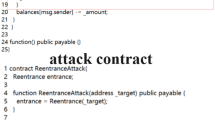
Abstract
Smart contracts have been under constant attack from outside, with frequent security problems causing great economic losses to the virtual currency market, and their security research has attracted much attention in the academic community. Traditional smart contract detection methods rely heavily on expert rules, resulting in low detection precision and efficiency. This paper explores the effectiveness of deep learning methods on smart contract detection and propose a multi-model smart contract detection method, which is based on a multi-model vulnerability detection method combining Bi-directional Gated Recurrent Unit (BiGRU) and Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) for smart contract vulnerability detection. Through a comparative study on the vulnerability detection of 10312 smart contract codes, the method can achieve an identification accuracy of 90.17% and a recall rate of 97.7%. Compared with other deep network models, the method used in this paper has superior performance in terms of recall and accuracy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qian, P., Liu, Z., He, Q., et al.: Smart contract vulnerability detection technique: a survey. J. Softw. 33(8), 3059–3085 (2022)
Chen, J., Xia, X., Lo, D., et al.: Defectchecker: automated smart contract defect detection by analyzing EVM bytecode. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 48(7), 2189–2207 (2021)
Zheng, P., Zheng, Z., Luo, X.: Park: accelerating smart contract vulnerability detection via parallel-fork symbolic execution. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis, pp. 740–751. Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), New York, NY, USA (2022)
Zhao, W., Zhang, W., Wang, J., et al.: Smart contract vulnerability detection scheme based on symbol execution. J. Comput. Appl. 40(4), 947–953 (2020)
Choi, J., Kim, D., Kim, S., et al.: Smartian: enhancing smart contract fuzzing with static and dynamic data-flow analyses. In: 2021 36th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE), pp. 227–239. IEEE, Melbourne, Australia (2021)
Jiang, B., Liu, Y., Chan W.: Contractfuzzer: fuzzing smart contracts for vulnerability detection. In: Proceedings of the 33rd ACM/IEEE International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, pp. 259–269. Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), New York, NY, USA (2018)
Zhao, Y., Zhu, X., Li, G., Bao, Y.: Time constraint patterns of smart contracts and their formal verification. J. Softw. 33(8), 2875–2895 (2022)
Li, Z., Lu, S., Zhang, R., et al.: SmartFast: an accurate and robust formal analysis tool for Ethereum smart contracts. Empir. Softw. Eng. 27(7), 197 (2022)
Qian, P., Liu, Z., He, Q., et al.: Towards automated reentrancy detection for smart contracts based on sequential models. IEEE Access 8, 19685–19695 (2020)
Zhang, G., Liu, Y., Wang, H., Yu, N.: Contract vulnerability detection scheme based on BiLSTM and attention mechanism. Netinfo Secur. 22(09), 46–54 (2022)
Chawla, N., Bowyer, K., Hall, L., et al.: SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 16, 321–357 (2002)
Chung, J., Gulcehre, C., Cho, K., et al.: Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling, arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.3555 (2014)
Etherscan Homepage,https://etherscan.io, Accessed 1 May 2023
Liao, J., Tsai, T., He, C., et al.: Soliaudit: smart contract vulnerability assessment based on machine learning and fuzz testing. In: Sixth International Conference on Internet of Things: Systems, Management and Security (IOTSMS), pp. 458–465 (2019)
Oyente-project, https://github.com/enzymefinance/oyente, Accessed 10 May 2023
Remix-project, https://github.com/ethereum/remix-project, Accessed 10 May 2023
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFB1005704).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Song, S., Yu, X., Ma, Y., Li, J., Yu, J. (2024). Multi-model Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection Based on BiGRU. In: Luo, B., Cheng, L., Wu, ZG., Li, H., Li, C. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1962. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8132-8_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8132-8_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-8131-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-8132-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)