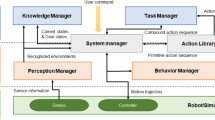
Abstract
Current service robots without learning ability are not qualified for many complex tasks. Therefore, it is very significant to decompose the complex task into repeatable execution unit. In this paper, we propose a complex task representation method based on dynamic motion primitives, and use hierarchical knowledge graph to represent the analytic results of complex tasks. To realize the execution of complex robot manipulation tasks, we decompose the semantic tasks into the minimum motion units that can be executed by the robot and combine the multi-modal information: posture, force and robot joint parameters, obtained by the sensors. We use the knowledge graph to record the end-effector required by the robot to perform different tasks and make appropriate selection of end-effector according to different needs. Finally, Taking the long sequence complex task of service scene as an example, we use UR5 robot to verify the effectiveness and feasibility of this design.
This work was supported by the Major Project of the New Generation of Artificial Intelli-gence (No. 2018AAA0102900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62173233), the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission project (JCYJ20210324094401005, JCYJ20220531102809022), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2021A1515011582).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paulius, D., Sun, Y.: A survey of knowledge representation in service robotics. Robot. Auton. Syst. (2019)
Yang, Y., Guha, A., Fermuller, C., et al.: Manipulation action tree bank: a knowledge resource for humanoids. In: IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots. IEEE (2016)
Yang, Y., Fermuller, C., Aloimonos, Y.: Detection of manipulation action consequences (MAC). In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE (2013)
Myers, A., Teo, C.L., Fermüller, C., Aloimonos, Y., et al.: Affordance detection of tool parts from geometric features. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, pp. 1374–1381. IEEE (2015)
Yang, Y., Aloimonos Y., Fermüller, C., et al.: Learning the semantics of manipulation action. In: Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL) (2015)
Colledanchise, M., Ögren, P., et al.: How behavior trees modularize hybrid control systems and generalize sequential behavior compositions, the subsumption architecture, and decision trees. IEEE Trans. Robot. (2017)
Colledanchise, M., Ogren, P.: Behavior Trees in Robotics and AI: An Introduction (2018)
Sun, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, J.: RTPO: a domain knowledge base for robot task planning. Electronics 8(10), 1105 (2019)
Beetz, M., Tenorth, M., Winkler, J.: Open-ease–a knowledge processing service for robots and robotics. AI Res. 374 (2015)
Beetz, M., Beßler, D., Haidu, A., et al.: Know rob 2.0—a 2nd generation knowledge processing framework for cognition-enabled robotic agents. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 512–519. IEEE (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Miao, S. et al. (2023). Hierarchical Knowledge Representation of Complex Tasks Based on Dynamic Motion Primitives. In: Sun, F., Cangelosi, A., Zhang, J., Yu, Y., Liu, H., Fang, B. (eds) Cognitive Systems and Information Processing. ICCSIP 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1787. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0617-8_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0617-8_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-0616-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-0617-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)