Abstract
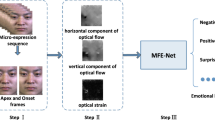
Micro-expression is usually generated by subtle movements of facial muscles when people control their true emotions. Micro-expression recognition aims to help people understand micro-expression by feature extraction and representation. However, most existing methods only use motion information or RGB image information to extract features, which ignore the feature fusion between these two types of information. To address this issue, we propose a novel fusion network based on motion learning and image feature representation with a hierarchical structure, including three components: a motion learning stream, an image feature representation stream and a heterogeneous information fusion mechanism. Firstly, the motion learning stream extracts multi-scale facial muscle motion features associated with micro-expression from inter-frame motion information. Secondly, the image feature representation stream divides the apex image into four parts based on the intensity of muscle movement and gradually extracts the local and global facial detail and semantic features. Finally, the heterogeneous information fusion mechanism is proposed to perform information interaction between motion features and image features and to integrate categorical information. Specifically, the cross-fusion module is designed to fuse features extracted from the two streams to produce a more comprehensive, richer representation where image features and motion features influence and enhance each other. The result integration strategy considers the results of the two streams as the classification result of the model, further integrating different feature information. Extensive experiments conducted on spontaneous micro-expression datasets show that the proposed model achieves the best performance compared with the existing state-of-the-art methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekman, P., Friesen, W.: Constants across cultures in the face and emotion. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 17(2), 124–129 (1971)
Li, X., Yi, X., Ye, J., et al.: SFTNet: a microexpression-based method for depression detection. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 243, 107923 (2024)
Ekman, P.: Lie catching and microexpressions. Philos. Deception 1(2), 118–136 (2009)
Zhao, G., Pietikainen, M.: Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(6), 915–928 (2007)
Liong, S.T., See, J., Wong, K., et al.: Less is more: Micro-expression recognition from video using apex frame. Signal Process. Image Commun. 62, 82–92 (2018)
Gan, Y.S., Liong, S.T., Yau, W., et al.: OFF-ApexNet on micro-expression recognition system. Signal Process. Image Commun. 74, 129–139 (2019)
Liong, S.T., Gan, Y.S., See, J., et al.: Shallow triple stream three-dimensional CNN (STSTNet) for micro-expression recognition. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (2019)
Zhou, L., Mao, Q., Xue, L., et al.: Feature refinement: an expression-specific feature learning and fusion method for micro-expression recognition. Pattern Recogn. 122, 108275 (2022)
Quang, N.V., Chun, J., Tokuyama, T.: CapsuleNet for micro-expression recognition. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (2019)
Wei, M., Zheng, W., Zong, Y., et al.: A novel micro-expression recognition approach using attention-based magnification-adaptive networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 2420–2424 (2022)
Pan, H., Yang, H., Xie, L., et al.: Multi-scale fusion visual attention network for facial micro-expression recognition. Front. Neurosci. 17, 1–11 (2023)
Zhai, Z., Zhao, J., Long, C., et al.: Feature representation learning with adaptive displacement generation and transformer fusion for micro-expression recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 22086–22095 (2023)
Wang, Y., See, J., Phan, R.C.W., et al.: LBP with six intersection points: Reducing redundant information in LBP-TOP for micro-expression recognition. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 525–537 (2014)
Li, X., Hong, X., Moilanen, A., et al.: Towards reading hidden emotions: a comparative study of spontaneous micro-expression spotting and recognition methods. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 9(4), 563–577 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Jiang, H., Li, W., et al.: A new framework combining local-region division and feature selection for micro-expressions recognition. IEEE Access. 8, 94499–94509 (2020)
Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Yan, W., et al.: A main directional mean optical flow feature for spontaneous micro-expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 7(4), 299–310 (2015)
Zhou, L., Mao, Q., Xue, L.: Dual-inception network for cross-database micro-expression recognition. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (2019)
Zhou, H., Huang, S., Li, J., et al.: Dual-atme: dual-branch attention network for micro-expression recognition. Entropy 25(3), 460 (2023)
Zhou, H., Huang, S., Xu, Y.: Inceptr: micro-expression recognition integrating inception-CBAM and vision transformer. Multimedia Syst. 29(6), 3863–3876 (2023)
Wang, Z., Zhang, K., Luo, W., et al.: HTNet for micro-expression recognition. arXiv 2023. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.14637 (2023)
Khor, H.Q., See, J., Phan, R.C.W., et al.: Enriched long-term recurrent convolutional network for facial micro-expression recognition. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, pp. 667–674 (2018)
Li, H., Sui, M., Zhu, Z., et al.: MMNet: Muscle motion-guided network for micro-expression recognition. arXiv 2022. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.05297 (2022)
Liong, S.T., See, J., Wong, K., et al.: Automatic apex frame spotting in micro-expression database. In: 2015 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 665–669 (2015)
Li, X., Pfister, T., Huang, X., et al.: A spontaneous micro-expression database: Inducement, collection and baseline. In: 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 1–6 (2013)
Chang, C., Zhong, Z., Liou, J.: A fpga implementation of farneback optical flow by high-level synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 2019 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, p. 309 (2019)
Jose, E., Greeshma, M., Haridas, M.T., et al.: Face recognition based surveillance system using facenet and mtcnn on jetson tx2. In: 2019 5th International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Systems, pp. 608–613 (2019)
Zheng, C., Matias, M., Chen, C.: POSTER: A pyramid cross-fusion transformer network for facial expression recognition. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp. 3138–3147 (2023)
Duan, S., Dadashzadeh, A., Whone, A., et al.: QAFE-Net: Quality Assessment of Facial Expressions with Landmark Heatmaps. arXiv 2023. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.00856 (2023)
See, J., Yap, M.H., Li, J., et al.: MEGC 2019 - The second facial micro-expressions grand challenge. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (2019)
Davison, A.K., Lansley, C., Costen, N., et al.: Samm: a spontaneous micro-facial movement dataset. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 9(1), 116–129 (2016)
Yan, W., Li, X., Wang, S.J., et al.: CASME II: An improved spontaneous micro-expression database and the baseline evaluation. PLoS ONE 9(1), e86041 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Colleges and Universities Twenty Terms Foundation of Jinan City (No.2021GXRC100), the Talent Research Projects in Schools (Institutions) (No. 2023RCKY249).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, X., Zhang, M., Li, B. (2025). Fusion Network Based on Motion Learning and Image Feature Representation for Micro-Expression Recognition. In: Lin, Z., et al. Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. PRCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15041. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-8795-1_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-8795-1_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-8794-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-8795-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)