Liu, Z, Lin, Y.: Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 9992–10002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986
Wang, X., Girshick, R.: Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7794–7803 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tu, Z., Lin, D., Jiang, B., Gu, L., Wang, K., Zhai, S. (2025). Bidirectional Alternating Fusion Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. In: Lin, Z., et al. Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. PRCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15038. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-8685-5_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-8685-5_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-8684-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-8685-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)