Abstract
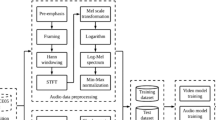
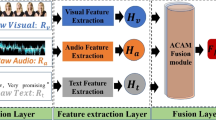
In indoor places, such as homes or offices, when abnormal events occur, the behavior and voice of individuals or groups will display abnormal signals. These signals can be both visual and auditory, and they interact and complement each other to jointly create a sense of emotional atmosphere within the scene. In order to achieve effective and accurate perception and response of abnormal emotion during the interaction in smart home, a model of abnormal emotion recognition based on audio-visual modality fusion is proposed. Human skeleton motion data and audio data are utilized to construct separate deep learning networks for action recognition and speech emotion recognition. The accuracy rate achieved on the G3D dataset is 100% and the accuracy rate achieved on the CASIA corpus is 90.83%. For decision-level multimodal fusion, the predicted results of actions and speech emotions are mapped to the “abnormal” axis through fuzzification and weighted average methods. In this process, considerations are taken into account for the varying contributions of different speech emotions and behaviors to the abnormal emotion, as well as the recognition recall rates of the unimodal emotion models. Then the two modalities are allowed to mutually modify each other and achieve quantitative analysis of abnormal emotion through weighted additive fusion.
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 82201753.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, J., Wang, M., Wang, X.: Research on general model of intelligence level for smart home. In: 2022 7th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems, pp. 123–129 (2022)
Canal, F.Z., Müller, T.R., Matias, J.C., et al.: A survey on facial emotion recognition techniques: a state-of-the-art literature review. Inf. Sci. 582 (2022)
Morais, E., Hoory, R., Zhu, W., et al.: Speech emotion recognition using self-supervised features. In: ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, 6922–6926 (2022)
Wang, S., Li, J., Cao, T., Wang, H., Tu, P., Li, Y.: Dance emotion recognition based on laban motion analysis using convolutional neural network and long short-term memory. IEEE Access 8, 124928–124938 (2020)
Zhang, J., Yin, Z., Chen, P., et al.: Emotion recognition using multi-modal data and machine learning techniques: a tutorial and review. Inf. Fusion 59, 103–126 (2020)
Middya, A.I., Nag, B., Roy, S.: Deep learning based multimodal emotion recognition using model-level fusion of audio-visual modalities. Knowl.-Based Syst. 244, 108580 (2022)
Abdelhamid, A.A., El-Kenawy, E.S.M., Alotaibi, B., et al.: Robust speech emotion recognition using CNN+ LSTM based on stochastic fractal search optimization algorithm. IEEE Access 10, 49265–49284 (2022)
Aggarwal, A., Srivastava, A., Agarwal, A., et al.: Two-way feature extraction for speech emotion recognition using deep learning. Sensors 22(6), 2378 (2022)
Song, Y.F., Zhang, Z., Shan, C., et al.: Constructing stronger and faster baselines for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(2), 1474–1488 (2022)
Muhammad, K., Ullah, A., Imran, A.S., et al.: Human action recognition using attention based LSTM network with dilated CNN features. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 125, 820–830 (2021)
Cai, L., Dong, J., Wei, M.: Multi-Modal Emotion Recognition From Speech and Facial Expression Based on Deep Learning. Chinese Autom. Congress (CAC) 2020, 5726–5729 (2020)
Koromilas, P., Giannakopoulos, T.: Deep multimodal emotion recognition on human speech: a review. Appl. Sci. 11(17), 7962 (2021)
Aggarwal, S., Sehgal, S.: Text independent data-level fusion network for multimodal sentiment analysis. Int. J. Performability Eng. 18(9) (2022)
Tan, Y., Sun, Z., Duan, F., et al.: A multimodal emotion recognition method based on facial expressions and electroencephalography. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 70, 103029 (2021)
Jin, S., Wang, X., Du, L., et al.: Evaluation and modeling of automotive transmission whine noise quality based on MFCC and CNN. Appl. Acoust. 172, 107562 (2021)
Bhatt, S., Dev, A., Jain, A.: Effects of the dynamic and energy based feature extraction on Hindi speech recognition. In: Recent Advances in Computer Science and Communications (Formerly: Recent Patents on Computer Science) 14(5), 1422–1430 (2021)
Paseddula, C., Gangashetty, S.V.: Late fusion framework for Acoustic Scene Classification using LPCC, SCMC, and log-Mel band energies with Deep Neural Networks[J]. Appl. Acoust. 172, 107568 (2021)
Zhang, Z.: Microsoft kinect sensor and its effect. IEEE Computer Society Press (2012)
Bloom, V., Argyriou, V., Makris, D.: Hierarchical transfer learning for online recognition of compound actions. Comput. Vision Image Understanding 144, 62–72 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jiang, Y., Hirota, K., Dai, Y., Ji, Y., Shao, S. (2023). Abnormal Emotion Recognition Based on Audio-Visual Modality Fusion. In: Yang, H., et al. Intelligent Robotics and Applications. ICIRA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14267. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6483-3_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6483-3_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-6482-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-6483-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)