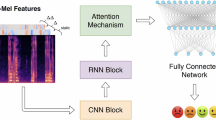
Abstract
Speech emotion recognition (SER) plays a crucial role in understanding user intent and improving human-computer interaction (HCI). Currently, the most widely used and effective methods are based on deep learning. In the existing research, the temporal information becomes more and more important in SER. Although some advanced deep learning methods can achieve good results, such as convolutional neural networks (CNN) and attention module, they often ignore the temporal information in speech, which can lead to insufficient representation and low classification accuracy. In order to make full use of temporal features, we proposed channel-aware multi-scale temporal convolutional networks (CM-TCN). Firstly, channel-aware temporal convolutional networks (CATCN) is used as the basic structure to extract multi-scale temporal features combining channel information. Then, global feature attention (GFA) captures the global information at different time scales and enhances the important information. Finally, we use the adaptive fusion module (AFM) to establish the overall dependency of different network layers and fuse features. We conduct extensive experiments on six dataset, and the experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of CM-TCN.
This research was funded by the Scientific and technological innovation 2030 major project under Grant 2022ZD0115800, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Tianshan Excellence Project under Grant 2022TSYCLJ0036.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schuller, B., Rigoll, G., Lang, M.: Hidden Markov model-based speech emotion recognition. In: 2003–2003 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1–401. IEEE, Baltimore (2003)
Mower, E., Mataric, M.J., Narayanan, S.: A framework for automatic human emotion classification using emotion profiles. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(5), 1057–1070 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2010.2076804
Han, K., Yu, D., Tashev, I.: Speech emotion recognition using deep neural network and extreme learning machine. In: Interspeech, pp. 223–227. ISCA, Singapore (2014)
Huang, Z., Dong, M., Mao,Q., Zhan, Y.: Speech emotion recognition using CNN. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 801–804 (2014)
Tarantino, L., Garner, P.N., Lazaridis, A., et al.: Self-attention for speech emotion recognition, In: Interspeech, pp. 2578–2582. ISCA, Graz (2019)
Xu, M., Zhang, F., Khan, S.U.: Head fusion: improving the accuracy and robustness of speech emotion recognition on the IEMOCAP and RAVDESS dataset. IEEE Access 9, 1058–1064 (2020)
Xu, M., Zhang, F., Cui, X., Zhang, W.: Speech emotion recognition with multiscale area attention and data augmentation. In: ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6319–6323. IEEE, Toronto (2021)
Jahangir, R., Teh, Y.W., Hanif, F., Mujtaba, G.: Deep learning approaches for speech emotion recognition: state of the art and research challenges. Speech Commun. 127, 73–81 (2021)
Zhang, S., Tao, X., Chuang, Y., Zhao, X.: Learning the sequential temporal information with recurrent neural networks. Multimedia Tools Appl. 80(16), 23745–23812 (2021)
Murugan, P.: Learning deep multimodal affective features for spontaneous speech emotion recognition. R abs 1807.02857 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1807.02857
Xie, Y., Liang, R., Liang, Z., Zhao, L.: Attention-based dense LSTM for speech emotion recognition. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 102(7), 1426–1429 (2019)
Su, B., Chang, C., Lin, Y., Lee, C.: Improving speech emotion recognition using graph attentive bi-directional gated recurrent unit network. In: Interspeech, pp. 506–510. ISCA, Shanghai (2020)
Lin, W., Busso, C.: An efficient temporal modeling approach for speech emotion recognition by mapping varied duration sentences into fixed number of chunks. In: Interspeech, pp. 2322–2326. ISCA, Shanghai (2020)
Wang, J., Xue, M., Culhane, R., et al.: Speech emotion recognition with dual-sequence LSTM architecture. In: ICASSP 2020–2020 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6474–6478. IEEE, Barcelona (2020)
Zhong, Y., Hu, Y., Huang, H., Silamu, W.: A lightweight model based on separable convolution for speech emotion recognition. In: Interspeech, pp. 3331–3335. ISCA, Shanghai (2020)
Rajamani, S.T., Rajamani, K.T., Mallol-Ragolta, A., et al.: A novel attention-based gated recurrent unit and its efficacy in speech emotion recognition. In: ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6294–6298. IEEE, Toronto (2021)
Zhao, Z., Zheng, Y., Zhang, Z., et al.: Exploring spatio-temporal representations by integrating attention-based bidirectional-LSTM-RNNs and FCNs for speech emotion recognition. In: Interspeech, pp. 272–276.ISCA , Hyderabad (2018)
Mustaqeem, S.K.: MLT-DNet: speech emotion recognition using 1D dilated CNN based on multi-learning trick approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 167, 114177 (2021)
Bai, S., Kolter, J.Z., Koltun, V.: An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling, CoRR abs/1803.01271 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1803.01271
Salehinejad, H., Baarbe, J., Sankar, S., Barfett, J., Colak, E., Valaee, S.: Recent advances in recurrent neural networks. CoRR abs/1801.01078 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1801.01078
Farha, Y.A., Gall, J.: MS-TCN: multi-stage temporal convolutional network for action segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(6), 6647–6658 (2018)
Zhao, Y., Wang, D., Xu, B., Zhang, T.: Monaural speech dereverberation using temporal convolutional networks with self attention. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 28, 1057–1070 (2020)
Luo, Y., Mesgarani, N.: Conv-TasNet: surpassing ideal time-frequency magnitude masking for speech separation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 27(8), 1256–1266 (2019)
Peng, Z., Lu, Y., Pan, S., et al.: Efficient speech emotion recognition using multi-scale CNN and attention. In: ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 3020–3024. IEEE, Toronto (2021)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7132–7141.IEEE, Salt Lake City (2018)
Wang, Q., Wu, B., Zhu, P., Li, P., Zuo, W., Hu, Q.: ECA-Net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In:2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11531–11539. IEEE, Seattle (2020)
Tao, J., Liu, F., Zhang, M., Jia, H.: Design of speech dataset for mandarin text to speech. In: Blizzard Challenge 2008 Workshop (2008)
Burkhardt, F., Paeschke, A., Rolfes, M., et al.: A database of German emotional speech. In: Interspeech, pp. 1517–1520. ISCA, Lisbon (2005)
Costantini, G., Iaderola, I., Paoloni, A., Todisco, M.: Emovo dataset: an Italian emotional speech database. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2014), pp. 3501–3504. European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Reykjavik (2014)
Busso, C., Bulut, M., Lee, C.C., et al.: IEMOCAP: interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database. Lang. Res. Eval. 42(4), 335–359 (2008)
Livingstone, S.R, Russo, F.A.: The ryerson audio-visual database of emotional speech and song (ravdess): a dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in North American English. PLOS ONE 13(5), e0196391 (2018)
Philip J., Haq, S.: Surrey Audio-Visual Expressed Emotion (savee) Database. University of Surrey, Guildford (2014)
Sun, L., Fu, S., Wang, F.: Decision tree SVM model with fisher feature selection for speech emotion recognition. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music. Process. 2019, 2 (2019)
Chen, L., Su, W., Feng, Y., et al.: Two-layer fuzzy multiple random forest for speech emotion recognition in human-robot interaction. Inf. Sci. 509, 150–163 (2020)
Ye, J., Wen, X., Wang, X., et al.: GM-TCNet: gated multi-scale temporal convolutional network using emotion causality for speech emotion recognition. Speech Commun. 145, 21–35 (2022)
Wen, X., Ye, J., Luo, Y., et al. CTL-MTNet: a novel capsnet and transfer learning-based mixed task net for single-dataset and cross-dataset speech emotion recognition. In: International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) 2022, Vienna, Austria, pp. 2305–2311 (2022)
Tuncer, T., Dogan, S., Acharya, U.R.: Automated accurate speech emotion recognition system using twine shuffle pattern and iterative neighborhood component analysis techniques. Knowl.-Based Syst. 211, 106547 (2021)
Aftab, A., Morsali, A., Ghaemmaghami, S., et al.: LIGHT-SERNET: a lightweight fully convolutional neural network for speech emotion recognition. In: ICASSP 2022–2022 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6912–6916. IEEE, Virtual and Singapore (2022)
Ozer, I.: Pseudo-colored rate map representation for speech emotion recognition. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 66, 102502 (2021)
Ancilin, J., Milton, A.: Improved speech emotion recognition with mel frequency magnitude coefficient. Appl. Acoust. 179, 108046 (2021)
Liu, J., Song, Y., Wang, L., Dang, J., Yu, R.: Time-frequency representation learning with graph convolutional network for dialogue-level speech emotion recognition. In: Interspeech, pp. 4523–4527. ISCA, Brno (2020)
Cao, Q., Hou, M., Chen, B., Zhang, Z., Lu, G.: Hierarchical network based on the fusion of static and dynamic features for speech emotion recognition. In: ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics. Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6334–6338. IEEE, Toronto (2021)
Mustaqeem, Kwon, S.: Optimal feature selection based speech emotion recognition using two-stream deep convolutional neural network. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 36(9), 5116–5135 (2021)
Hajarolasvadi, N., Demirel, H.: 3D CNN-based speech emotion recognition using k-means clustering and spectrograms. Entropy 21(5), 479 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, T., Wang, L., Zhang, J. (2024). CM-TCN: Channel-Aware Multi-scale Temporal Convolutional Networks for Speech Emotion Recognition. In: Luo, B., Cheng, L., Wu, ZG., Li, H., Li, C. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14449. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8067-3_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8067-3_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-8066-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-8067-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)